Polyaxial Pedicle Spine Screw
Product Overview
A Polyaxial Pedicle Spine Screw is a medical device used in spinal surgery. It is designed to stabilize and immobilize the spine by anchoring screws into the pedicles, which are small bony projections on the vertebral bodies. What sets Polyaxial Screws apart is their ability to move in multiple directions, providing surgeons with greater flexibility during placement. This allows for better alignment and fixation of the spinal instrumentation. The Polyaxial design enables the Screw head to rotate, tilt, and angulate, which helps accommodate the natural curvature and variations in spinal anatomy. Ultimately, the polyaxial pedicle spine screw aids in enhancing surgical outcomes and promoting spinal stability.
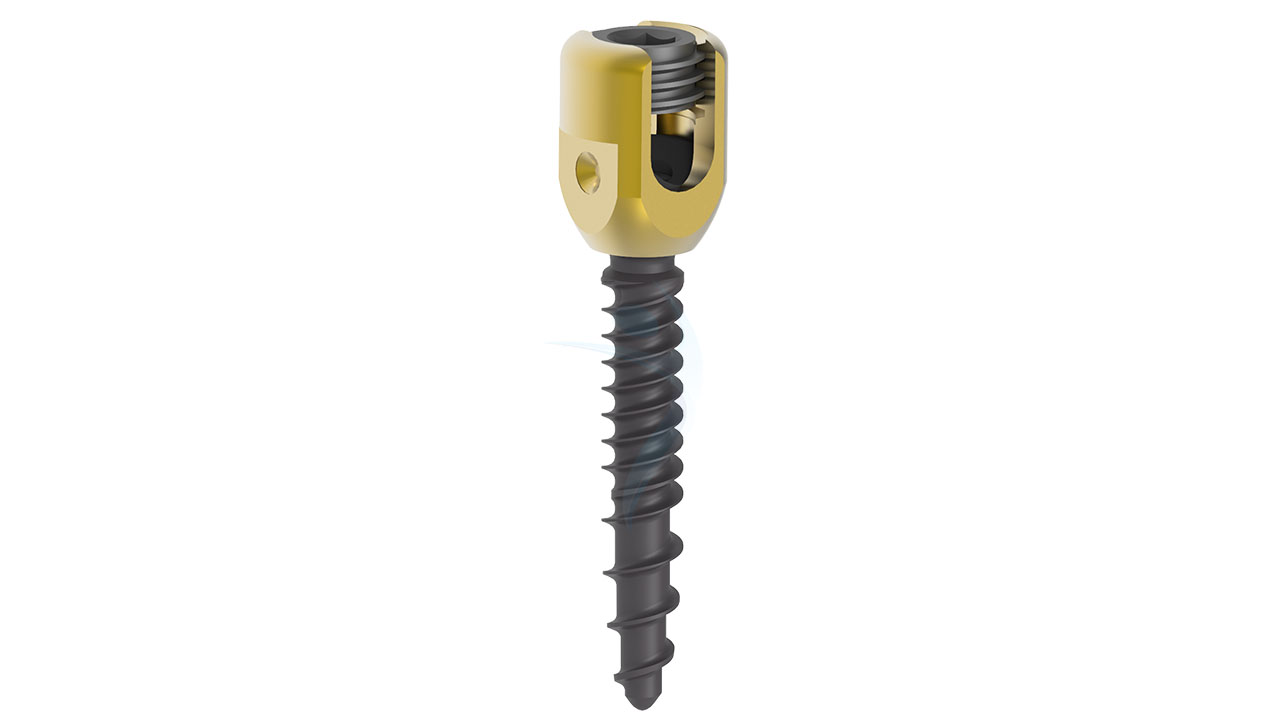
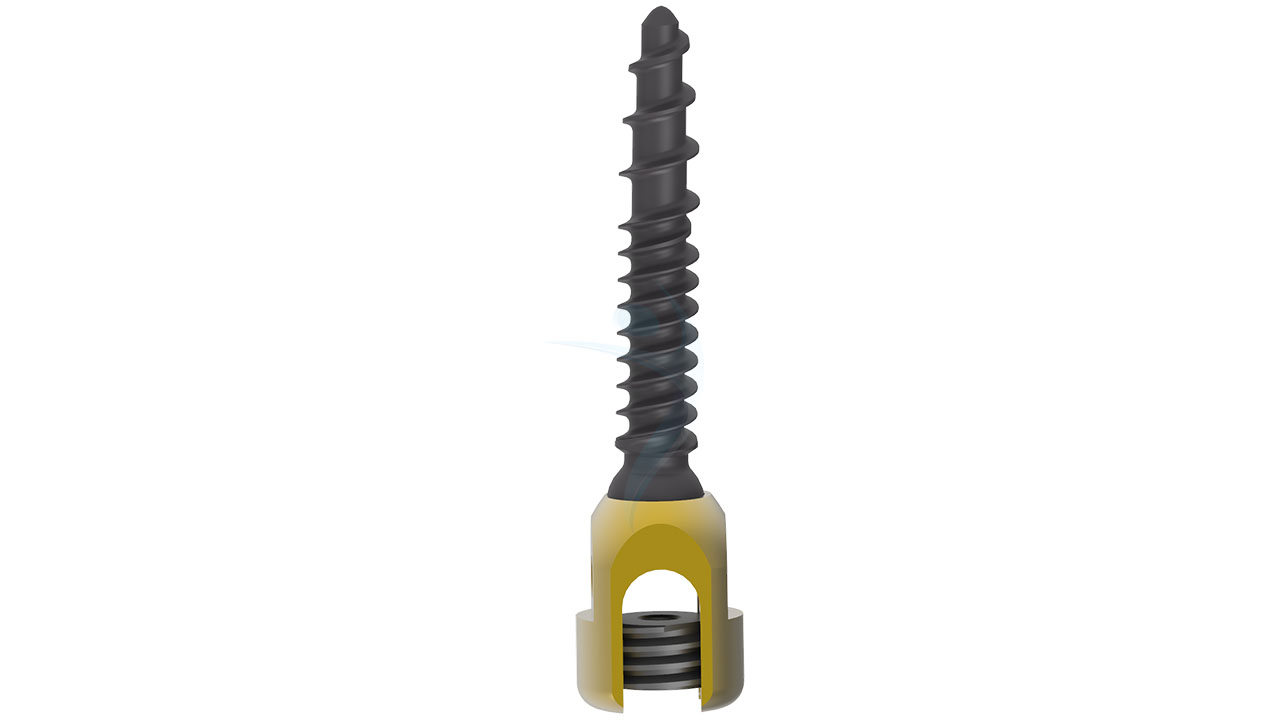
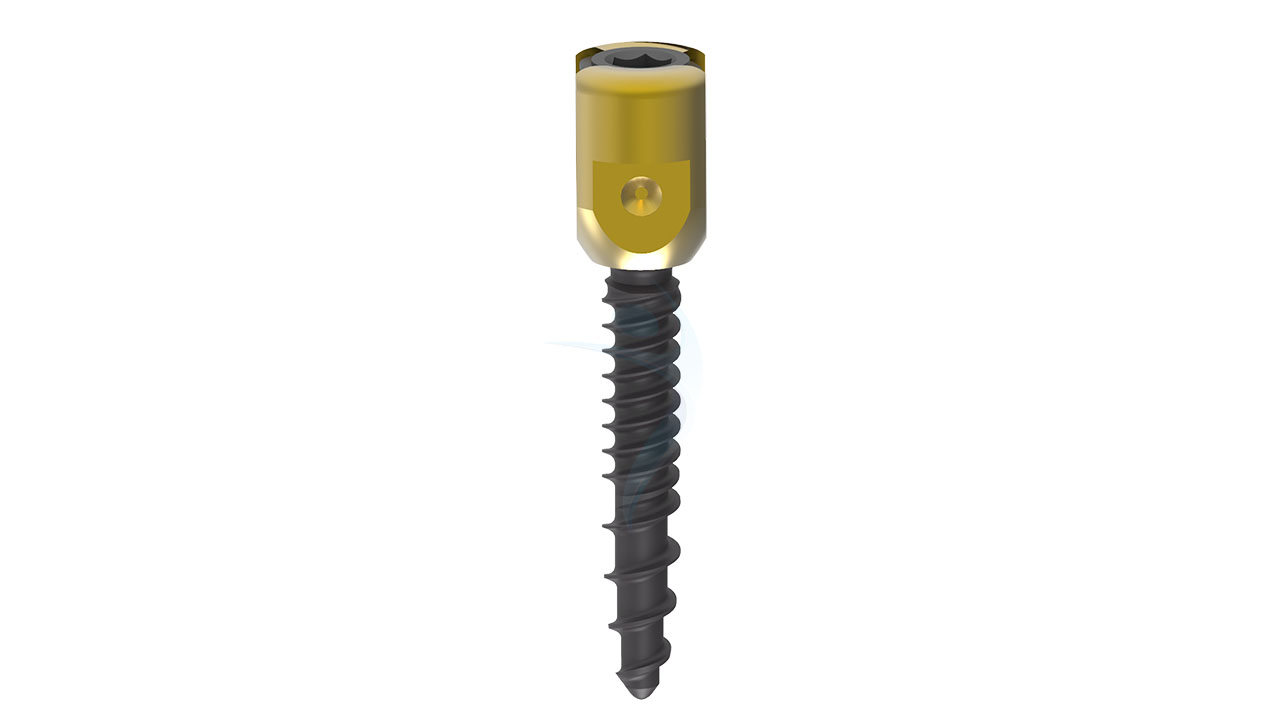
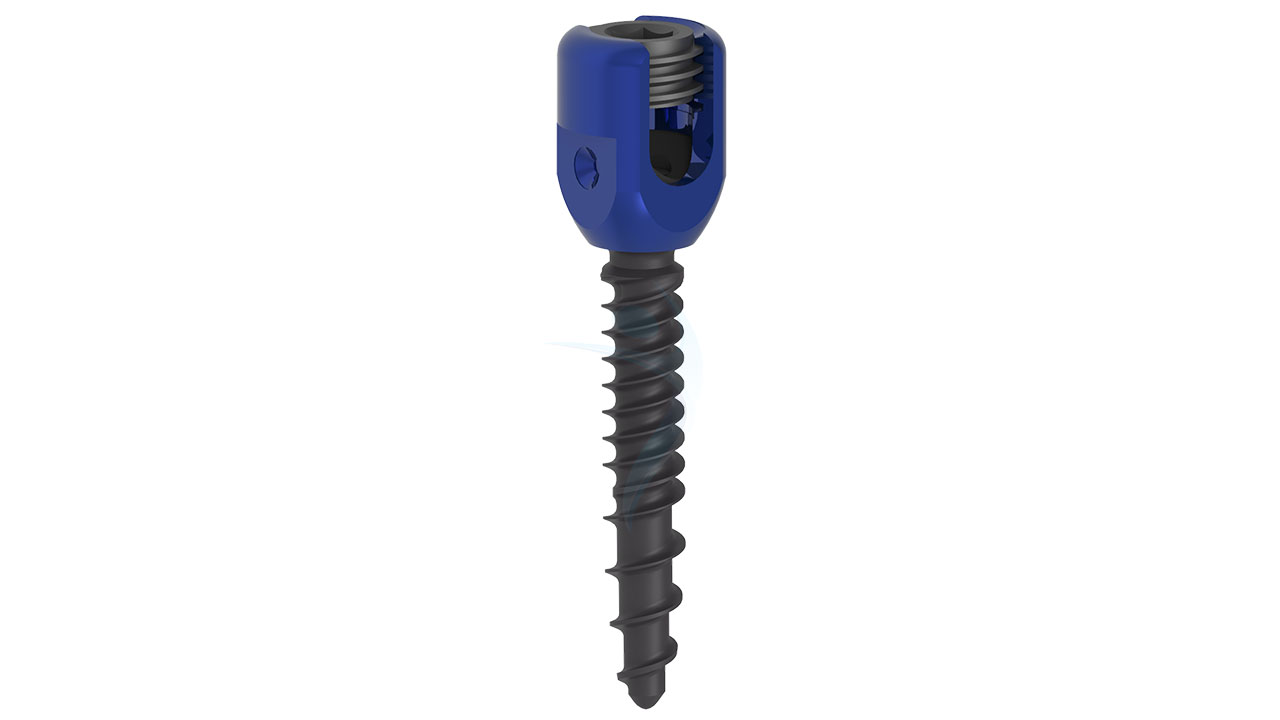
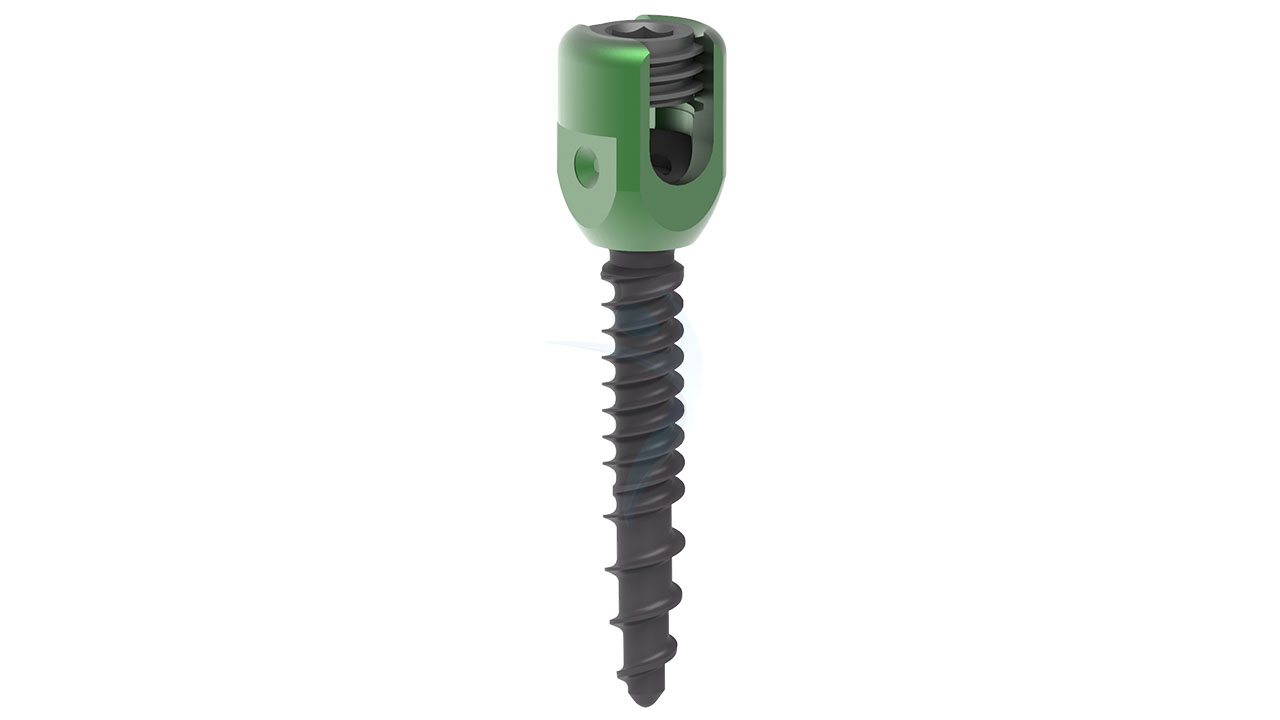
