Herbert Screw - (Compression Screw) 2.4 mm
Product Overview
Miraclus Herbert Screw 2.4 mm also known as headless compression screw is a versatile implant used in orthopedic surgeries, specifically for small bone fixation. With its self-drilling and self-tapping design, it offers efficient insertion and excellent stability. Made from high-quality titanium material, it ensures biocompatibility and durability. The Herbert Screw 2.4 mm is commonly employed in procedures like osteotomies, fractures, and arthrodesis, providing reliable fixation and promoting optimal bone healing. Its compact size and reliable performance make it a valuable tool in orthopedic surgery.
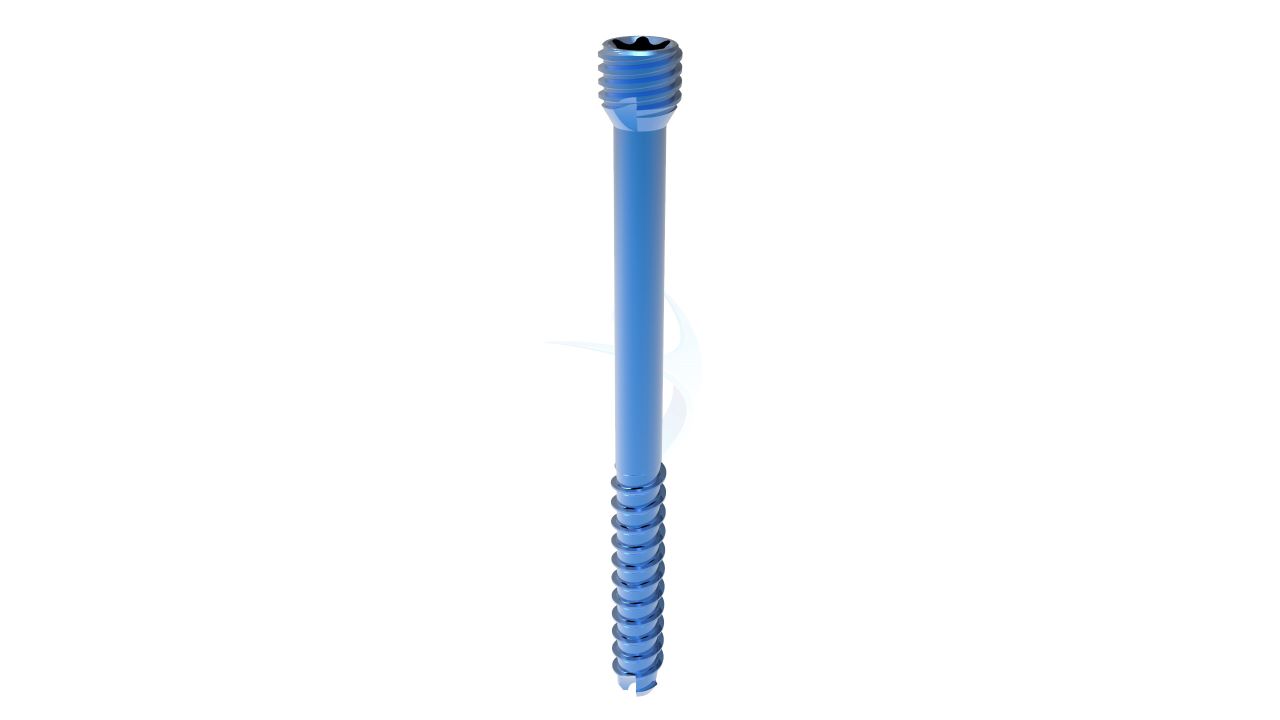
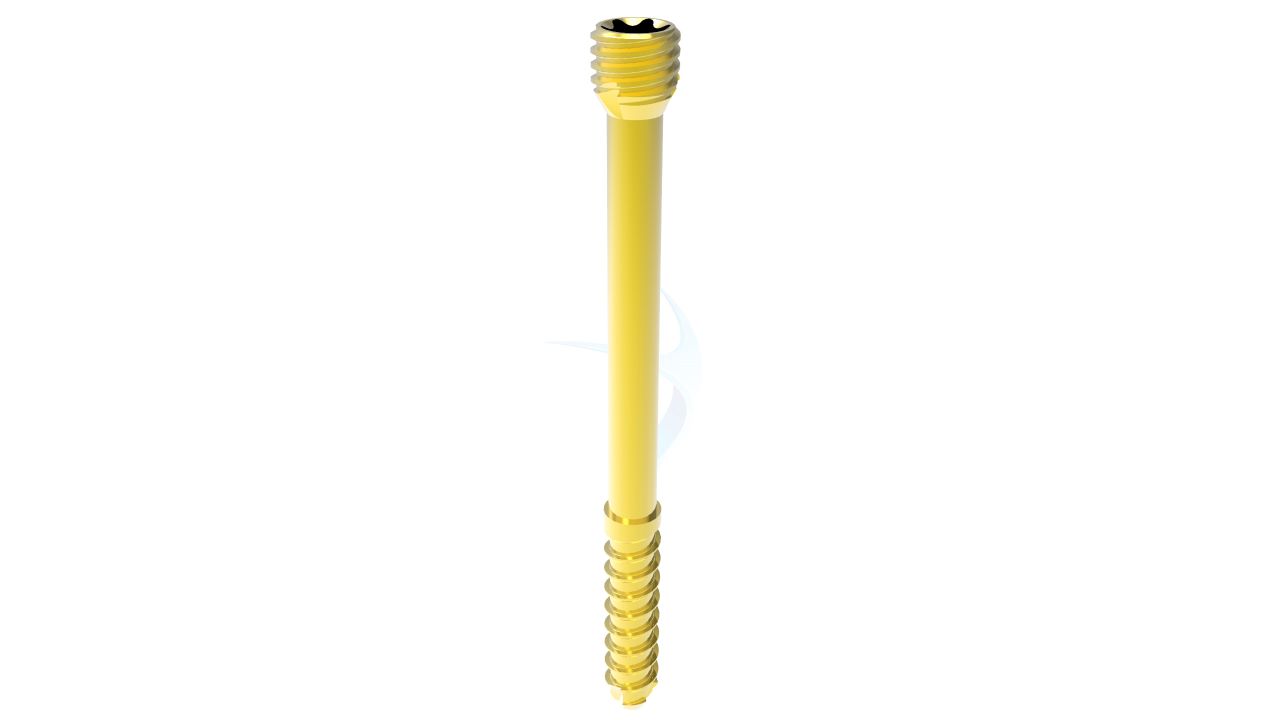
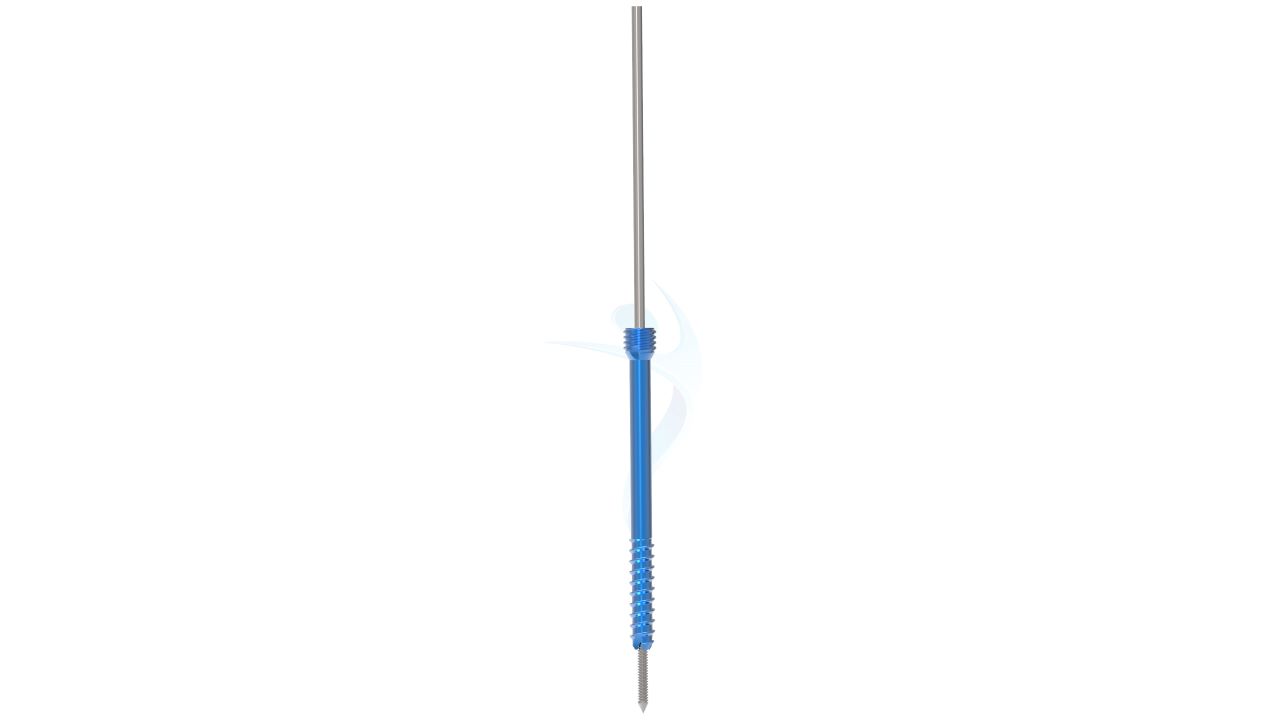
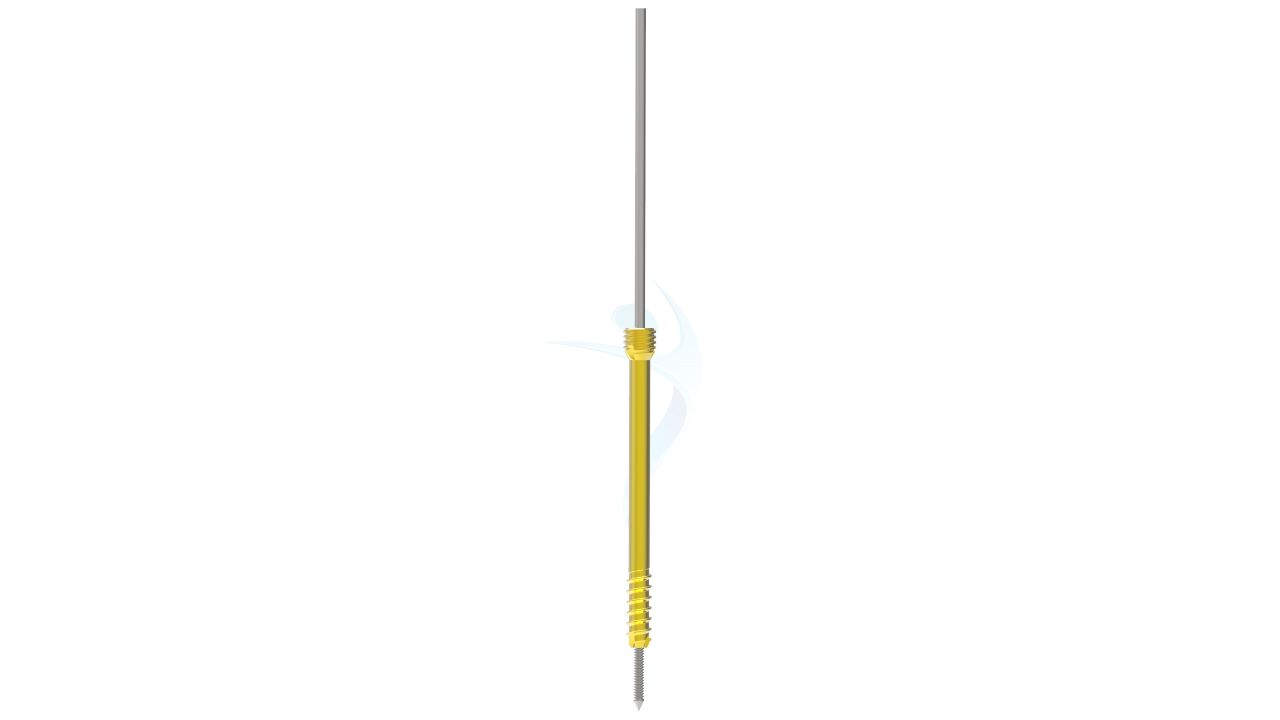
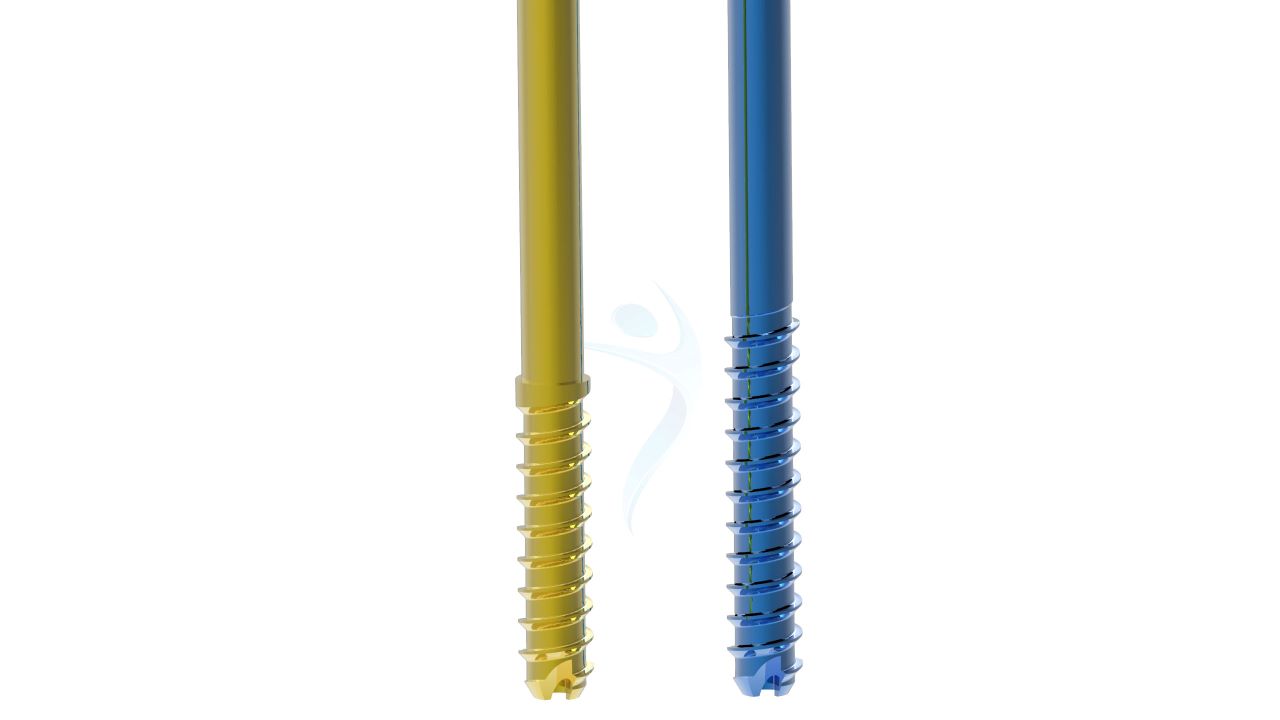






Product Uses
- Fracture Fixation :The 2.4 mm Headless Compression Screw is commonly used for the fixation of fractures, particularly in small bones and joints such as the hand, wrist, foot, and ankle.
- Osteotomies :The 2.4 mm Herbert screw is often employed in osteotomy procedures, which involve cutting and reshaping bones.
- Bone Graft Fixation : When bone grafts are used to assist in bone healing or fusion, 2.4 mm Headless Screw can be employed to secure the grafts in place, ensuring their stability and promoting graft integration.
- Corrective Procedures : In certain cases, the 2.4 mm Herbert Screw is utilized in corrective procedures to address deformities or misalignments of bones, such as in the correction of angular deformities or malunions.
- Implant Profile :The screw has a low-profile design to minimize soft tissue irritation and allow for proper wound healing post-surgery.
