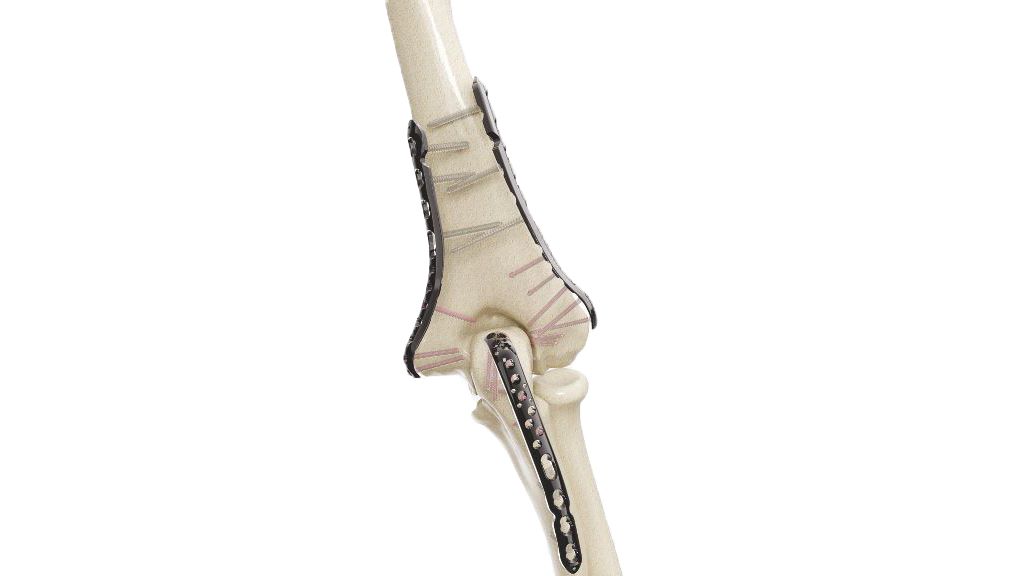
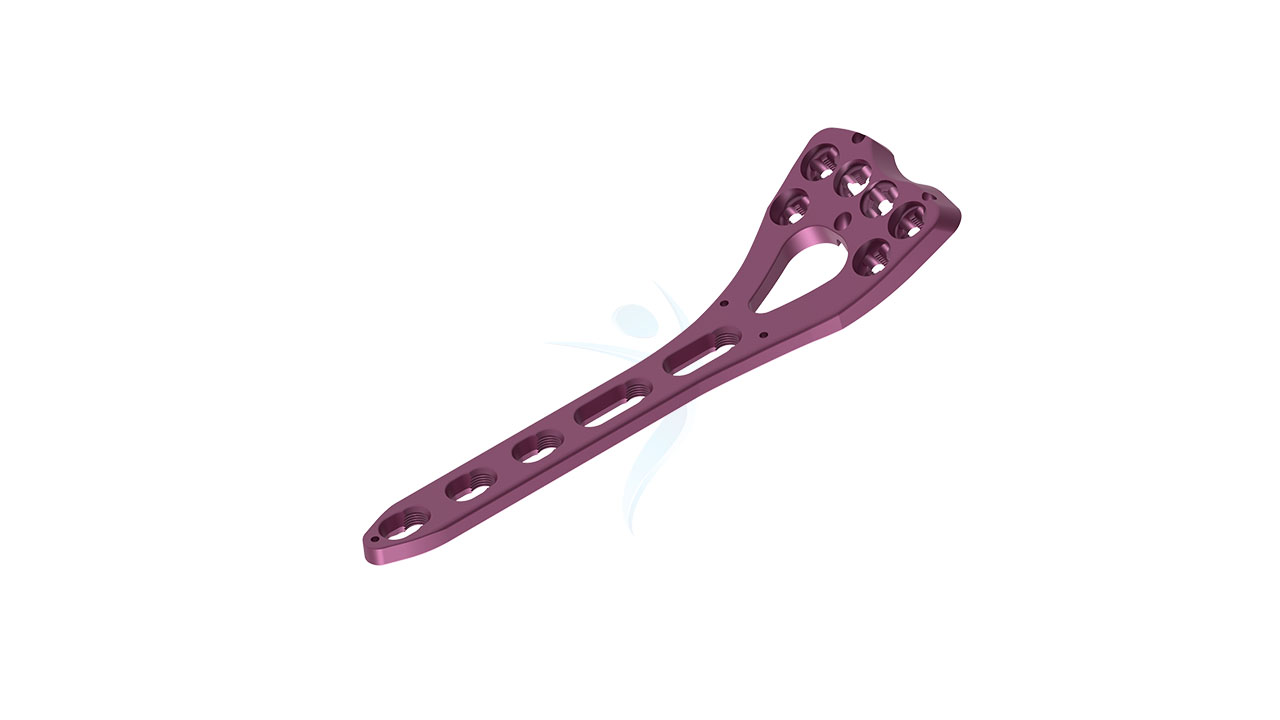
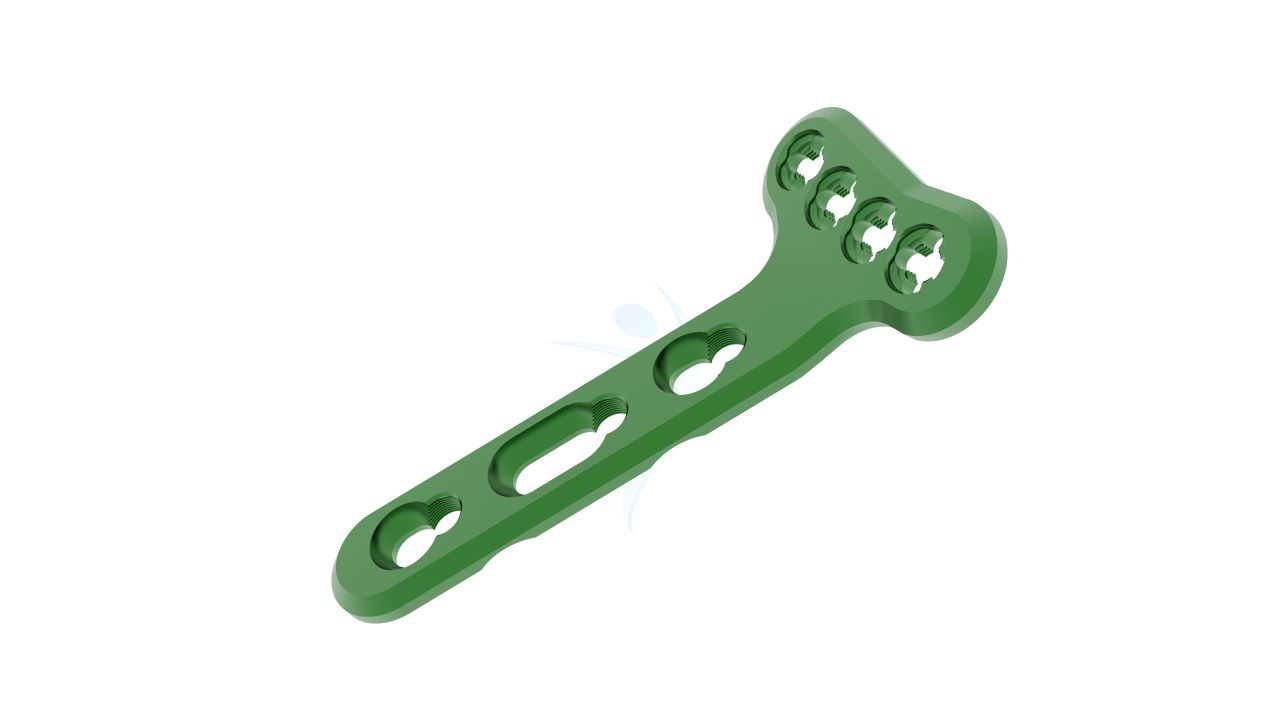
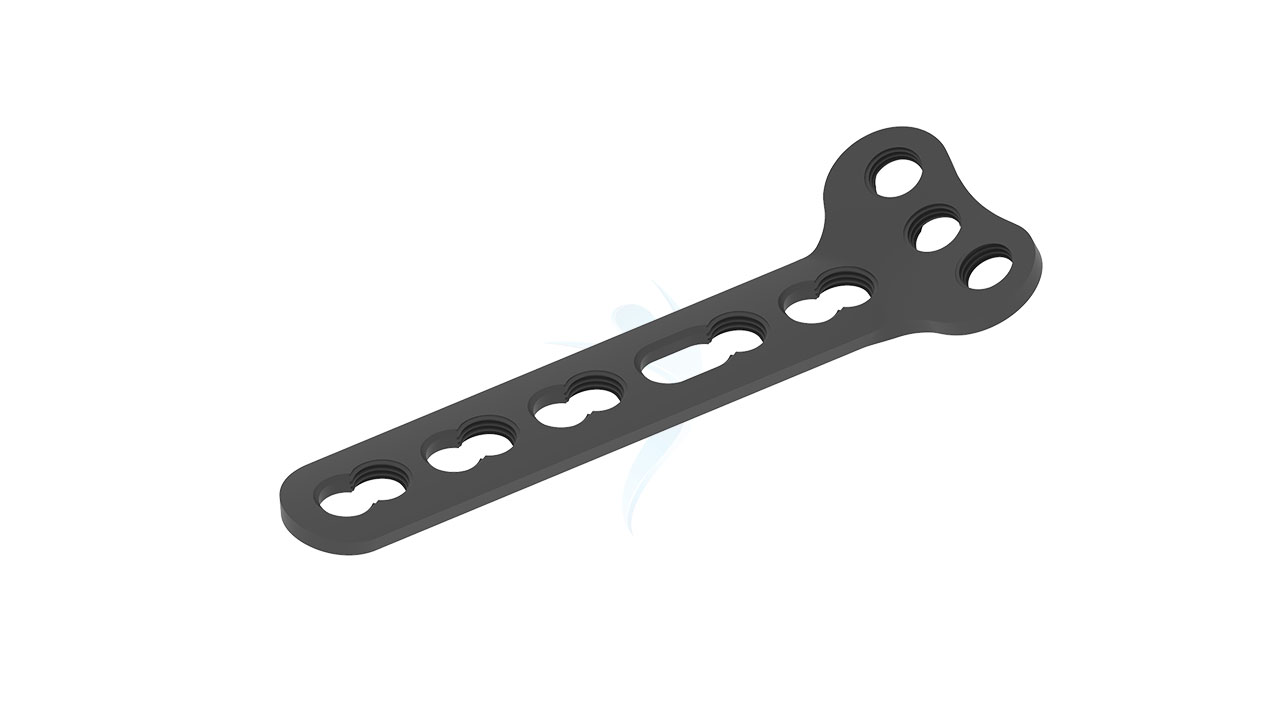
