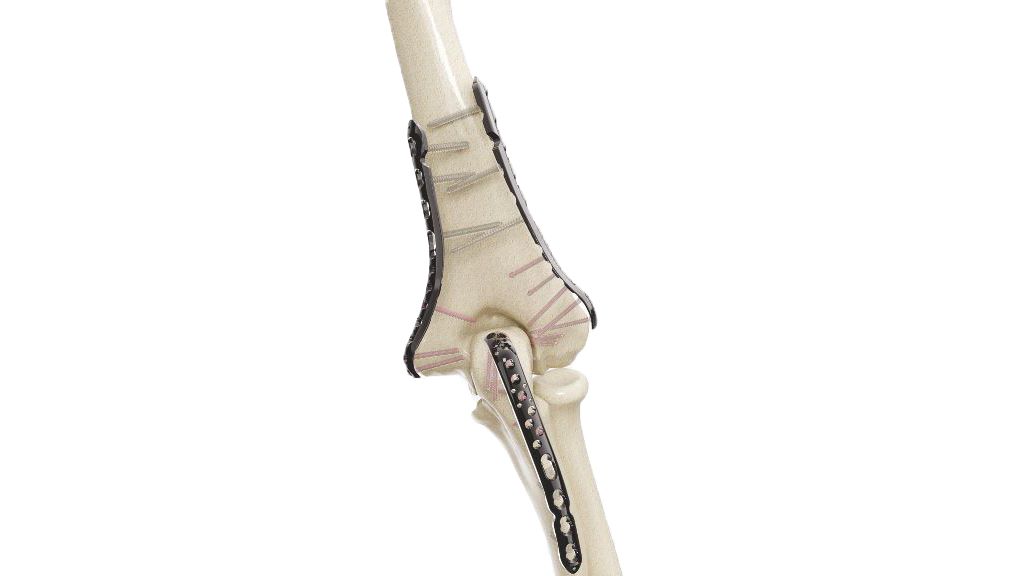
Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA - Blade)
Product Overview
The PFNA Blade is an innovative orthopedic implant designed for proximal femoral fractures, particularly in elderly patients. Featuring a unique