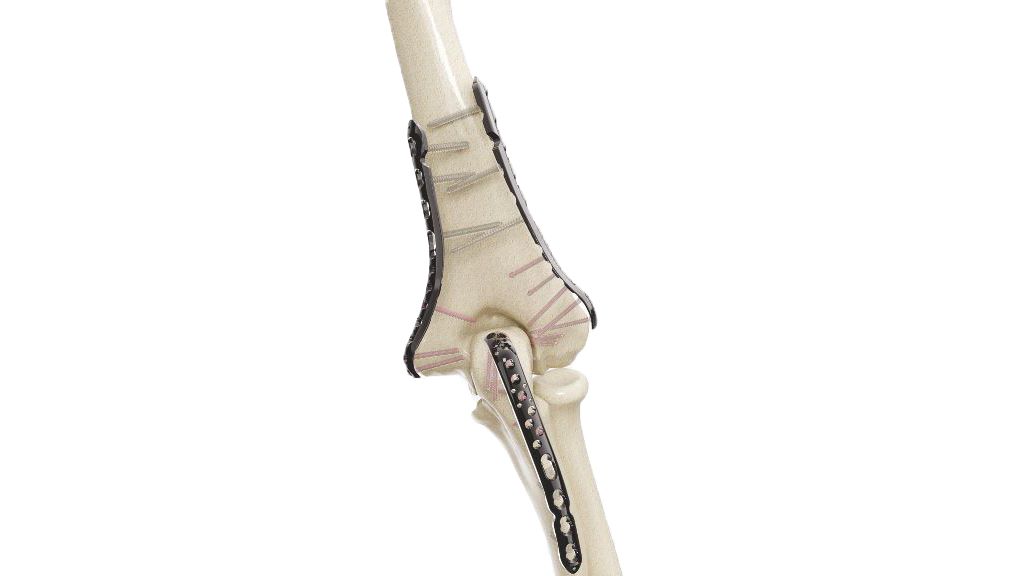
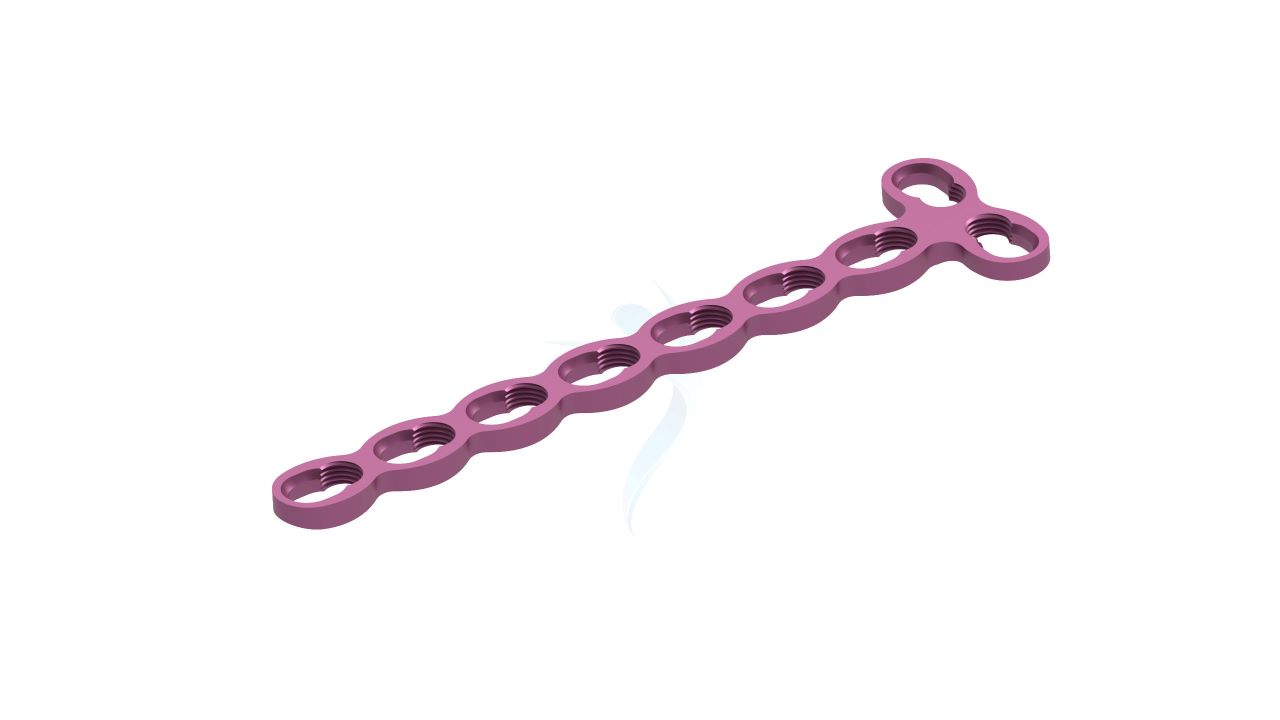
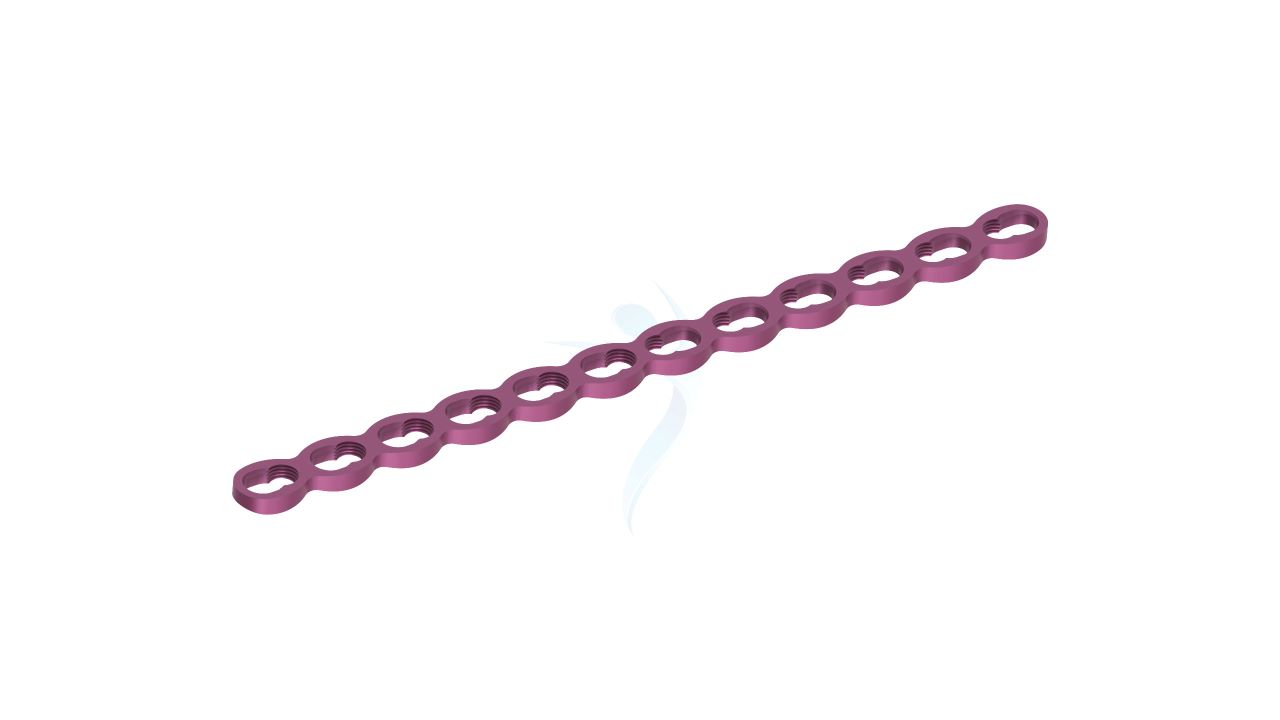
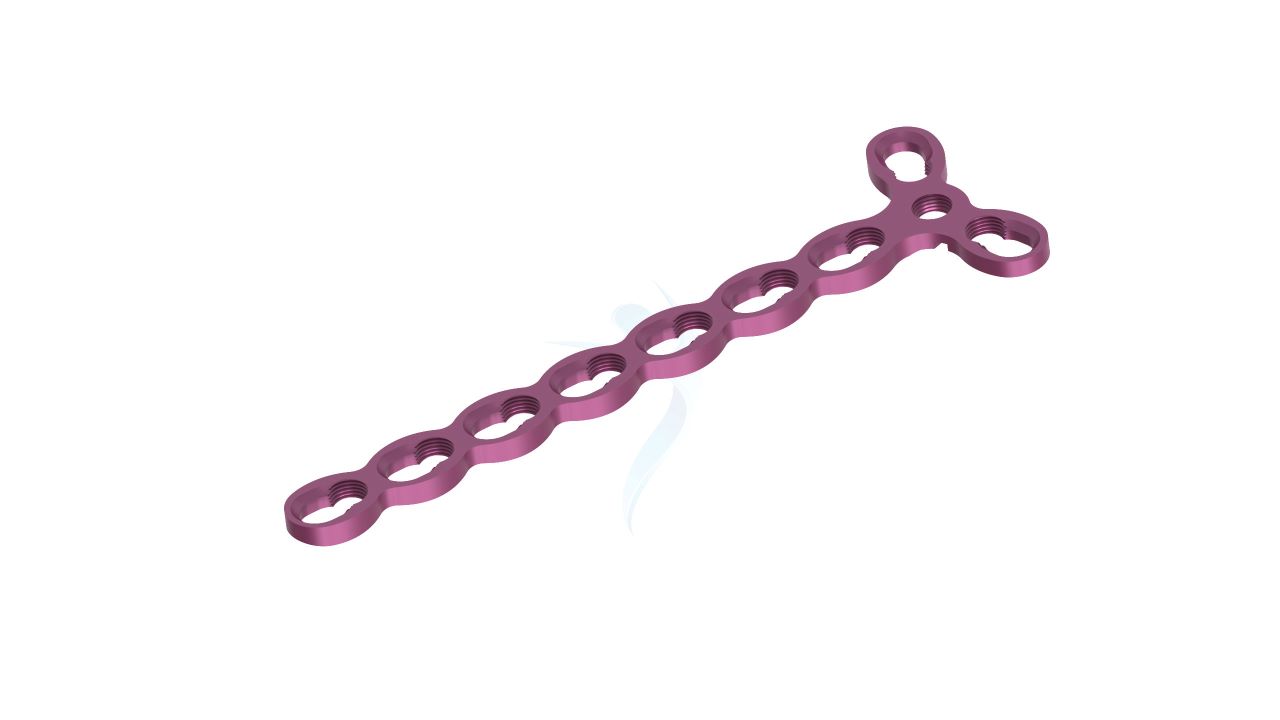
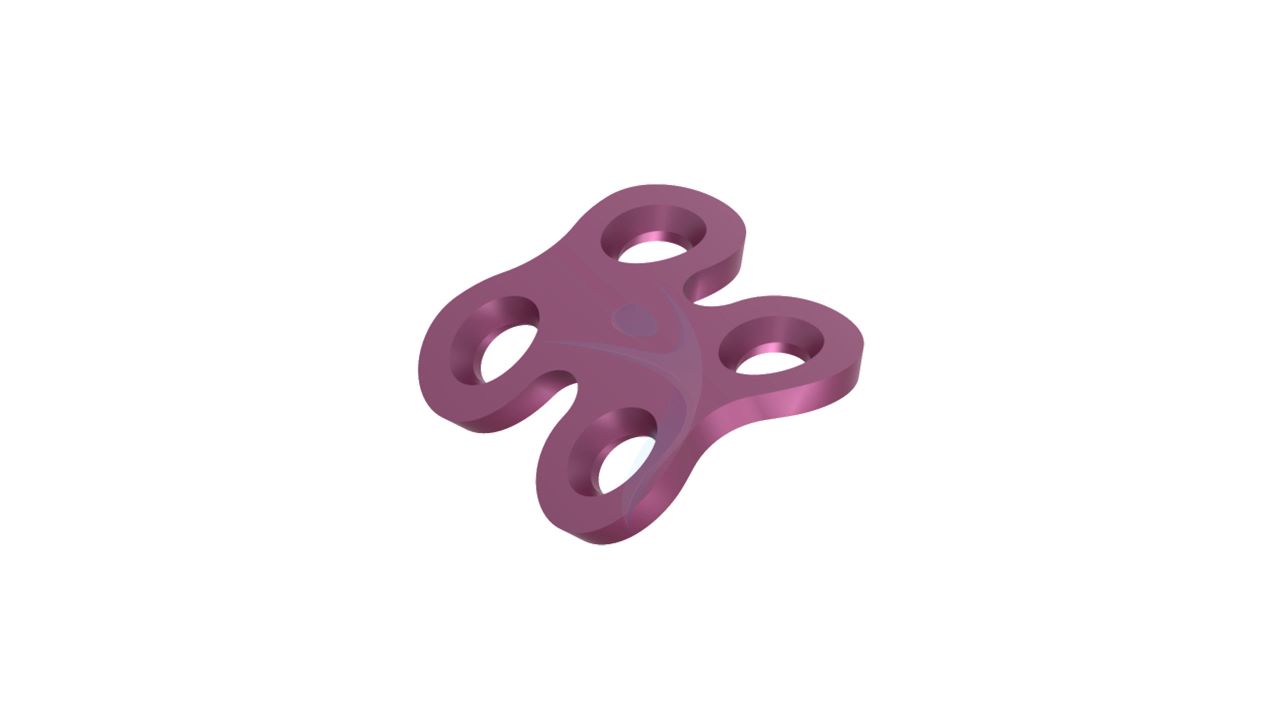