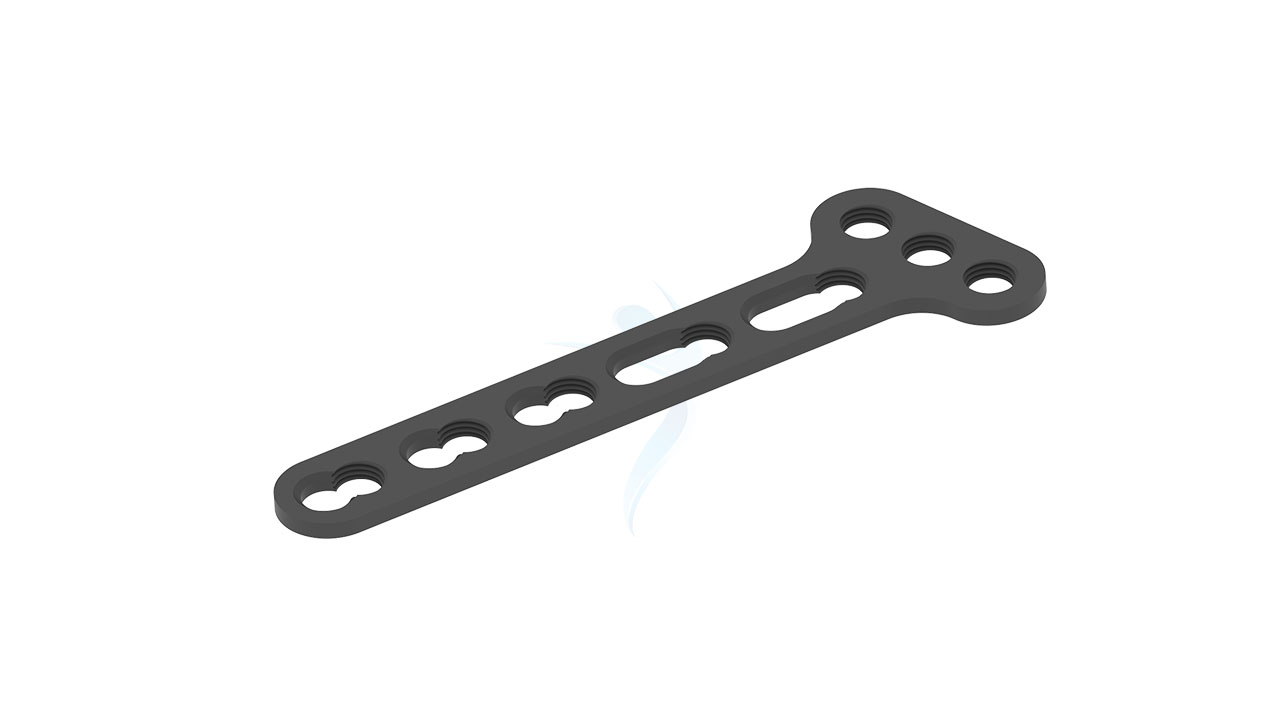
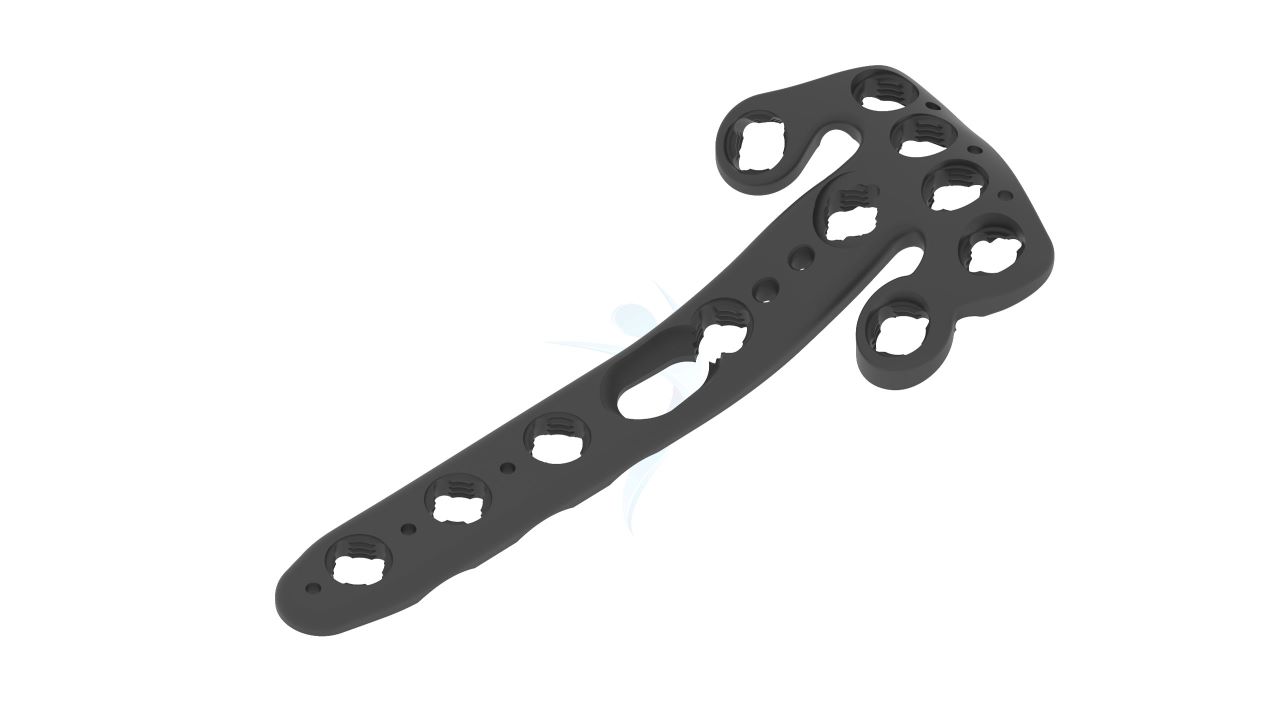
Volar Distal Radius Plate - (ASLP)
Product Overview
Introducing our advanced