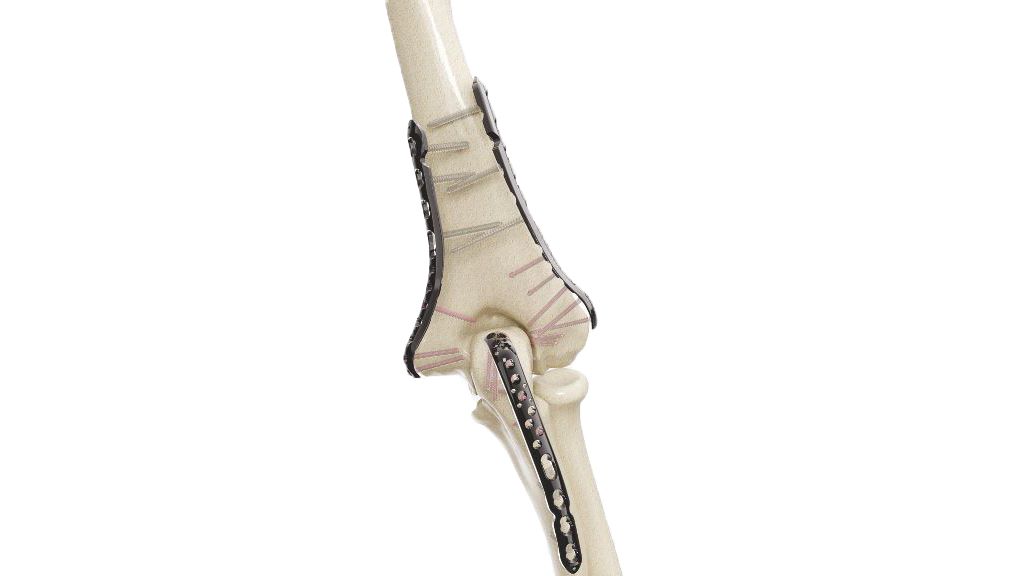
Cannulated Cancellous Screw - 4.5 mm
Product Overview
The screw is manufactured using high-quality titanium material, ensuring biocompatibility , durability and longevity. Its corrosion-resistant properties provide assurance of long-term performance, promoting successful bone healing and patient recovery. Our Cannulated Cancellous Screw 4.5 mm is accompanied by a comprehensive set of instrumentation, enabling surgeons to perform procedures with confidence and ease. The instrumentation set includes specialized tools for efficient drilling, tapping, and screw insertion, ensuring a seamless surgical experience.




Product Uses
- Fracture fixation: The 4.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw is often used for fracture fixation in bones with cancellous (spongy) bone quality.
- Bone grafting: The 4.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw can be used in conjunction with bone grafts for reconstructive procedures.
- Osteotomies: Osteotomies involve cutting and reshaping bones. The 4.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw can be used for fixation after performing corrective osteotomies, such as in the treatment of malunions or deformities.
- Arthrodesis: Arthrodesis refers to joint fusion, typically performed to address severe joint arthritis or instability. The 4.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw may be utilized to stabilize the fused joint during the healing process.
