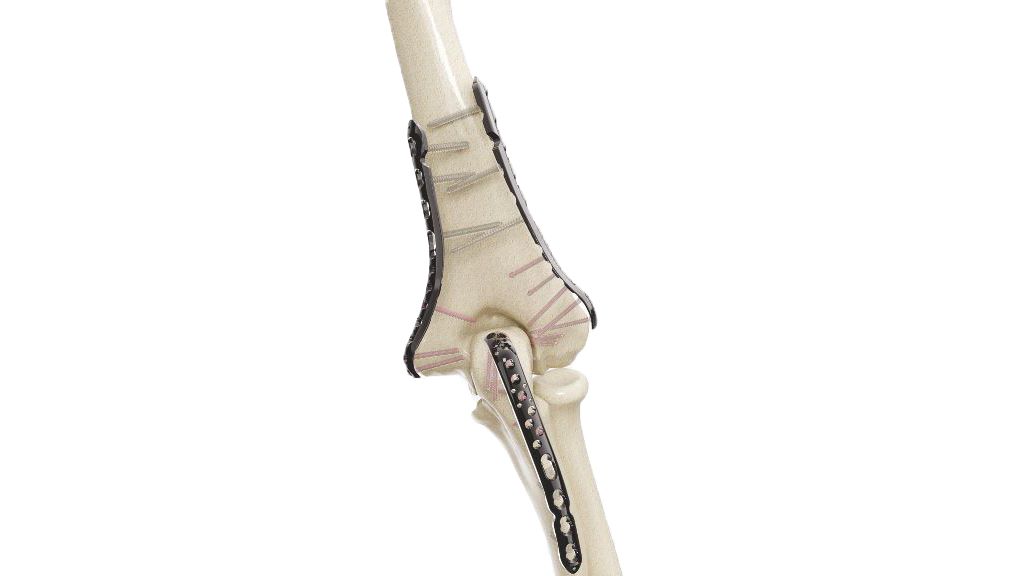
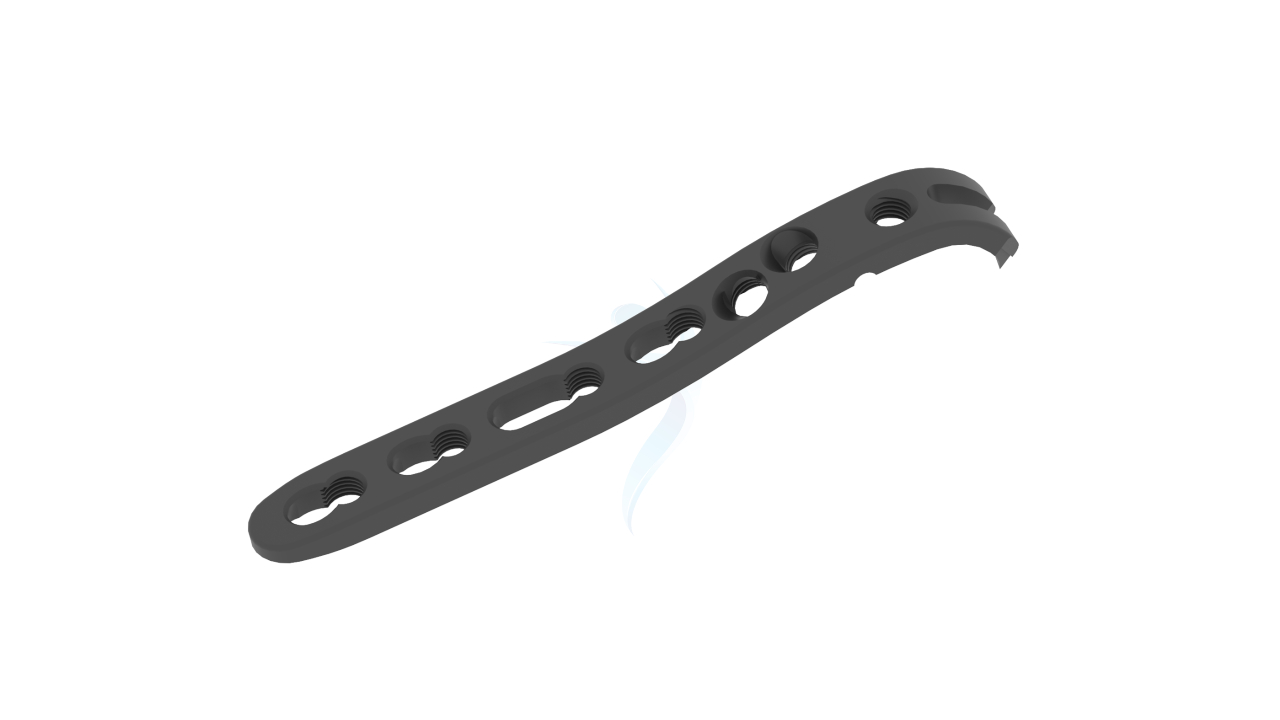
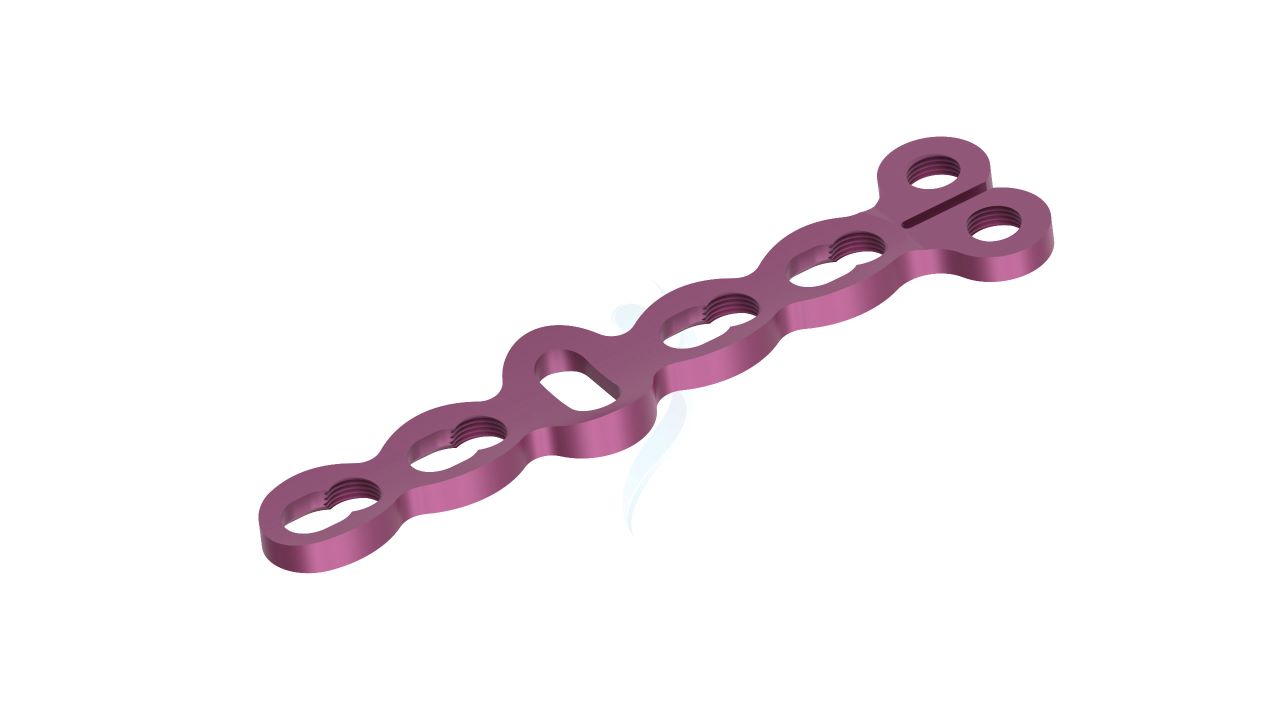
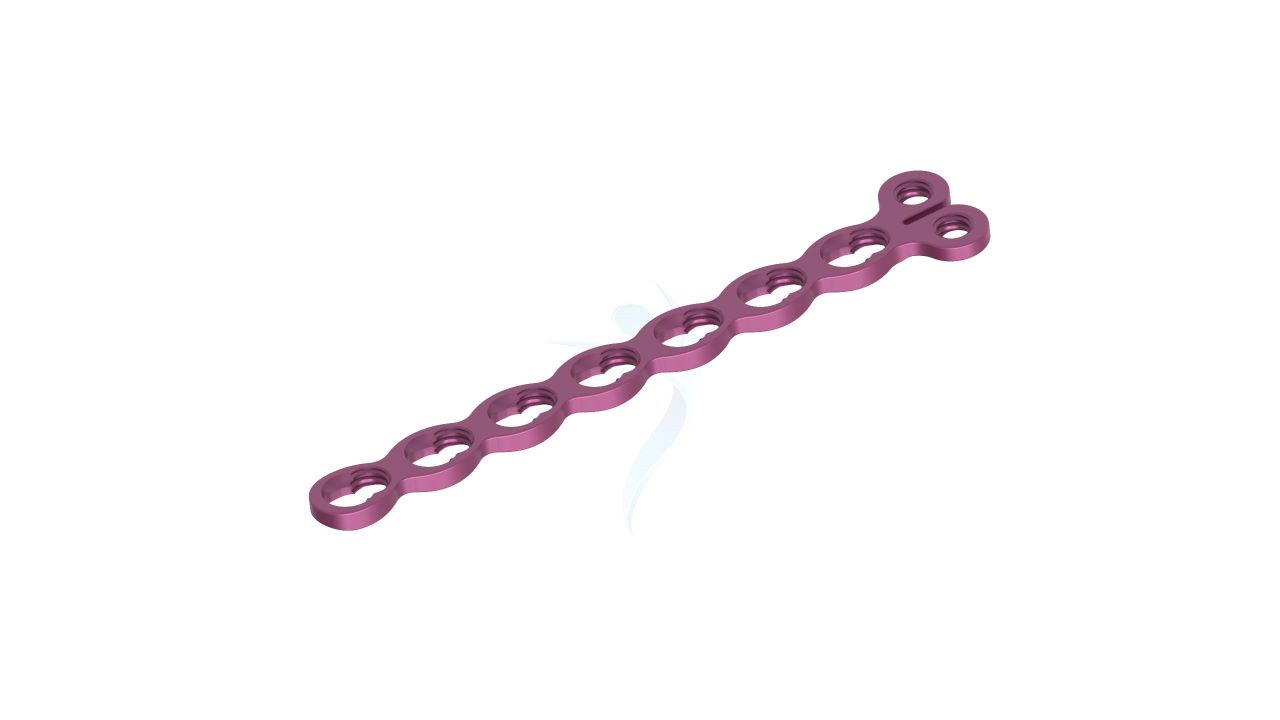
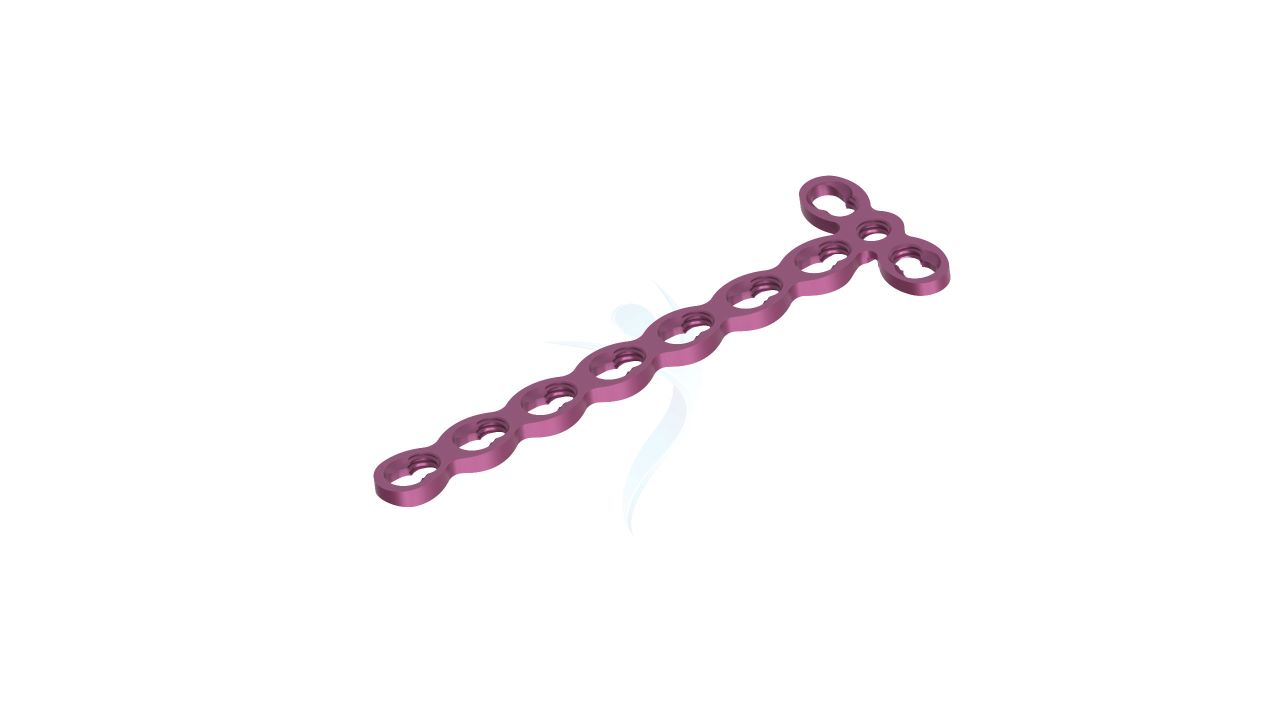
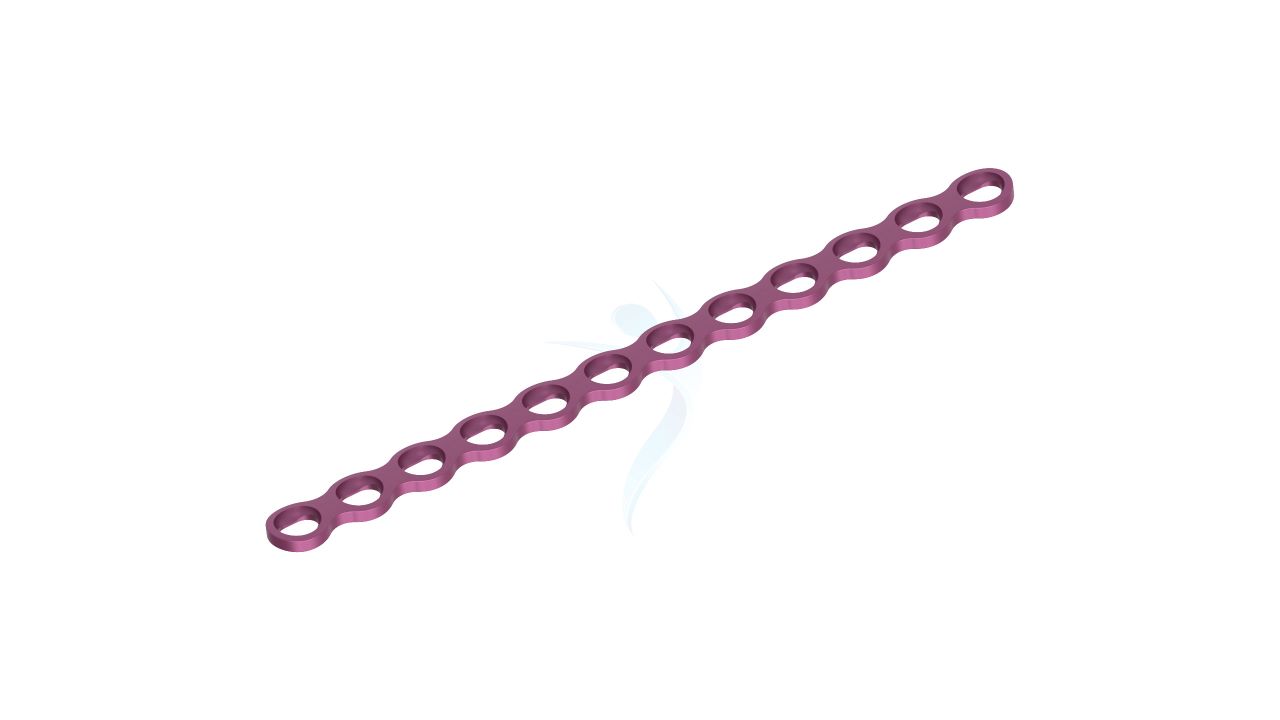
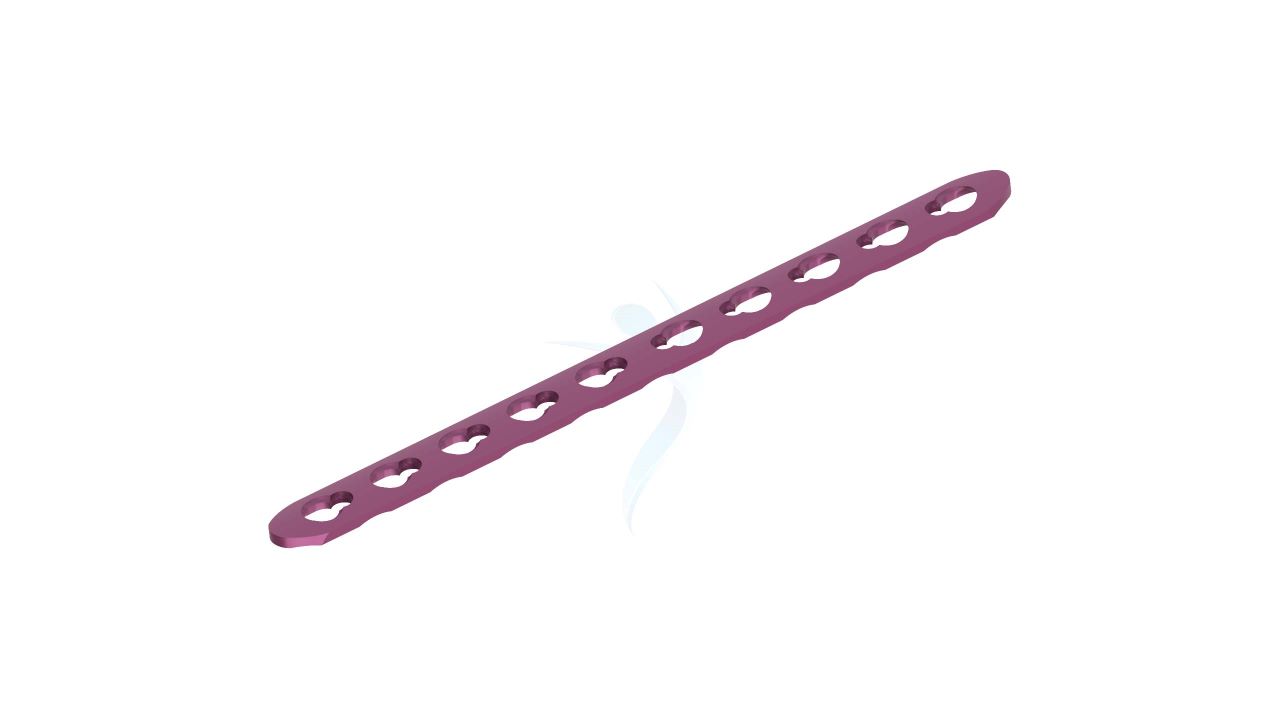
Compact Hand Plates - 2.0 mm Adaption
Product Overview
Introducing our precision-engineered orthopedic implant, the Compact Hand Plates - 2.0 mm adaption. These plates are expertly designed for superior stability and support in hand and wrist surgeries, ensuring optimal healing outcomes. With their advanced adaptability, they provide versatility in various orthopedic procedures. Trust in our high-quality implant for reliable solutions in bone fixation and restoration. Elevate your orthopedic practice with the precision of Compact Hand Plates.