blade design for precise insertion and an antirotation mechanism, it provides superior stability and fixation. The implant facilitates minimally invasive surgery, accelerates recovery, and reduces revision rates. Clinical studies support its efficacy, making it a preferred choice for treating proximal femoral fractures, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life.
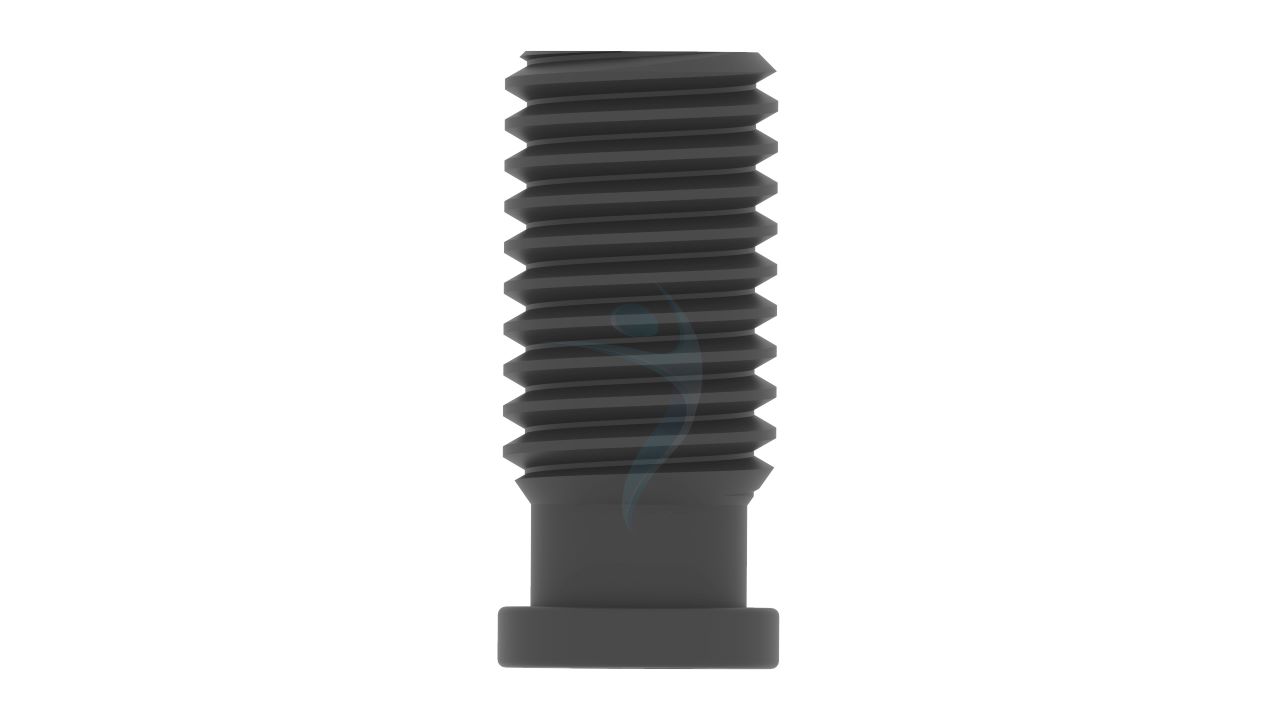
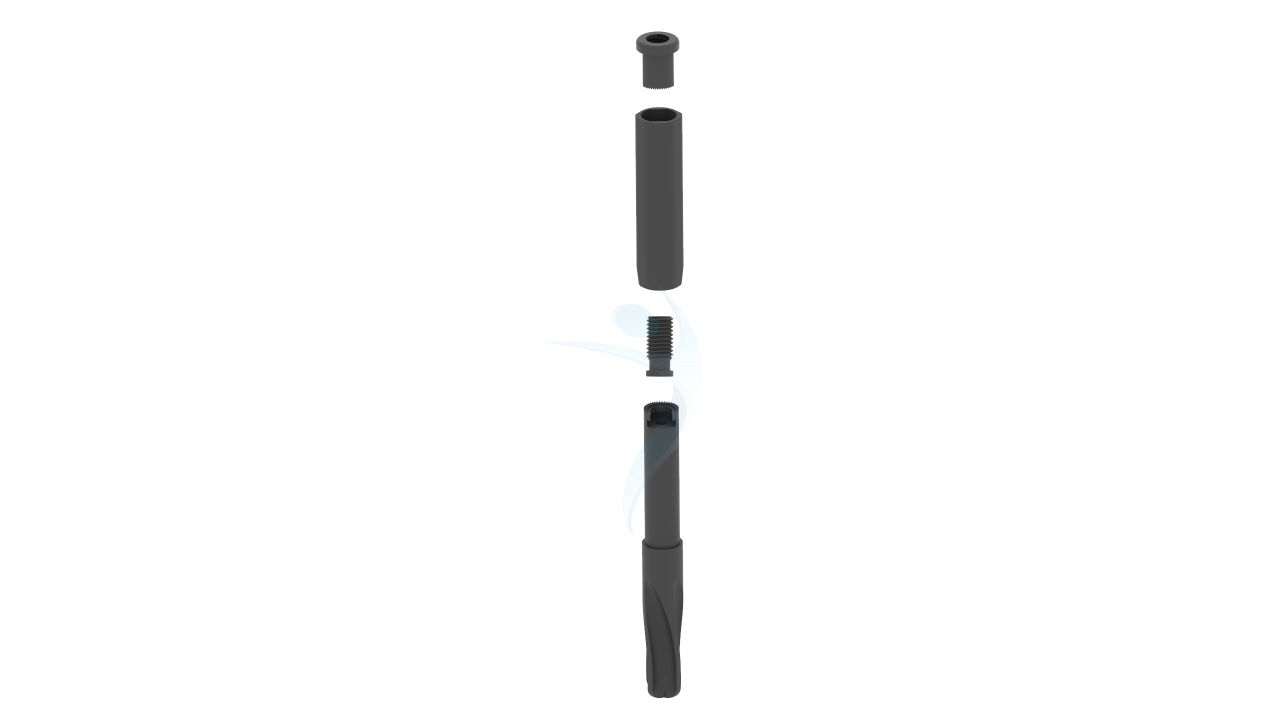
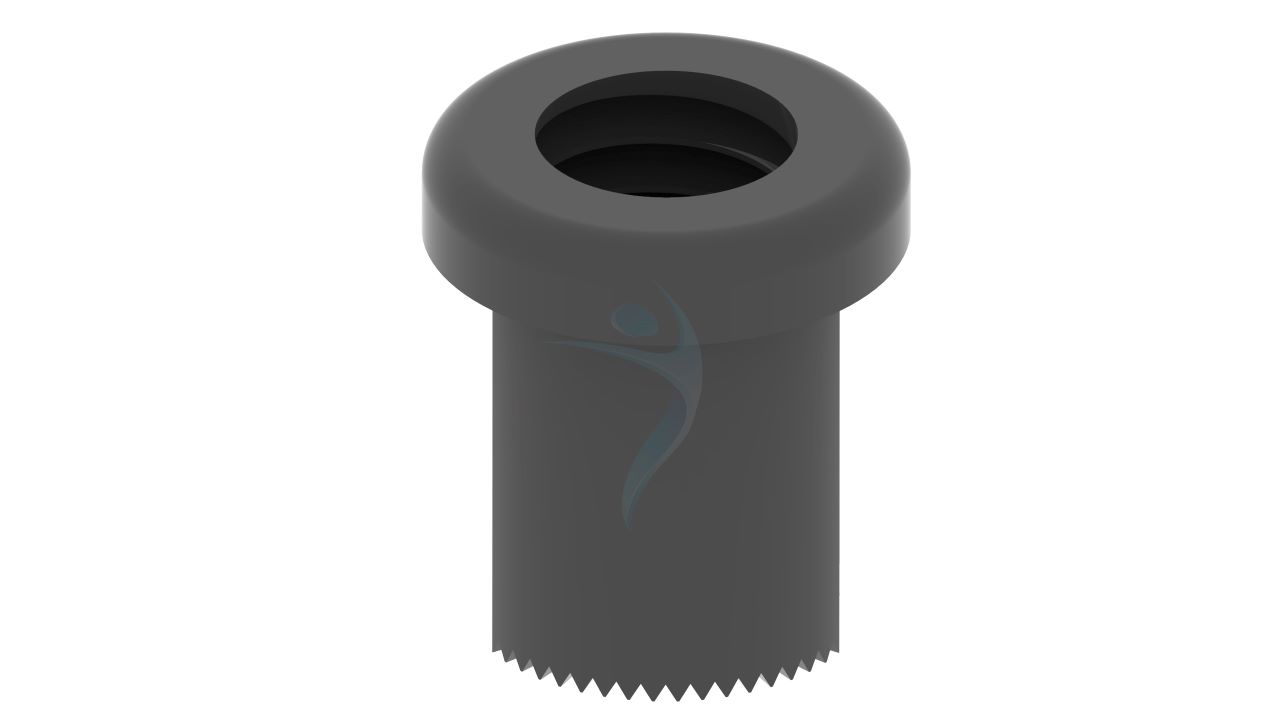
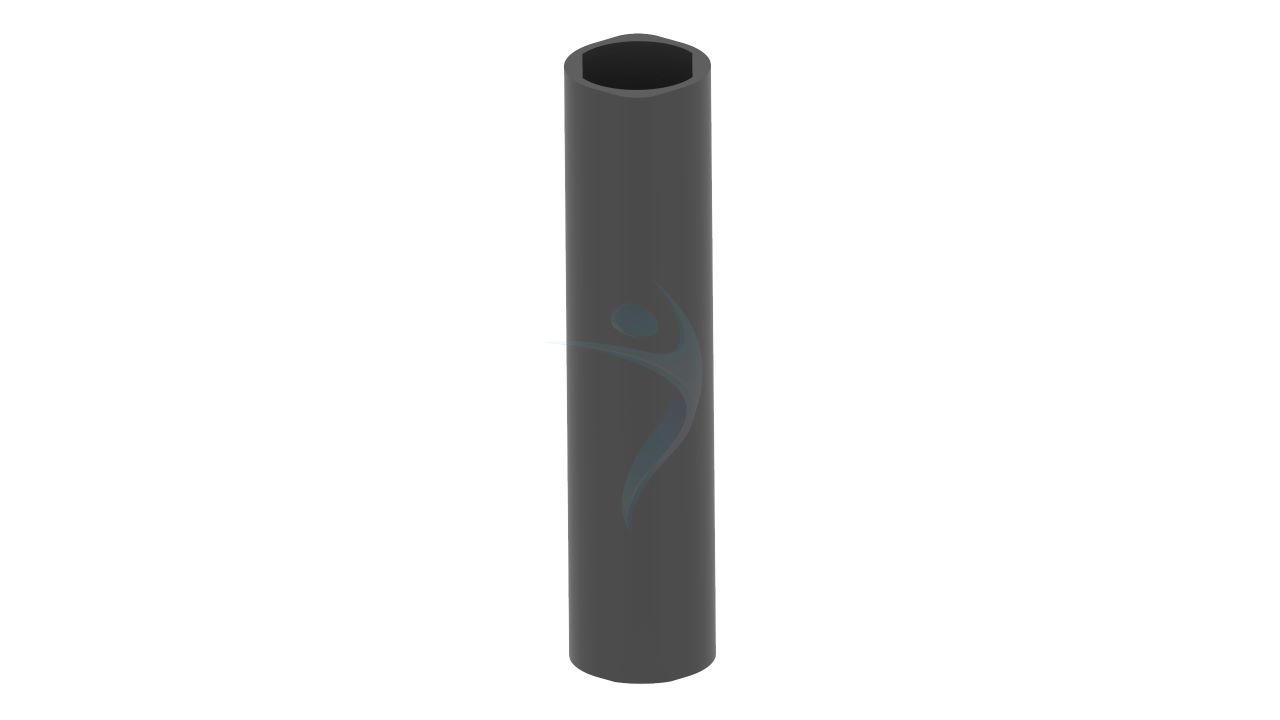