Product Specification
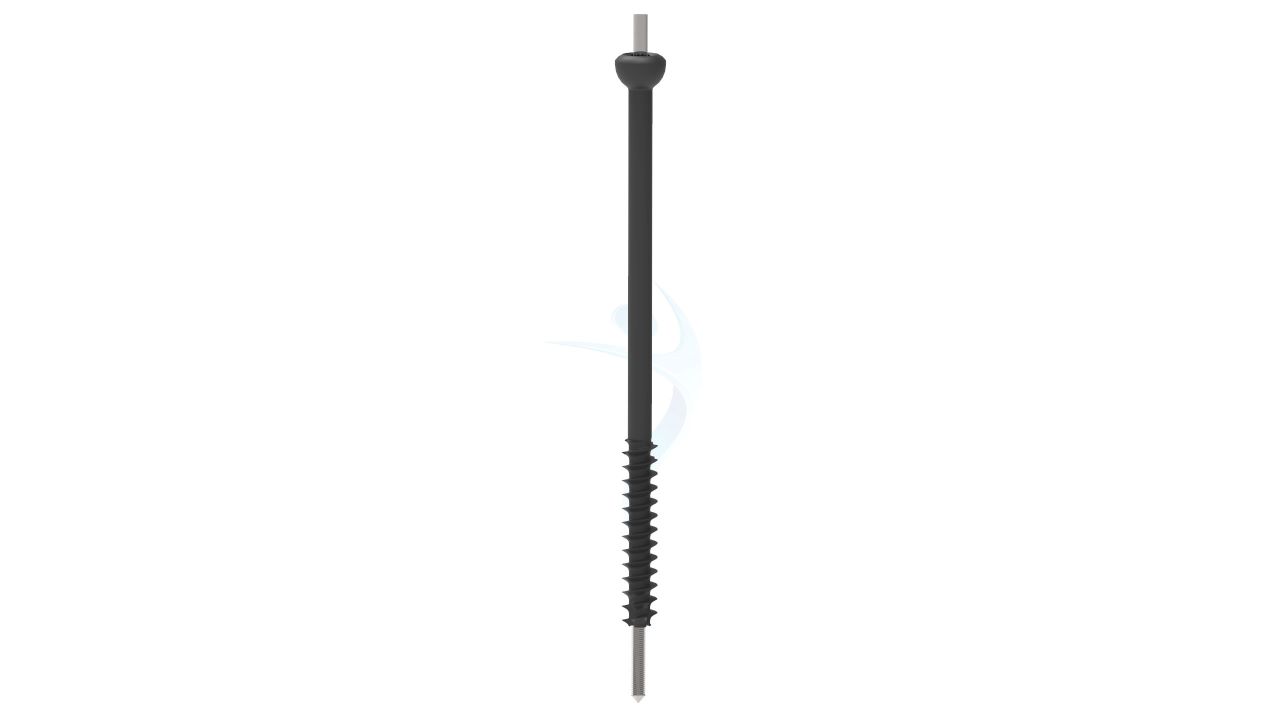
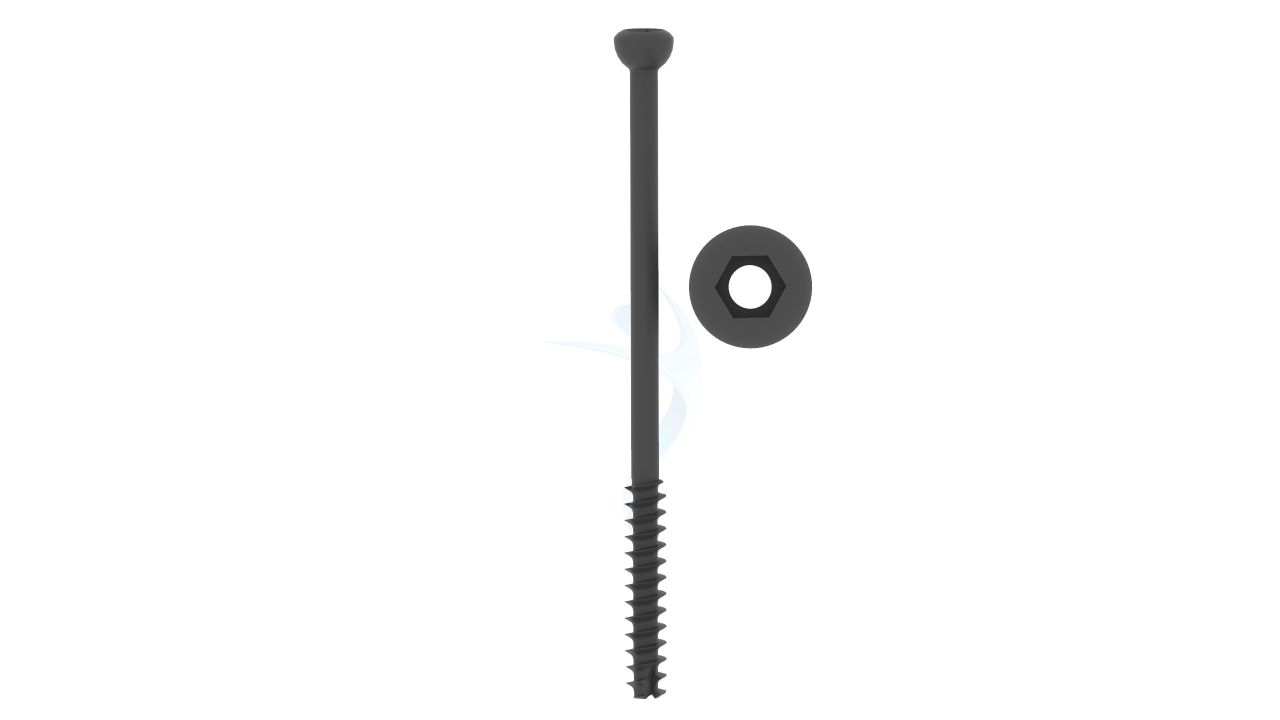
- Cannulated design: The 4.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw has a hollow core, allowing it to be guided over a guide wire during surgical insertion.