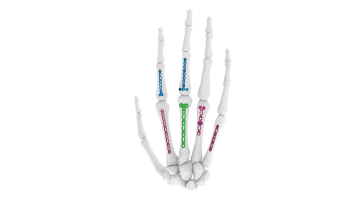
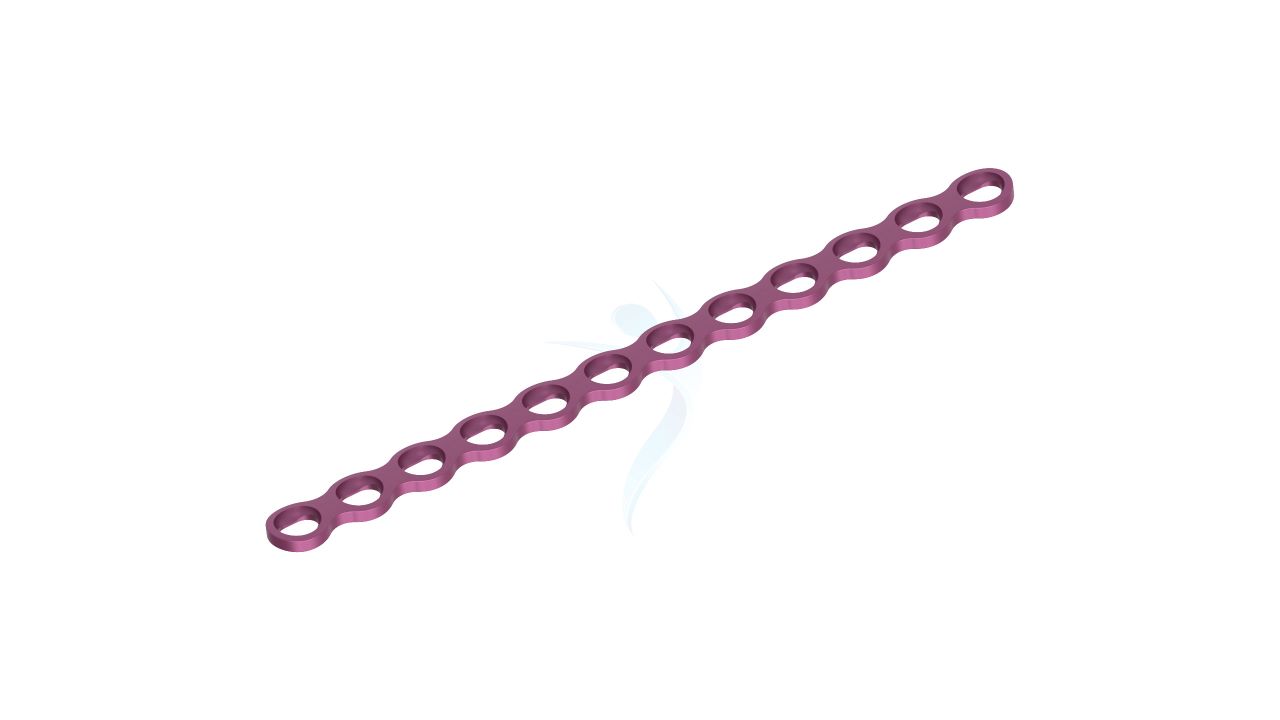
Compact Hand Plates - 2.0 mm Straight
Product Overview
Introducing our Compact Hand Plates - 2.0 mm Straight , precision-engineered orthopedic implants designed to provide exceptional stability and support for hand and wrist surgeries. Crafted with the utmost precision, these implants are ideal for bone fixation and optimal healing. Whether you're a surgeon looking for reliable tools or a patient seeking effective orthopedic solutions, our Compact Hand Plates are your trusted choice. Experience enhanced outcomes and a quicker road to recovery with our cutting-edge orthopedic implants.