Product Specification
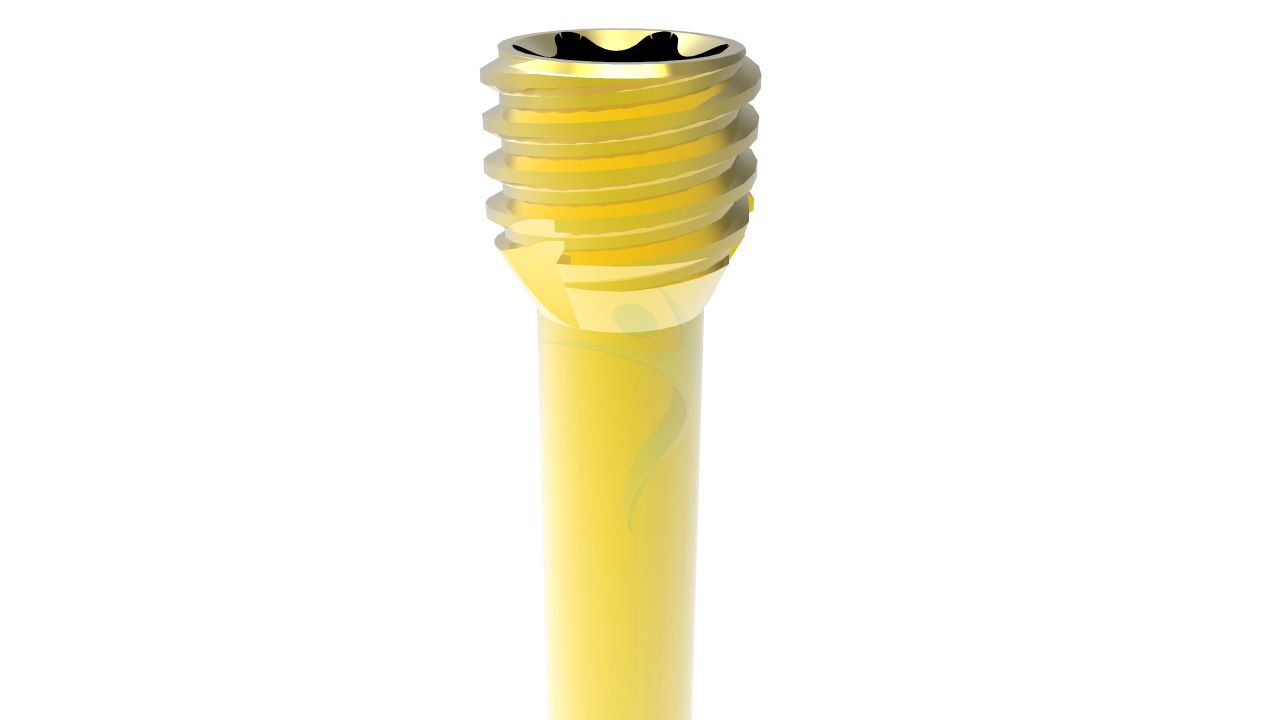
- Headless Design : The 2.4 mm Herbert screw has a unique design without a traditional screw head.
- Compression Function : The 2.4 mm Headless Screw is designed to provide compression across a fracture or fusion site.
- Cannulated Structure : Many 2.4 mm Headless Compression Screws have a hollow, cannulated structure.
- Self-Tapping Threads : The 2.4 mm Herbert screw typically has self-tapping threads, allowing it to be inserted directly into bone without the need for pre-drilling.
Herbert Screw - (Compression Screw) 2.4 mm sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Herbert Screw - 2.4 mm (Headless Compression Screw)
- Medical Evaluation: Prior to the surgery, a thorough medical evaluation will be conducted by your orthopedic surgeon. This evaluation includes assessing your overall health, reviewing your medical history, and identifying any preexisting conditions or factors that may affect the surgery or healing process.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, CT scans, or other imaging studies may be performed to evaluate the extent of the fracture or the condition of the bone. These imaging studies help the surgeon determine the appropriate size and placement of the Herbert Screw.
- Medications: Inform your surgeon about any medications you are currently taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and supplements. Your surgeon may provide specific instructions regarding the use of certain medications before the surgery, such as blood thinners, which may need to be temporarily stopped or adjusted.
- Fasting: Follow the fasting instructions provided by your surgeon or anesthesiologist. Typically, you will be advised to refrain from eating or drinking anything for a specific period before the surgery. This is necessary to minimize the risk of complications related to anesthesia.
- Patient Preparation:The patient is prepared for surgery, which includes administering anesthesia based on the surgeon's recommendation. This may involve general anesthesia, regional anesthesia, or local anesthesia, depending on the specific case and patient's condition.