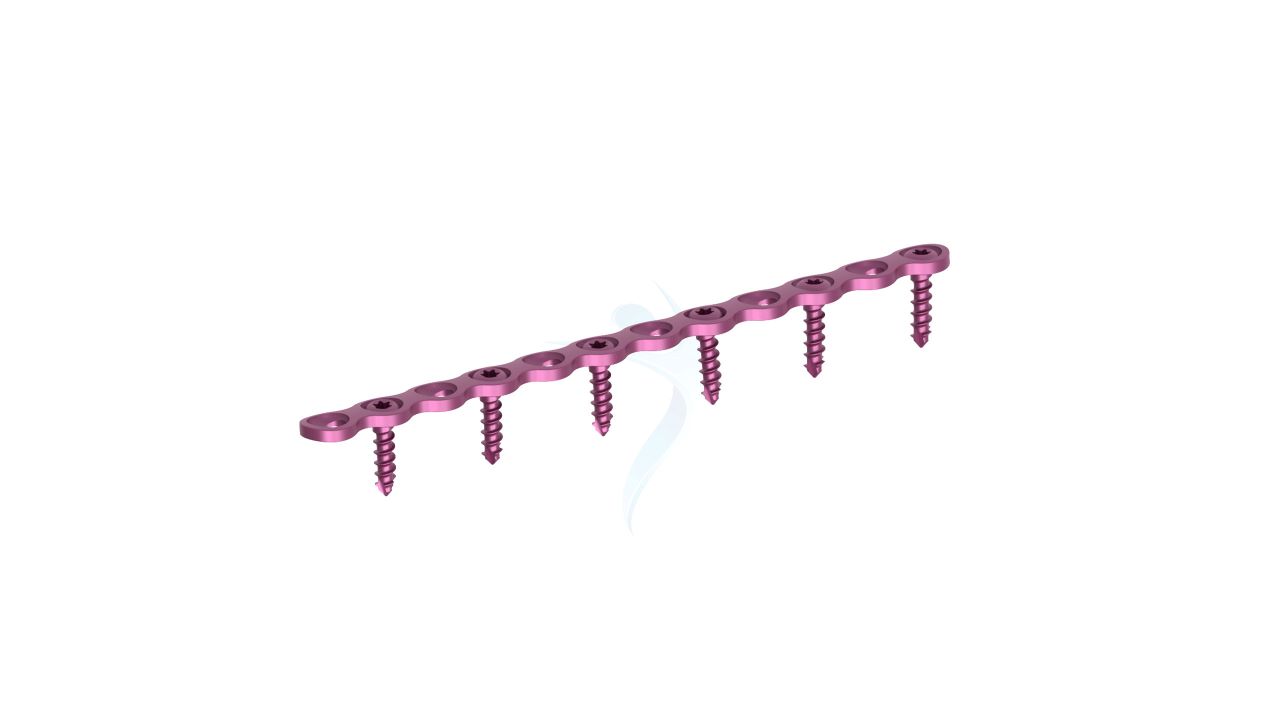
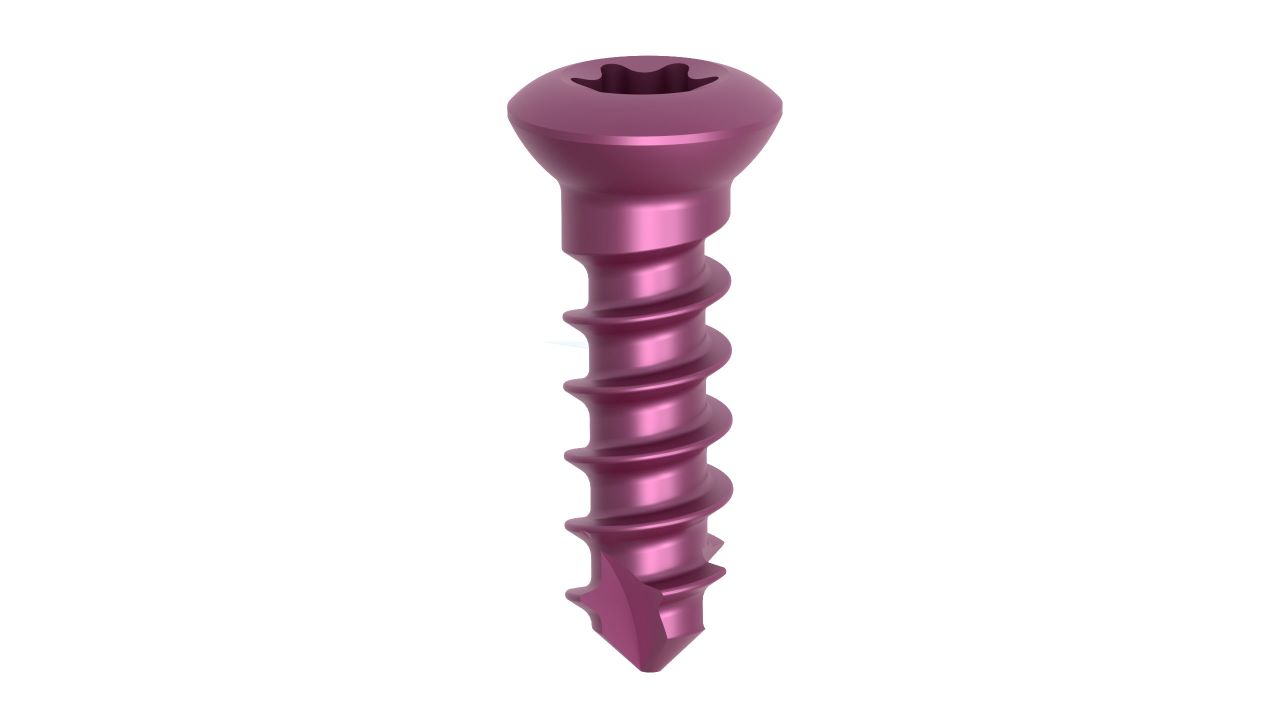
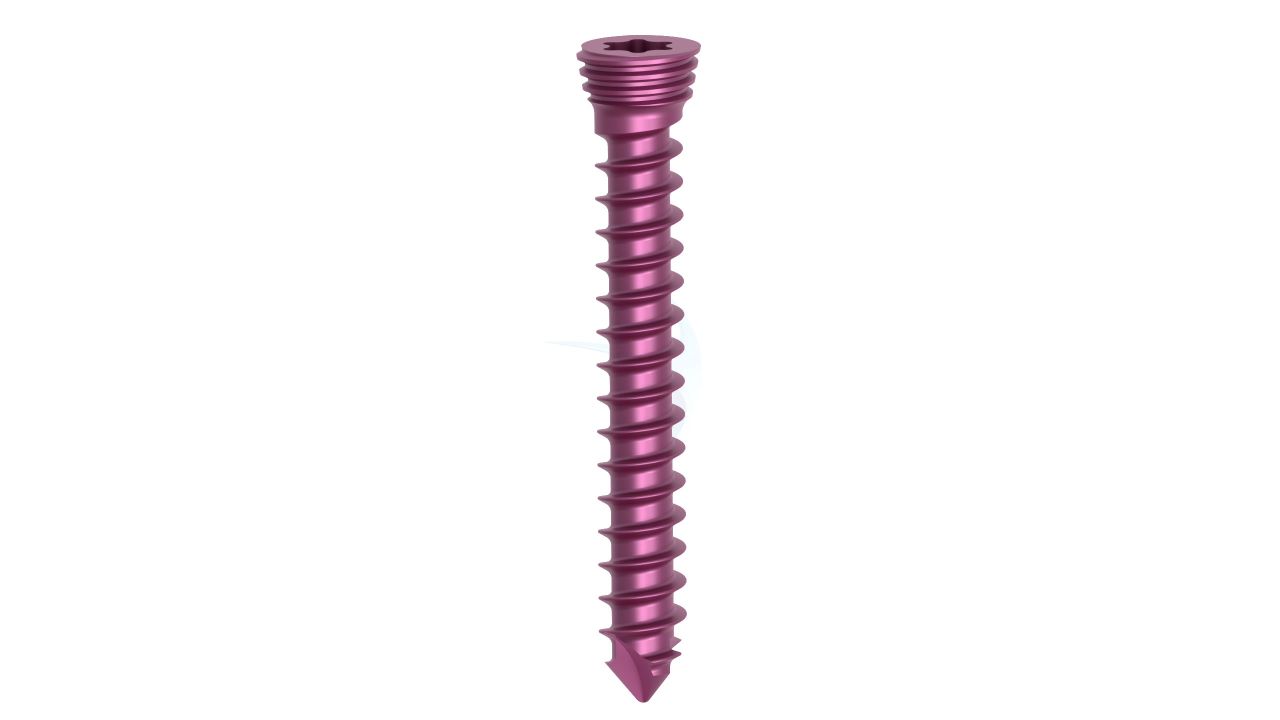
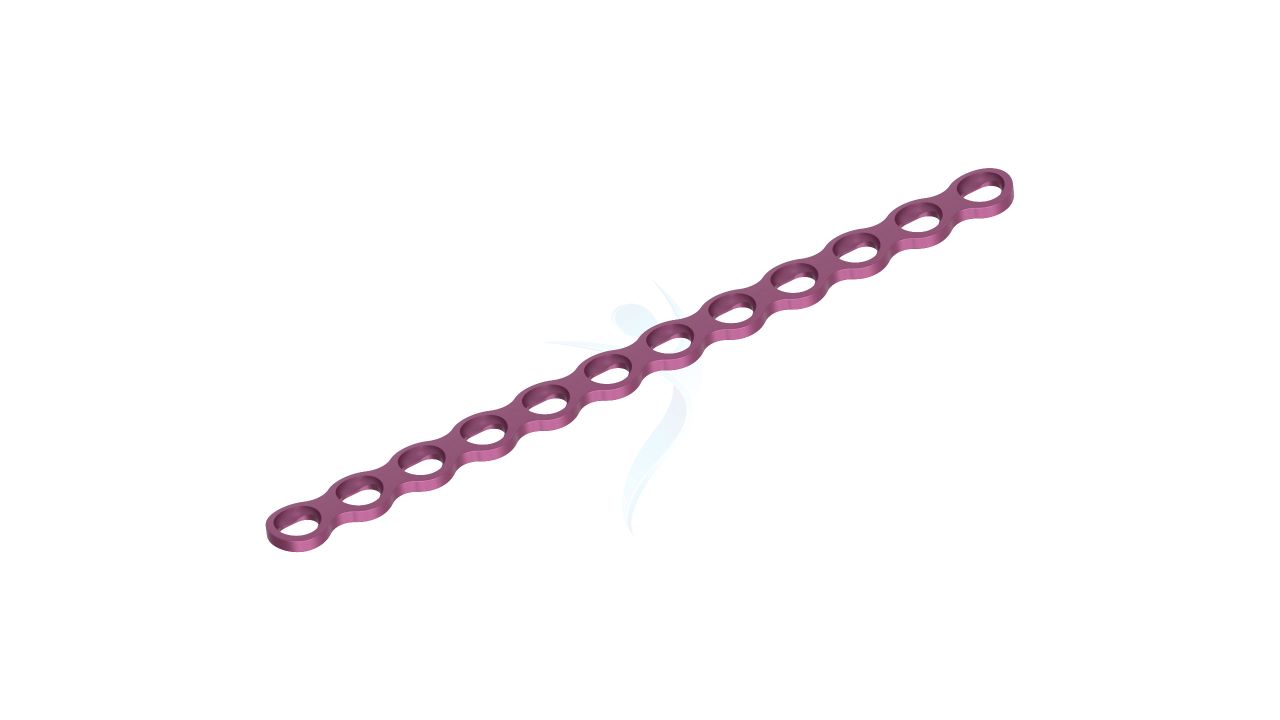



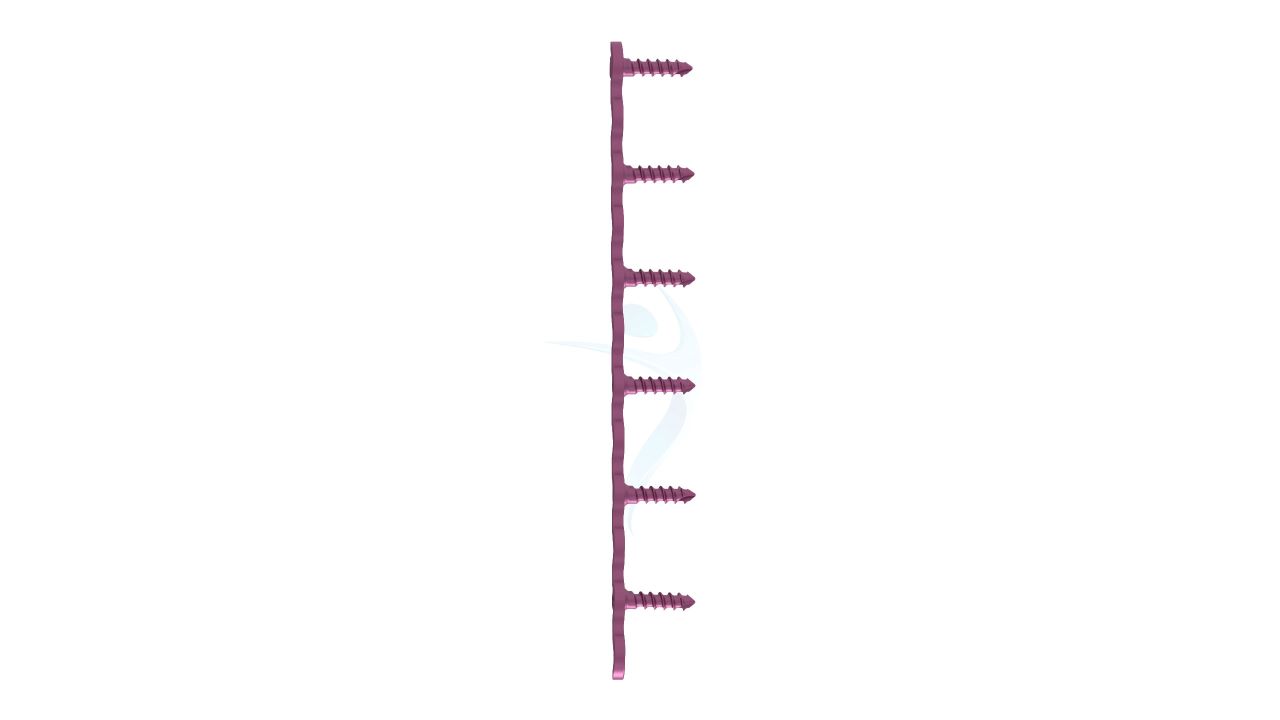


Product Uses
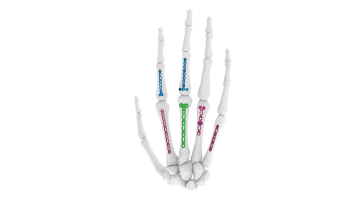
- Hand Fracture Fixation : Compact Hand Plates are used to stabilize and support fractured or broken hand bones, promoting proper healing and alignment.
- Wrist Fracture Repair : These plates are employed in the treatment of wrist fractures, ensuring stable fixation for a swift recovery.
- Carpal Tunnel Release : Surgeons may utilize Compact Hand Plates during carpal tunnel release procedures to alleviate pressure on the median nerve.
- Bone Fusion (Arthrodesis) : In cases where joint fusion is necessary, these plates assist in joining hand and wrist bones to address conditions like arthritis or instability.
- Tendon Repair :Compact Hand Plates are employed in tendon repair surgeries to provide stability and support for tendon reattachment.
Product Specification
- Plate Thickness : 2.0 mm , providing a balance of strength and low profile for optimal hand and wrist surgeries.
- Plate Design : Adaptable design suitable for various hand and wrist surgical applications, offering flexibility in addressing specific patient needs.