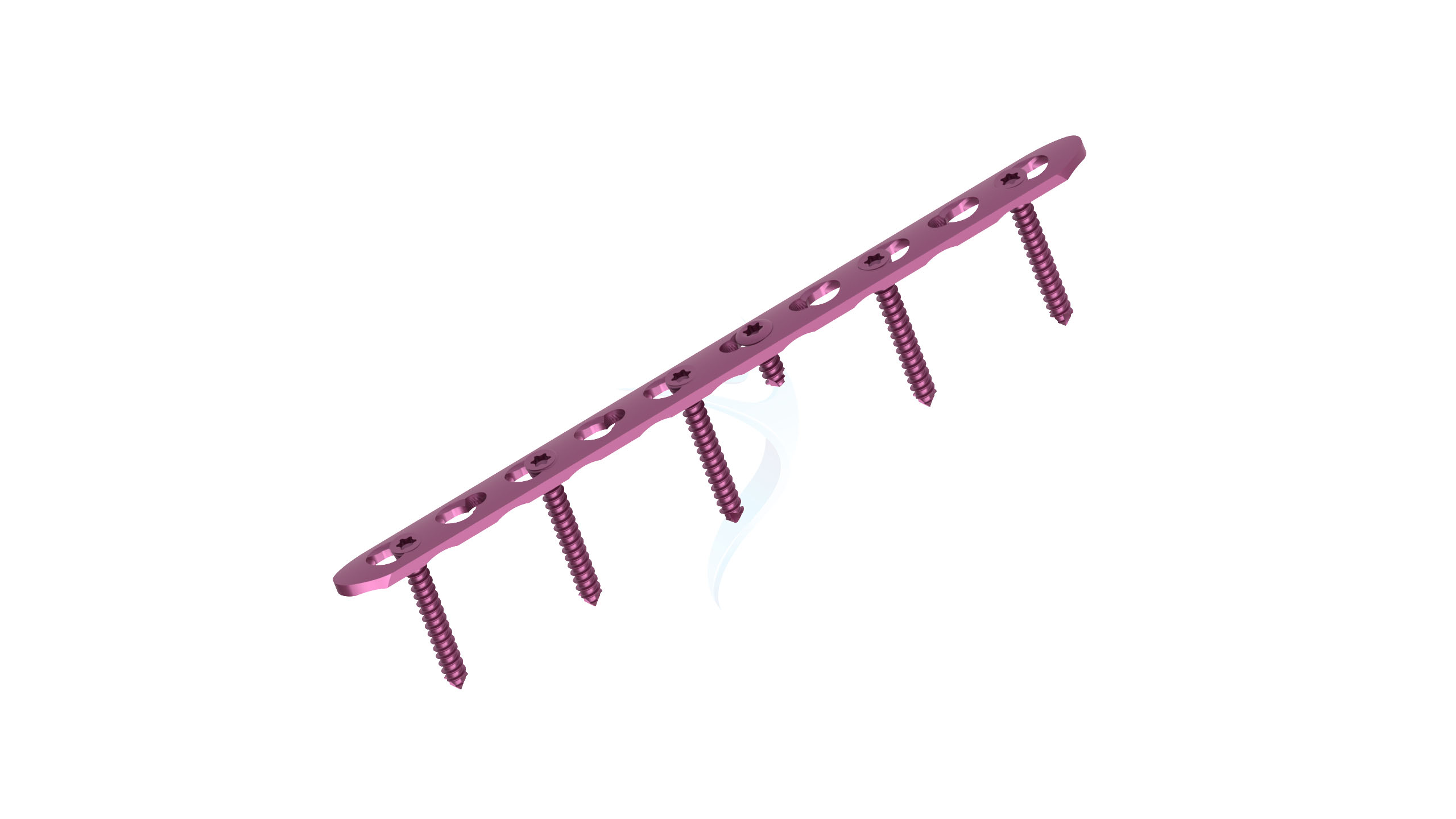
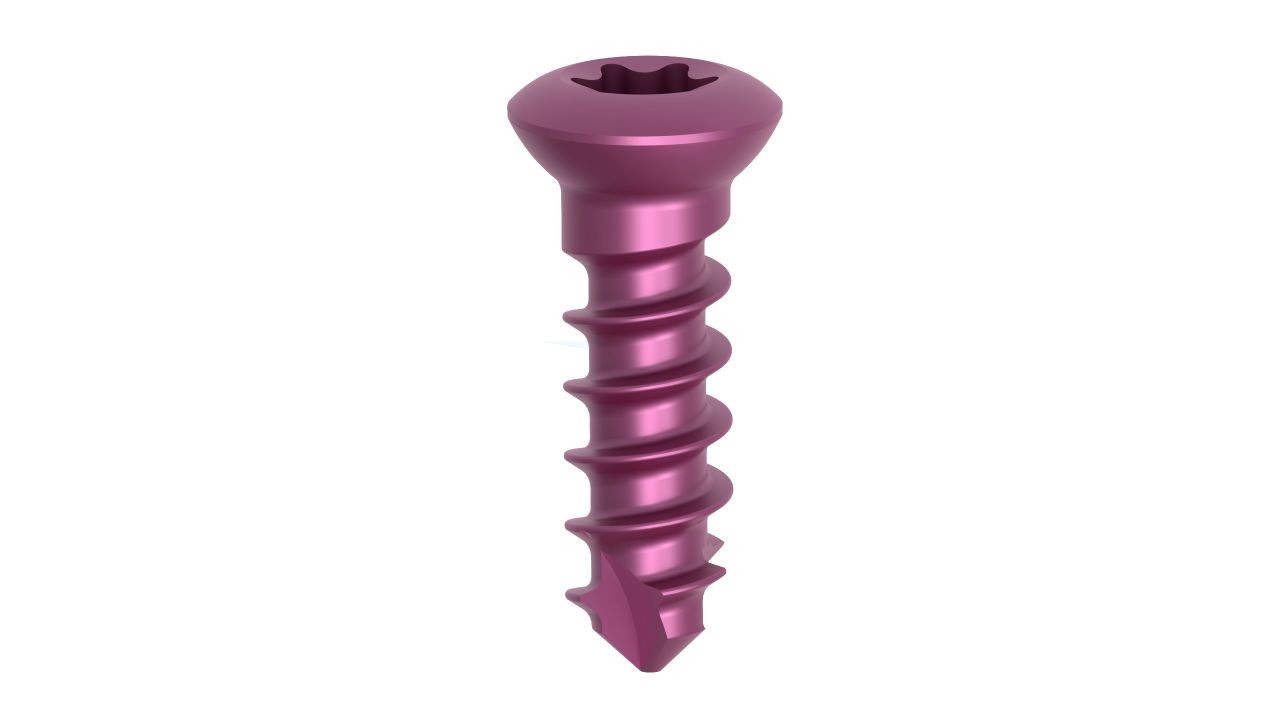
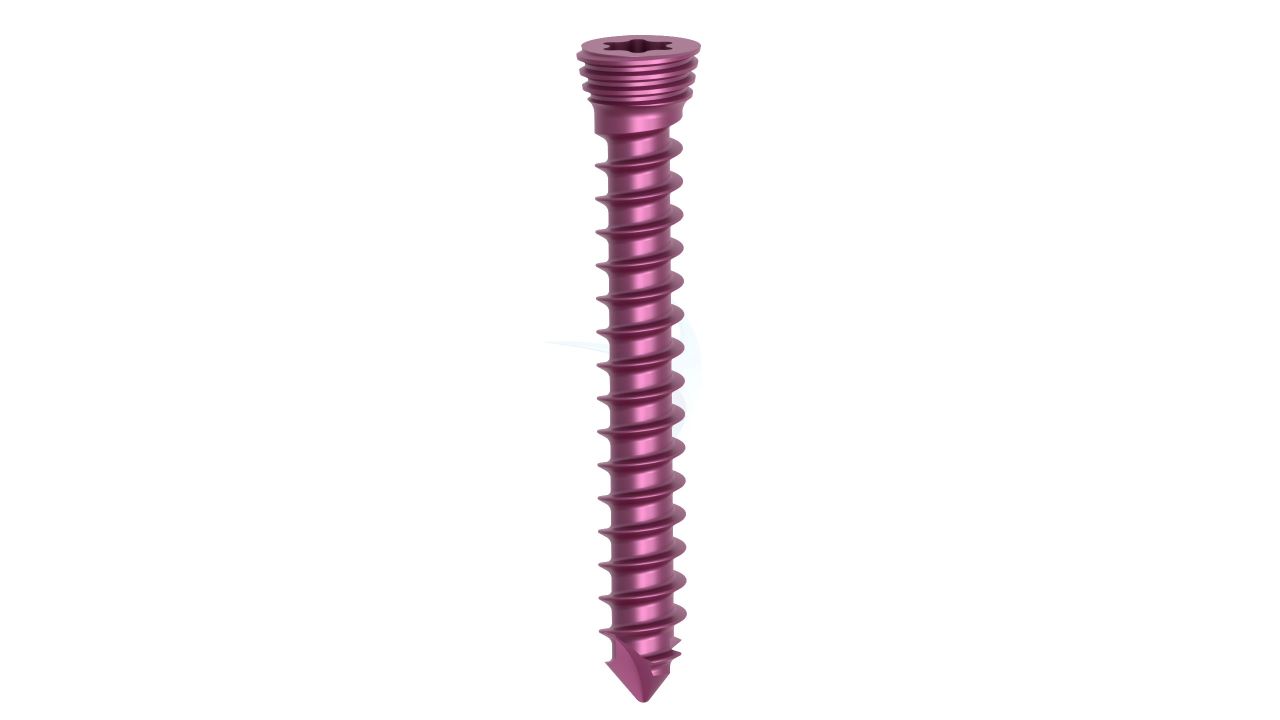
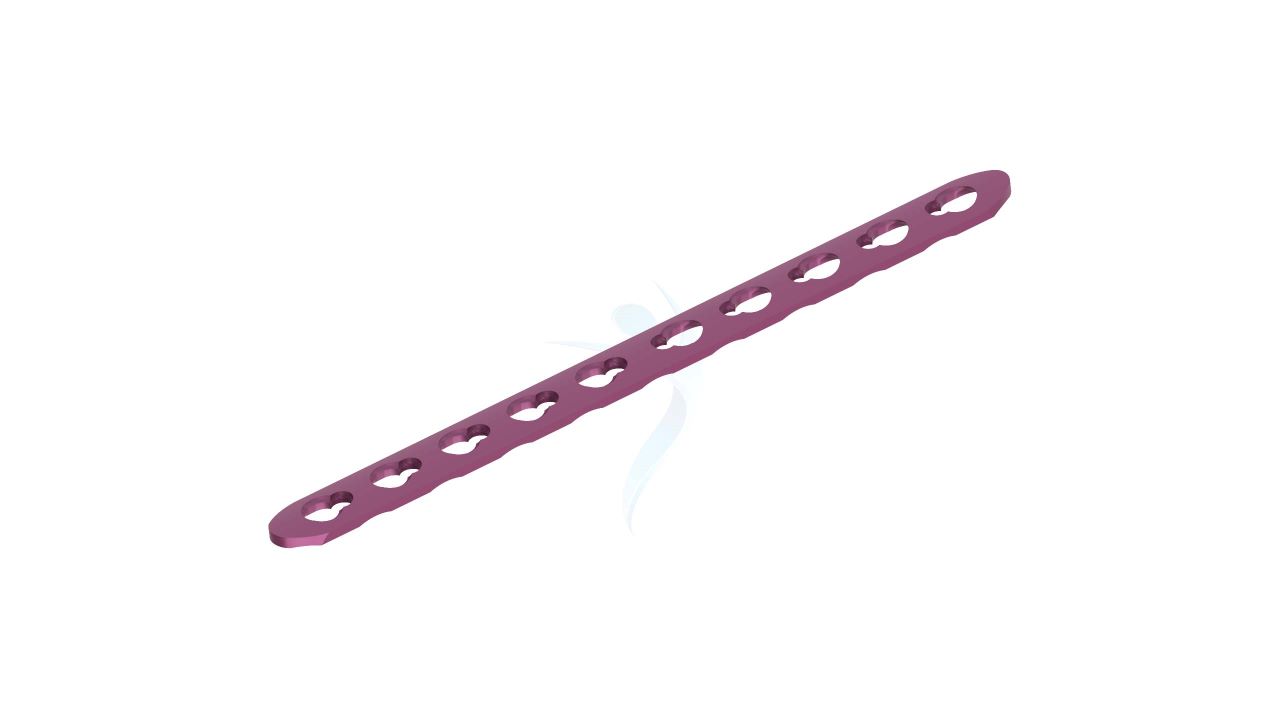



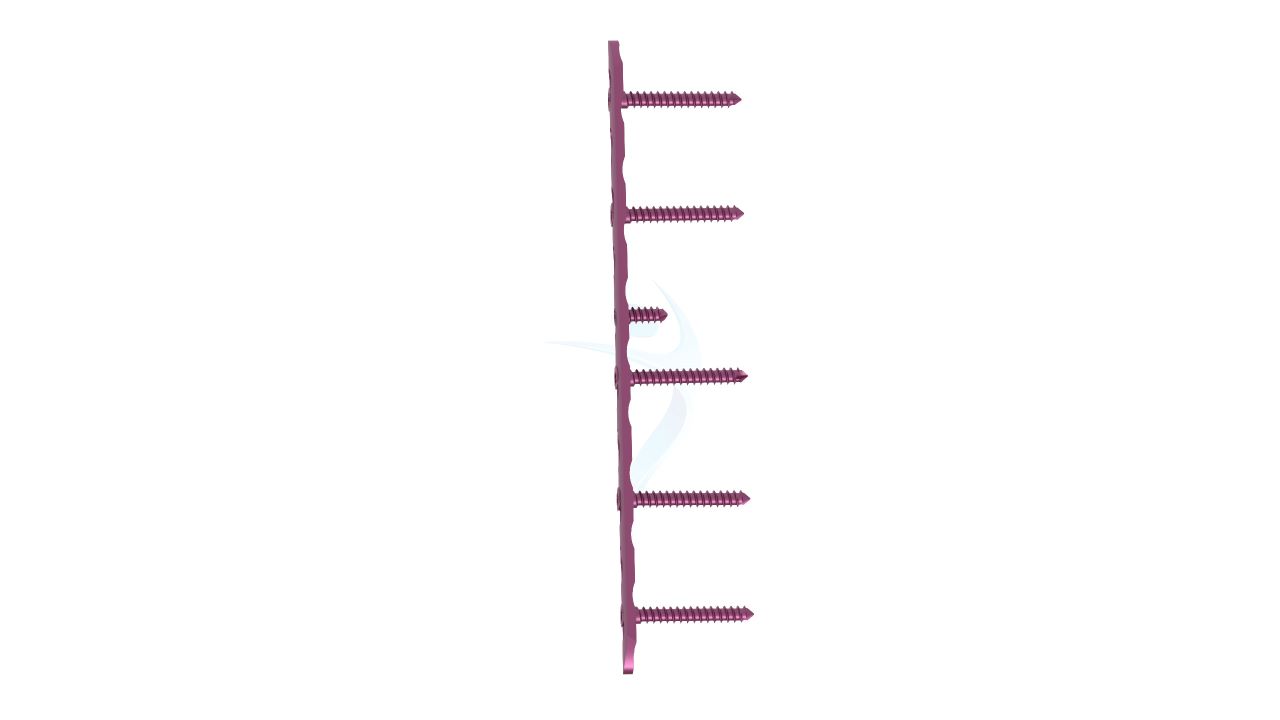


Product Uses
- Fracture Fixation : These plates are used to stabilize and align fractured or broken bones in the hand and wrist.
- Joint Fusion : Compact Hand Plates can assist in fusing joints, such as those affected by arthritis, to alleviate pain and improve joint function.
- Corrective Surgeries : They are employed in corrective surgeries for conditions like deformities, malunions, or nonunions of the hand and wrist bones.
- Trauma Cases : In cases of hand and wrist trauma, such as sports injuries or accidents, these plates provide essential support for bone healing.
- Tendon Repair : Surgeons may use these plates to secure and support tendons during repair procedures.
Product Specification
- Plate Size : 2.0 mm thickness for optimal strength and stability.
- Plate Type : Straight design for various hand and wrist surgical applications.