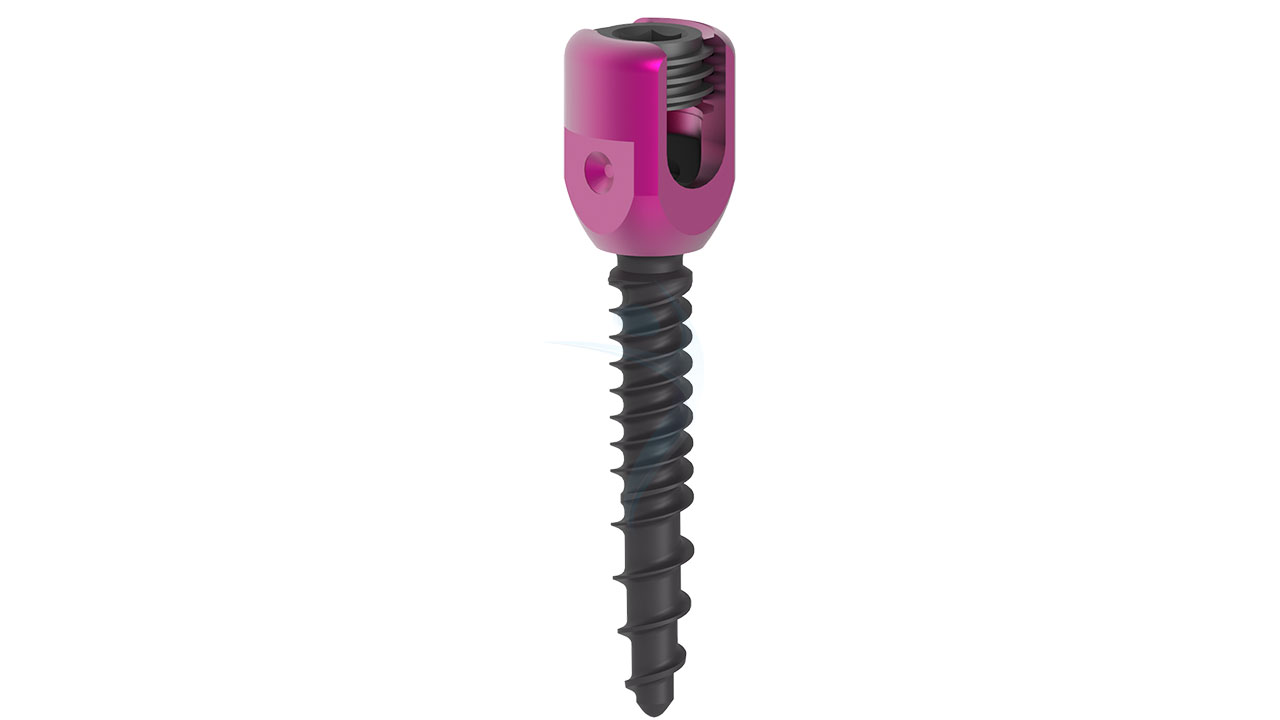







Product Uses
- Spinal Fusion:Polyaxial pedicle screws are utilized in spinal fusion procedures to stabilize and fuse adjacent vertebrae. By anchoring the screws into the pedicles, they provide a stable foundation for the placement of rods or plates, facilitating the fusion process.