- Cancellous thread profile: The 4.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw has a thread design optimized for engagement in cancellous bone, which typically has a spongy or trabecular structure.
- Self-tapping capability:The 4.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw is typically self-tapping, meaning it can create its own thread as it is inserted into the bone.
- Variable lengths: The 4.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw is available in various lengths to accommodate different anatomical sites and patient requirements.
Cannulated Cancellous Screw - 4.5 mm sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Cannulated Cancellous Screw - 4.5 mm
- Surgical Procedure : The surgeon will explain the specific surgical procedure that will involve the use of the Cannulated Cancellous Screw 4.5 mm. They will provide details regarding the purpose of the procedure, the expected outcomes, and any potential risks or complications.
- Pre-operative Preparations : The patient will receive instructions on pre-operative preparations, such as fasting requirements before surgery, restrictions on medication or supplements, and any necessary diagnostic tests or imaging scans.
- Surgical Risks and Benefits : The surgeon will discuss the potential risks and benefits associated with the use of the Cannulated Cancellous Screw 4.5 mm. This may include risks of infection, bleeding, nerve damage, or hardware-related complications, as well as the anticipated benefits of improved bone fixation and stability.
- Anesthesia Options : The patient will be informed about the type of anesthesia that will be administered during the surgery. This may range from local anesthesia to general anesthesia, and the associated risks and recovery considerations will be explained.
- Post-operative Care : Pre-operative information will also cover post-operative care instructions. This may include guidelines on wound care, pain management, weight-bearing restrictions, and rehabilitation exercises.
- Patient Positioning : The patient is positioned appropriately based on the specific surgical site and access needed for the procedure. This may involve lying on their back, side, or stomach, depending on the location of the bone requiring fixation.
- Incision and Exposure : A small incision is made at the surgical site to access the bone. The surrounding soft tissues are carefully dissected to provide clear visibility and access to the target area. This allows the surgeon to visualize the bone fragments that require fixation.
- Pre-Drilling : The surgeon uses specialized drills to create a pilot hole in the bone. The diameter of the pilot hole is determined by the size of the Cannulated Cancellous Screw being used. The pilot hole is carefully drilled to the appropriate depth, ensuring proper engagement and stability of the screw.
- Screw Insertion : The Cannulated Cancellous Screw is inserted into the pilot hole. The screw is guided through the cannulated channel, often with the assistance of a guide wire. The surgeon carefully advances the screw into the bone until it is properly seated, achieving the desired compression or fixation.
- Closure and Recovery : Once the screw is securely in place, the incision is closed with sutures or staples. The wound is typically covered with a sterile dressing. The patient may be placed in a cast or provided with appropriate post-operative immobilization, depending on the specific surgical case.
- Wound Care : The patient will receive detailed instructions on how to care for the surgical incision site. This may include guidelines on keeping the wound clean, changing dressings, and watching for any signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or drainage.
- Pain Management : The surgeon will prescribe appropriate pain medication to manage post-operative discomfort. The patient will be informed about the proper dosage, frequency, and any potential side effects of the medication.
- Weight-Bearing and Activity Restrictions : The patient will be given specific instructions on weight-bearing restrictions and limitations on physical activities. These guidelines may vary depending on the surgical procedure and individual patient factors.
- Follow-up Appointments : The patient will be informed about the schedule of follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider. These appointments are essential for monitoring the healing process, removing stitches or sutures if necessary, and assessing overall progress.
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy : In some cases, post-operative rehabilitation or physical therapy may be recommended to promote optimal recovery and restore joint or limb functionality.






.png)