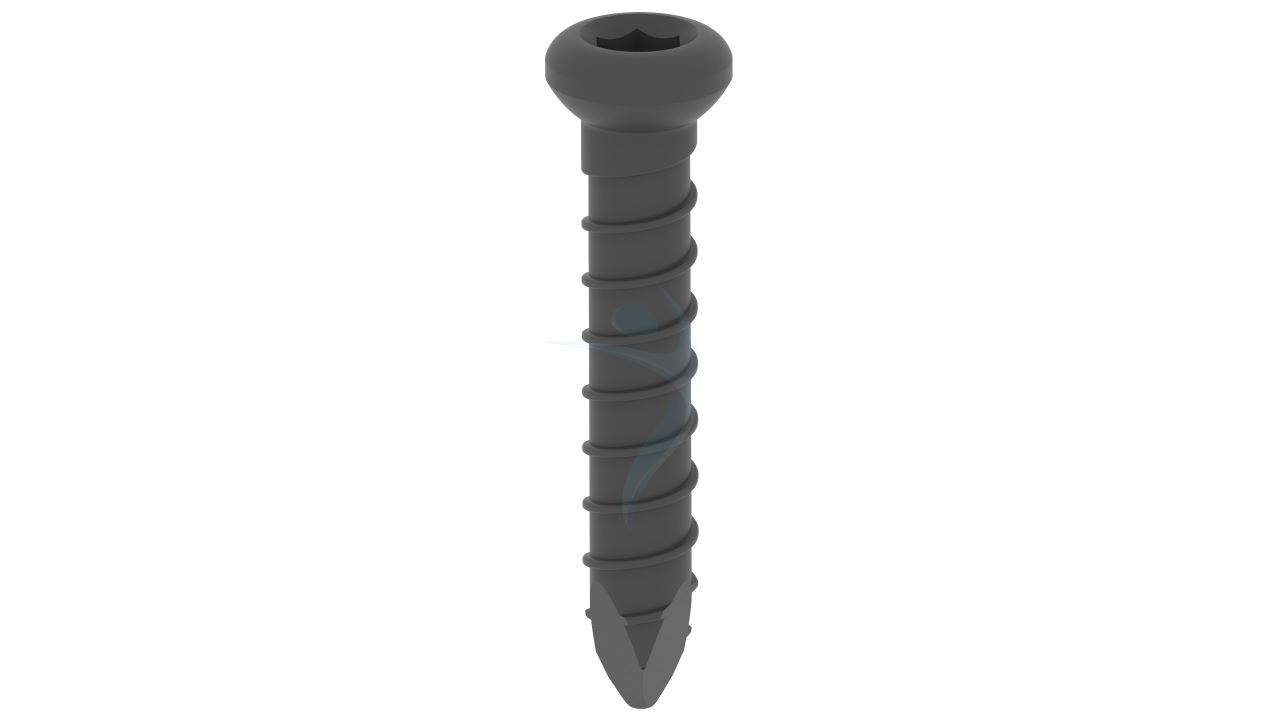











Product Uses
- Intertrochanteric Fractures : The PFNA Blade is commonly used to stabilize and treat intertrochanteric fractures, which occur between the greater and lesser trochanters of the femur.