- Correction of Spinal Deformities: These screws are employed in the correction of spinal deformities such as scoliosis, kyphosis, or lordosis. By connecting the deformed vertebrae to the corrective instrumentation, polyaxial screws help realign the spine into a more anatomically normal position.
- Fracture Fixation: Polyaxial pedicle screws can be used to stabilize spinal fractures. The screws are inserted into the pedicles above and below the fractured vertebra to provide stability and support during the healing process.
- Spinal Tumor or Infection Treatment: In cases of spinal tumors or infections, polyaxial pedicle screws may be utilized to provide stability and support to the affected spinal segment after tumor resection or during the treatment of infections.
Product Specification
- Diameter: Polyaxial screws are available in various diameters, typically ranging from 4.0 mm to 8.5 mm. The diameter is chosen based on the patient's anatomy and the surgical procedure's requirements.
- Length: The length of polyaxial screws can range from 25 mm to 60 mm or more. The appropriate screw length is determined based on the depth of the pedicle and the desired level of fixation.
- Material: Polyaxial screws are usually made of biocompatible materials such as titanium or stainless steel. These materials offer strength, durability, and compatibility with the human body.
- Thread Design:Polyaxial screws feature threads along their length, which provide stability and engagement with the bone. The thread design may vary, including variable pitch or constant pitch, depending on the manufacturer.
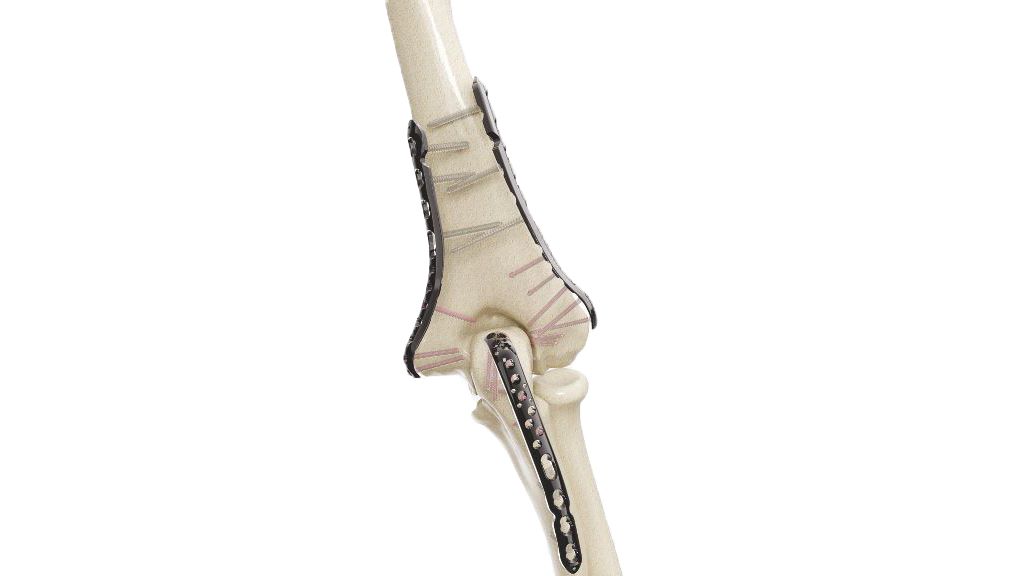
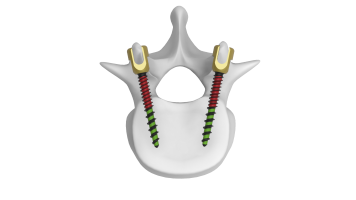
- Polyaxial Head:The distinguishing feature of polyaxial screws is their polyaxial head. This head allows for multi-directional movement and facilitates angulation and alignment during screw placement. The polyaxial head typically includes a mechanism to secure the connecting rod or plate.