- Material : Manufacturedfrom high-quality surgical-grade biocompatible titanium for excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance.
- Locking Mechanism : May feature locking options to ensure robust stability and prevent screw backout, especially in high-stress areas.
- Hole Configuration : Precision-engineered screw holes designed for secure screw fixation, enabling stable implant placement.
Compact Hand Plates - 2.0 mm Adaption Sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Compact Hand Plates 2.0 mm Adaption
- Patient Evaluation : Thoroughly assess the patient's medical history, current health status, and any potential contraindications for surgery.Review imaging studies (X-rays, CT scans, MRI) to understand the extent of the condition and plan the surgery accordingly.
- Surgical Planning : Determine the surgical approach, including the specific procedure and location of implantation.Select the appropriate size and type of Compact Hand Plates - 2.0 mm adaption based on the patient's anatomy and surgical requirements.
- Patient Education :Inform the patient about the surgical procedure, expected outcomes, potential risks, and post-operative recovery.Obtain informed consent for the surgery.
- Anesthesia Consultation : Collaborate with an anesthesiologist to assess the patient's suitability for anesthesia and determine the anesthesia plan (local, regional, or general).
- Pre-operative Instructions : Provide the patient with pre-operative instructions, including fasting guidelines and medication management.
- Patient Preparation : Position the patient on the operating table, ensuring access to the surgical site while maintaining comfort.
- Surgical Site Preparation : Thoroughly clean and sterilize the surgical area.Drape the patient with sterile drapes to maintain aseptic conditions.
- Anesthesia Administration : Administer the chosen anesthesia to keep the patient comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
- Incision and Exposure : Make an appropriate incision to access the affected area of the hand or wrist.Use surgical techniques to expose the bones and soft tissues in the surgical area.
- Compact Hand Plates - 2.0 mm adaption Placement : Carefully position the Compact Hand Plates in accordance with the surgical plan.Use surgical instruments to secure the plates to the bone.Ensure proper alignment and fixation.