- Subtrochanteric Fractures : It is effective in managing subtrochanteric fractures, which occur just below the lesser trochanter of the femur.
- Reverse Obliquity Fractures : The PFNA Blade is specifically designed to address reverse obliquity fractures, a type of intertrochanteric fracture that is more challenging to treat.
- Unstable Fractures : It provides excellent stability and rotational control for treating unstable femoral fractures, promoting early mobilization and quicker recovery.
- Fractures in Osteoporotic Bone : The PFNA Blade is particularly useful for fractures occurring in osteoporotic bone due to its strong fixation capabilities.
Product Specification
- Material : made from high-quality medical-grade titanium alloy for strength and biocompatibility.
- Design: The PFNA Blade has a blade-like configuration designed to fit the proximal part of the femur, providing antirotation stability and fixation.
- Blade Length : Different blade lengths available to accommodate various patient anatomies and fracture patterns.
- Blade Width : The width of the blade is designed to match the medullary canal size of the femur.
- Locking Mechanism : The blade may feature locking options to prevent rotation and maintain stability.
- Compression : The PFNA Blade may offer compression capabilities to ensure optimal bone-to-implant contact.
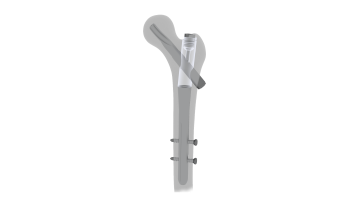
Comprehensive Guide for (PFNA - Blade) Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation
- Patient Evaluation :Assess the patient's medical history, current medications, allergies, and any previous surgeries.
- Imaging Studies : Obtain X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to assess the extent of the fracture and to plan the surgical approach.
- Informed Consent : Discuss the procedure, potential risks, benefits, and alternatives with the patient or their legal guardian. Ensure the patient understands the procedure and gives informed consent.
- Preoperative Preparation : Ensure the patient is adequately prepared for surgery, which may include fasting, discontinuation of certain medications, and preoperative skin preparation.
- Anesthesia : An anesthesiologist will administer the appropriate anesthesia, which may be general or regional anesthesia depending on the patient's condition and surgeon preference
- Patient Positioning : The patient is positioned on the operating table in a supine position.
- Sterile Preparation :The surgical site is cleaned and prepared using antiseptic solutions, and the surrounding area is draped with sterile drapes.
- Incision : The surgeon makes a surgical incision over the proximal femur, typically along the lateral aspect of the thigh, to access the fracture site.
- Fracture Reduction : The fracture fragments are carefully manipulated and aligned using specialized instruments under fluoroscopic guidance to achieve anatomic reduction.
- Nail Insertion : The PFNA blade is inserted into the intramedullary canal of the femur through the proximal aspect of the incision.
- Wound Closure : The incision is closed in layers using sutures or staples, and a sterile dressing is applied to the wound.
- Pain Management : Adequate pain control is provided to ensure patient comfort and facilitate early mobilization.
- Wound Care : The surgical incision site is monitored for signs of infection or complications. Dressings are changed as needed, and the wound is kept clean and dry.
- Rehabilitation : Physical therapy is initiated to improve range of motion, strength, and functional mobility.
- Follow-Up : The patient is scheduled for regular follow-up visits with the orthopedic surgeon to monitor healing progress, assess implant position, and address any concerns or complications.
- Activity Restrictions : Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting until cleared by their surgeon.
- X-ray Evaluation : Follow-up X-rays are obtained at specific intervals to evaluate fracture healing, implant position, and alignment.


.png)