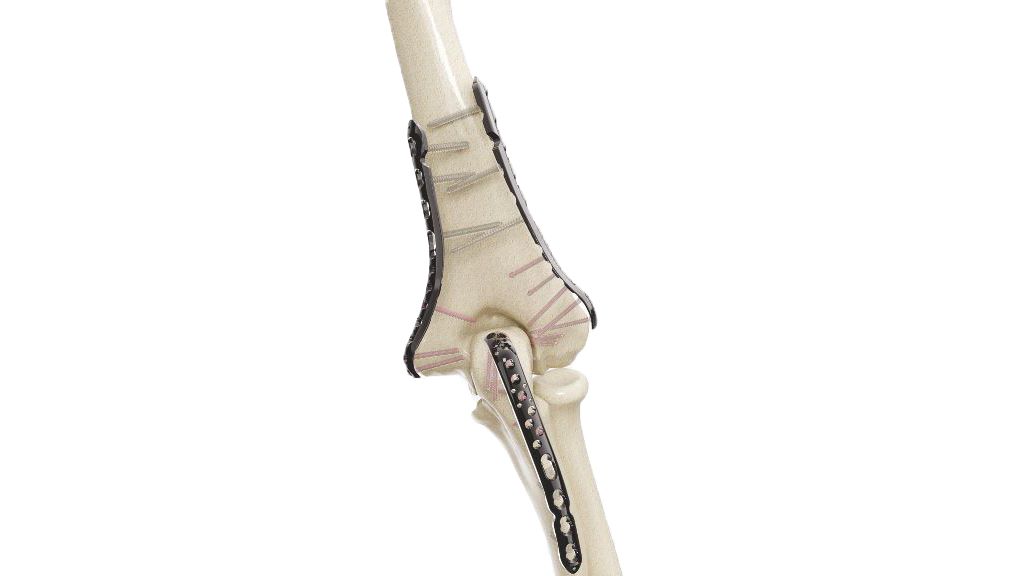
- Incision: The surgeon makes a small incision at the surgical site, typically over the area where the fracture or bone defect is located. The incision allows access to the bone for the insertion of the Herbert Screw.
- Fracture Reduction:If the procedure is performed to treat a fracture, the surgeon carefully aligns the fractured bone fragments to restore proper alignment and anatomical position. This step ensures optimal healing and functional recovery.
- Screw Insertion: Using specialized instruments, the surgeon drills a hole into the bone to accommodate the Herbert Screw. The size of the hole corresponds to the diameter of the chosen 4.5 mm Herbert Screw. The screw is then carefully inserted into the hole, penetrating both bone fragments and providing compression to stabilize the fracture site.
- Weight-Bearing:The weight-bearing instructions after Herbert Screw fixation may vary depending on the specific fracture or surgical procedure. It is essential to follow the surgeon's instructions regarding weight-bearing limitations, partial weight-bearing, or non-weight bearing during the healing period.