- Screw Fixation : Insert screws through the screw holes in the plates to secure them to the bone.Use fluoroscopy or other imaging methods to verify screw placement and alignment.
- Recovery Room : Transfer the patient to the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) or recovery area for monitoring. Monitor vital signs, pain levels, and anesthesia recovery.
- Pain Management : Administer pain medication as needed to ensure patient comfort.
- Immobilization and Rehabilitation : Prescribe or provide appropriate immobilization devices (splints or casts) based on the surgical procedure. Plan post-operative rehabilitation exercises and therapy as necessary.
- Follow-up Care : Schedule follow-up appointments to monitor the patient's progress and assess wound healing.
- Rehabilitation :Initiate or coordinate a rehabilitation program to restore hand and wrist function gradually.
- Long-Term Follow-up : Continue monitoring the patient's progress and addressing any concerns during subsequent appointments.
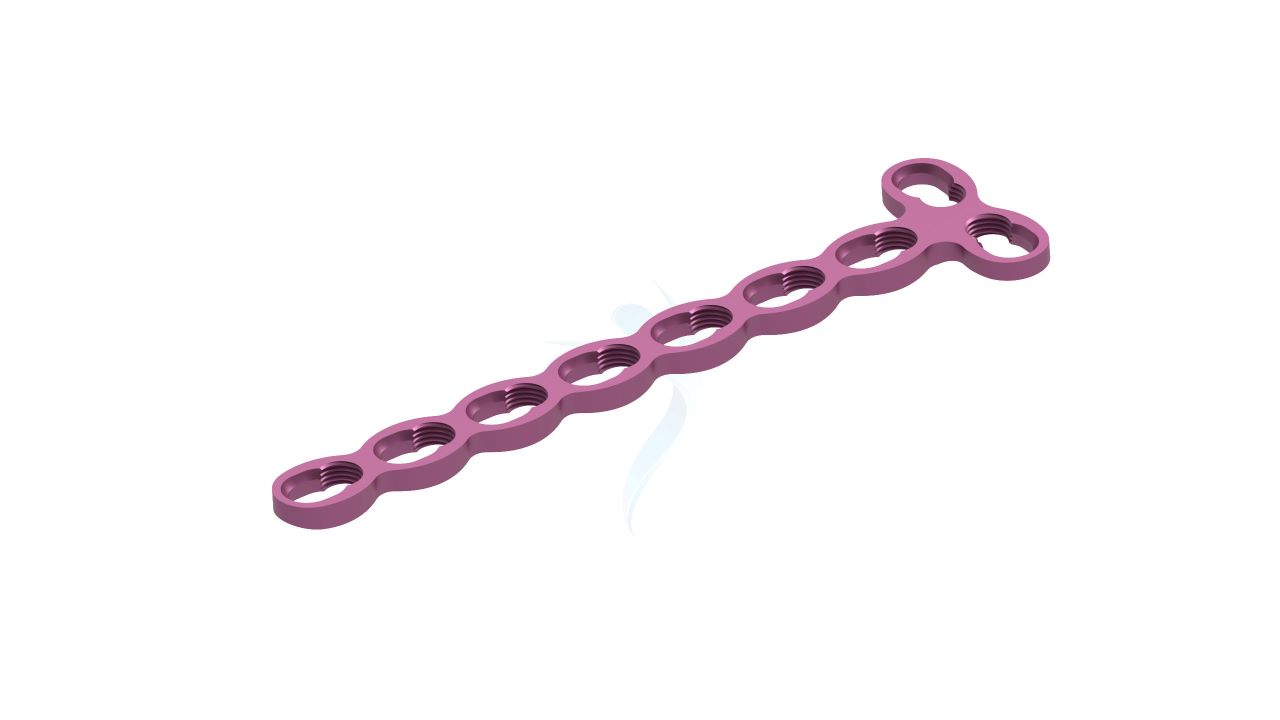
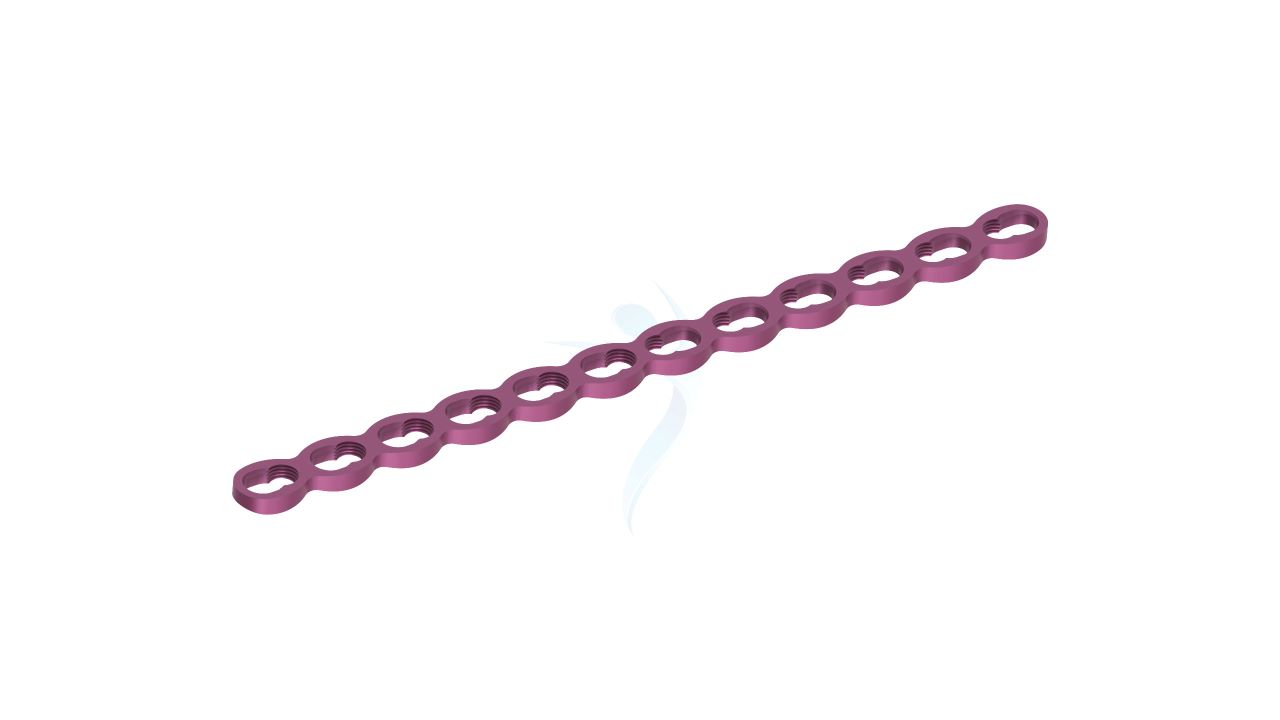
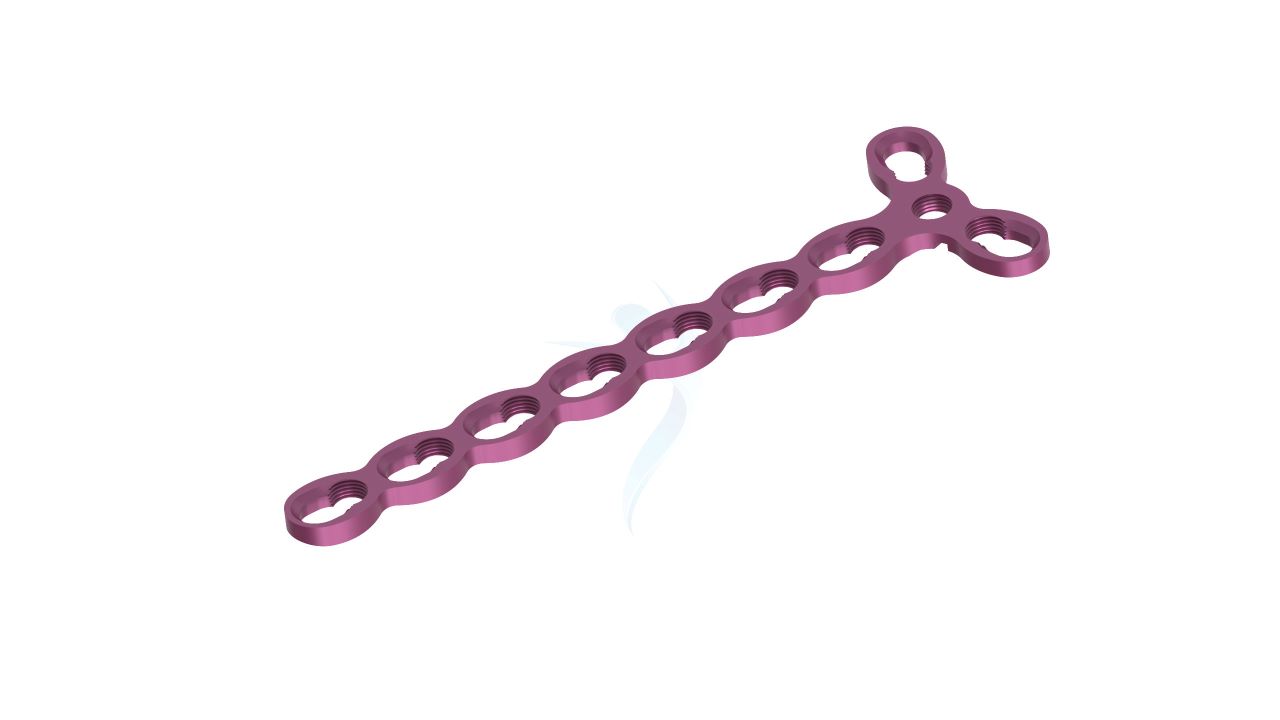
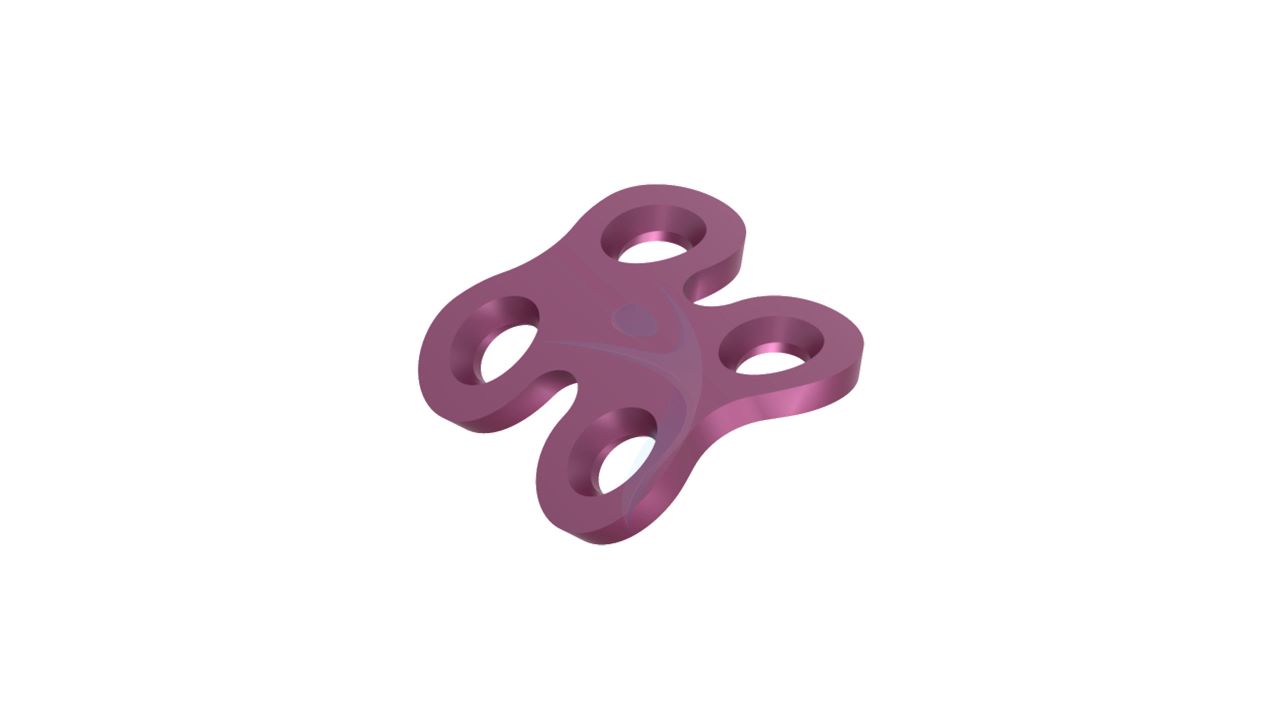











.png)