- Material : Made from surgical-grade titanium for biocompatibility and corrosion resistance.
- Hole Configuration : Precisely designed screw holes for secure fixation.
- Surface Finish : Smooth and low-profile finish to minimize tissue irritation.
- Locking Mechanism : May feature locking options to enhance stability and prevent screw backout.
Compact Hand Plates - 2.0 mm Straight Sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Compact Hand Plates 2.0 mm Straight
- Patient Evaluation : Conduct a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and imaging studies (X-rays, CT scans, MRI).Evaluate the patient's overall health, comorbidities, and potential contraindications for surgery.
- Surgical Planning : Determine the surgical approach, including the specific procedure and location of implantation.Select the appropriate size and type of Compact Hand Plates based on the patient's anatomy and surgical requirements.
- Patient Education : Inform the patient about the surgical procedure, expected outcomes, potential risks, and post-operative recovery.Obtain informed consent for the surgery.
- Anesthesia Consultation : Collaborate with an anesthesiologist to assess the patient's suitability for anesthesia and determine the anesthesia plan (local, regional, or general).
- Pre-operative Instructions : Provide the patient with pre-operative instructions, including fasting guidelines and medication management.
- Patient Preparation : Position the patient on the operating table, ensuring access to the surgical site while maintaining comfort.
- Surgical Site Preparation : Thoroughly clean and sterilize the surgical area.Drape the patient with sterile drapes to maintain aseptic conditions.
- Anesthesia Administration : Administer the chosen anesthesia to keep the patient comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
- Incision and Exposure : Make an appropriate incision to access the affected area of the hand or wrist.Use surgical techniques to expose the bones and soft tissues in the surgical area.
- Compact Hand Plates Placement : Carefully position the Compact Hand Plates in accordance with the surgical plan. Use surgical instruments to secure the plates to the bone.
- Screw Fixation : Insert screws through the screw holes in the plates to secure them to the bone.
- Recovery Room : Transfer the patient to the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) or recovery area for monitoring.
- Pain Management : Administer pain medication as needed to ensure patient comfort.
- Immobilization and Rehabilitation : Prescribe or provide appropriate immobilization devices (splints or casts) based on the surgical procedure.
- Follow-up Care : Schedule follow-up appointments to monitor the patient's progress and assess wound healing.
- Complication Monitoring : Keep a watchful eye for potential complications such as infection, implant-related issues, or delayed healing.
- Rehabilitation : Initiate or coordinate a rehabilitation program to restore hand and wrist function gradually.











.png)