- Dressings and Wound Care:The surgical incision site should be kept clean and dry to prevent infection. Follow the surgeon's instructions regarding dressing changes, wound care, and any prescribed medications.
- Immobilization: In some cases, a splint, cast, or brace may be applied to immobilize the affected area and provide stability during the initial healing phase. The duration of immobilization will depend on the fracture type, location, and individual healing progress.
- Physical Therapy: Depending on the specific rehabilitation protocol, physical therapy may be recommended to aid in the recovery process. Physical therapy exercises and rehabilitation techniques help restore range of motion, strength, and function in the affected area. Follow the prescribed physical therapy program as directed by your surgeon or physical therapist.
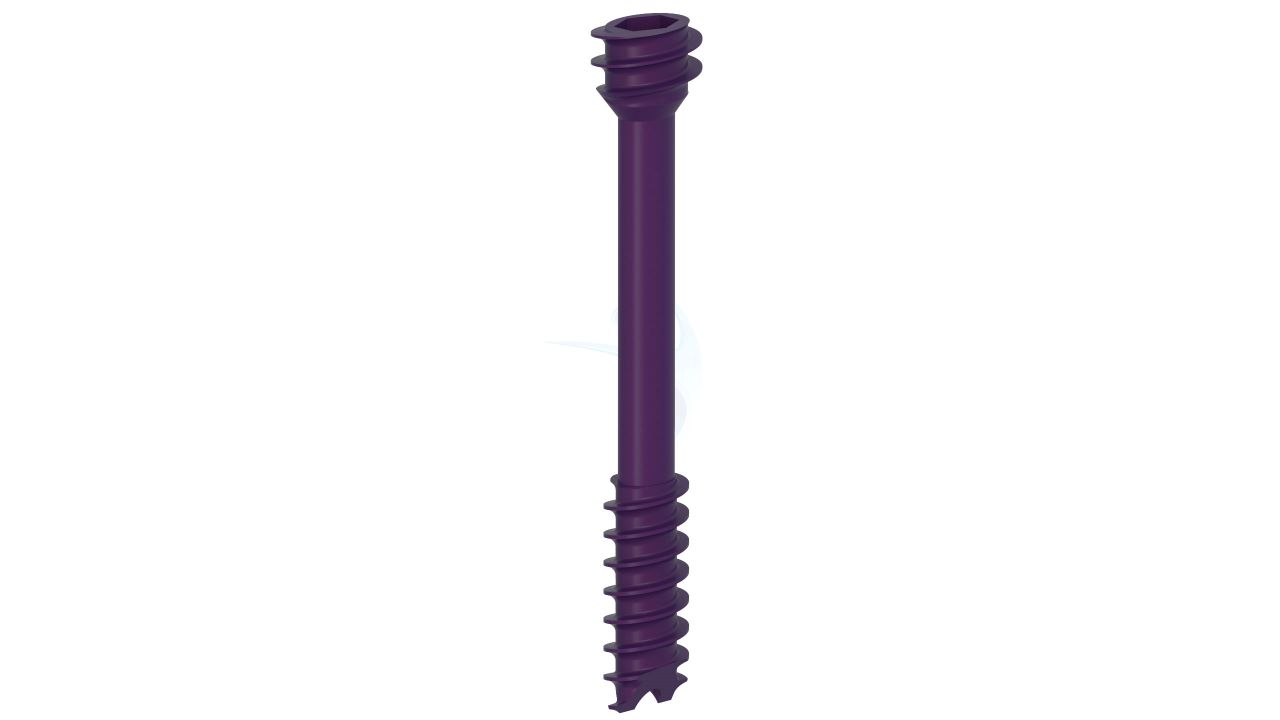
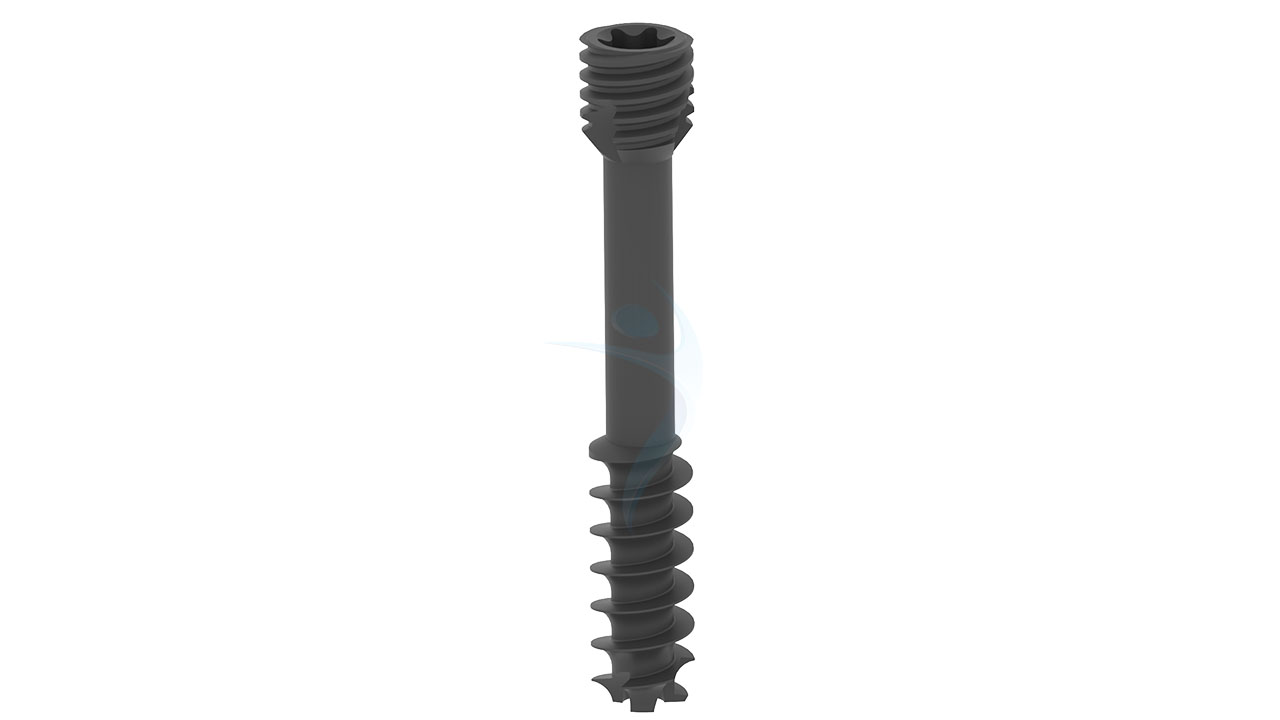






.png)