Polyaxial Pedicle Spine Screw Sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Polyaxial Pedicle Spine Screw
- Medical Evaluation : The patient's medical history will be reviewed, including any previous surgeries, medications, allergies, and existing medical conditions. Pre-existing conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or infections may require additional evaluation and management before the surgery.
- Imaging Studies : X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans of the spine will be performed to assess the spinal anatomy, identify the target area for screw placement, and evaluate the condition being treated (such as spinal deformities, fractures, or tumors).
- Blood Tests : Blood tests may be conducted to assess the patient's overall health, check for any underlying medical conditions, and ensure adequate clotting function.
- Medication Review : Current medications, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and blood-thinning medications, will be evaluated. Some medications may need to be temporarily stopped or adjusted to reduce the risk of bleeding or complications during the surgery.
- Fasting : The patient will be instructed to fast (not eat or drink) for a certain period of time before the surgery. This is typically around six to eight hours to ensure an empty stomach during the procedure.
- Pre-operative Instructions : The patient will receive specific instructions regarding pre-operative care, which may include information about showering with antiseptic soap before surgery, discontinuing specific medications, and restrictions on eating or drinking.
- Anesthesia Evaluation : A pre-operative evaluation by an anesthesiologist will be conducted to assess the patient's suitability for anesthesia. The anesthesiologist will review the patient's medical history, discuss anesthesia options, and address any concerns.
- Anesthesia : The patient will be given general anesthesia or, in some cases, spinal anesthesia to ensure they are comfortable and unconscious during the procedure.
- Patient Positioning : The patient will be positioned face-down on the operating table, and appropriate padding and supports will be used to maintain proper alignment of the spine.
- Incision : The surgeon will make a small incision in the midline of the back over the desired level of the spine where the screws will be inserted.
- Exposure : Soft tissues, such as muscles and ligaments, will be gently retracted or dissected to expose the bony structures of the spine, including the pedicles.
- Pedicle Preparation : The surgeon will use specialized tools, such as drills or awls, to carefully create a pathway or pilot hole in each pedicle of the vertebrae where the screw will be placed. Fluoroscopy (real-time X-ray) may be used to guide the placement and ensure accurate positioning.
- Screw Placement : Polyaxial screws are inserted into the prepared pedicle holes using screwdrivers or instruments designed for that purpose. The polyaxial head of the screw allows for multi-directional movement, enabling the surgeon to adjust the screw's angle and alignment to fit the patient's specific anatomy. The screws are typically placed bilaterally, on both sides of the spine, for stability and support.
- Connecting Rods or Plates : After the screws are in place, connecting rods or plates made of titanium or other biocompatible materials are attached to the polyaxial heads of the screws. These rods or plates help to stabilize the spine, maintain alignment, and facilitate fusion in certain cases.
- Hospital Stay : The patient will typically remain in the hospital for a few days for monitoring and pain management. The length of the hospital stay may vary depending on the patient's overall health and the complexity of the surgery.
- Pain Management : Pain medication will be administered to alleviate discomfort during the recovery period. The medical team will determine the appropriate pain management plan, which may include oral medications, intravenous (IV) pain relievers, or patient-controlled analgesia (PCA).
- Monitoring : Vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, will be monitored regularly to ensure stability. The surgical site will also be inspected for signs of infection or complications.
- Mobilization and Rehabilitation : Physical therapy and mobility exercises will be initiated to help the patient regain strength, flexibility, and mobility. The physical therapist will provide guidance on exercises, movements, and any restrictions to promote healing and prevent complications.
- Wound Care : The surgical incision site will require regular dressing changes and monitoring for signs of infection. The medical team will provide instructions on how to keep the incision clean and dry, as well as when to follow up for suture or staple removal.
- Medications : Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection, and other medications, such as muscle relaxants or anti-inflammatory drugs, may be given to manage symptoms or promote healing. The patient should follow the prescribed medication regimen as instructed.



.png)