Volar Distal Radius Plate ASLP a cutting-edge orthopedic solution designed for precise and stable fracture fixation. Engineered with angle-stable locking technology, this plate ensures reliable support during the healing process. Its unique design allows for optimal alignment and restoration of normal bone function. Trust in the quality and innovation of our ASLP plate to provide exceptional outcomes for patients with distal radius fractures. Surgeons can confidently rely on this state-of-the-art product, backed by rigorous testing and industry-leading expertise.
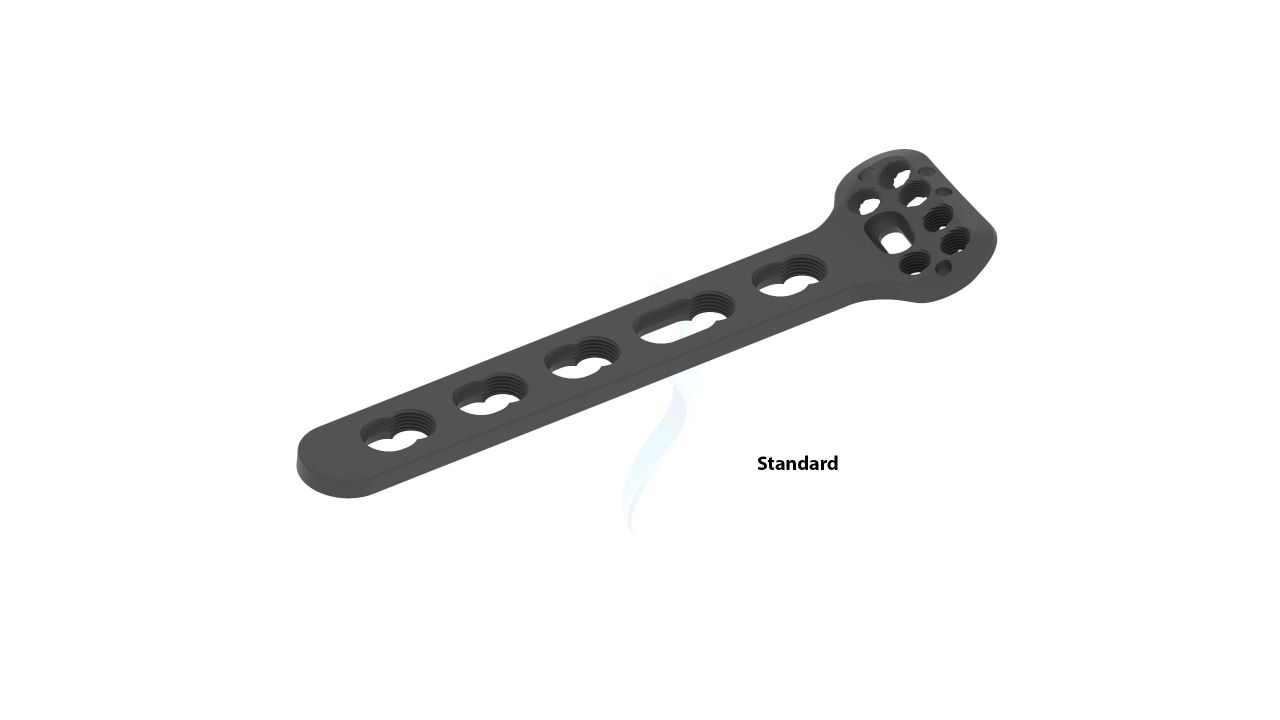
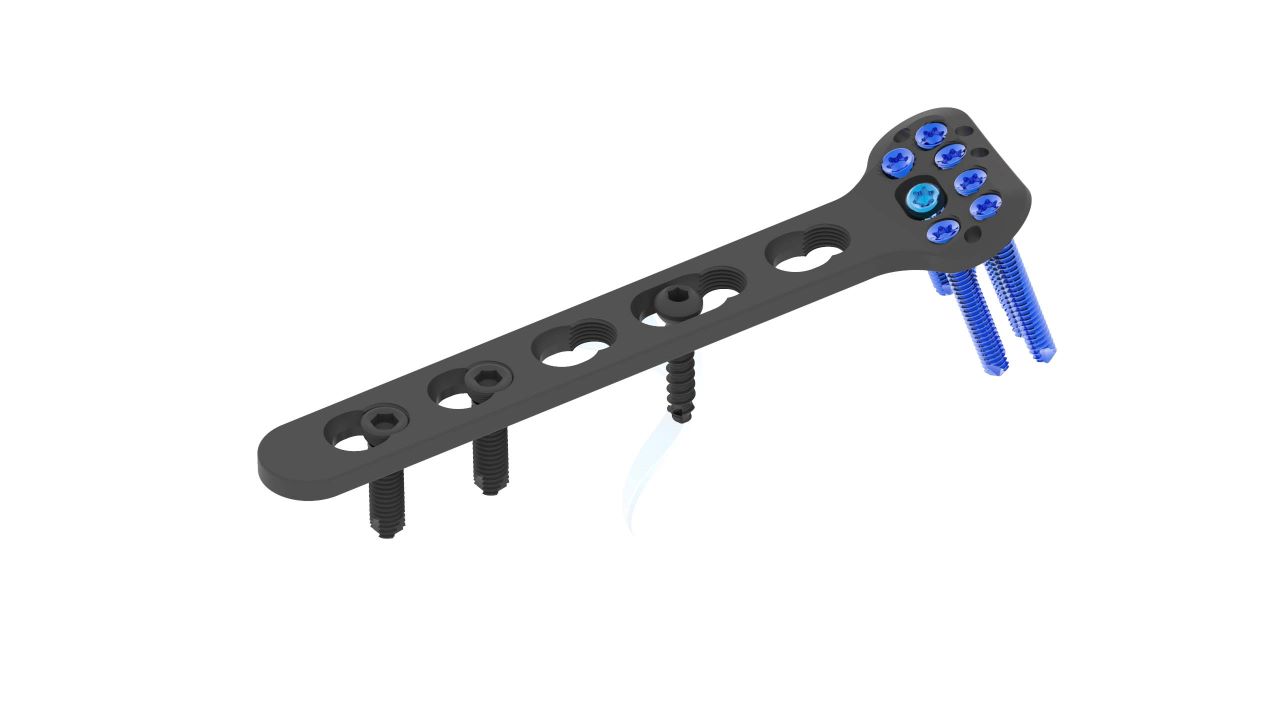
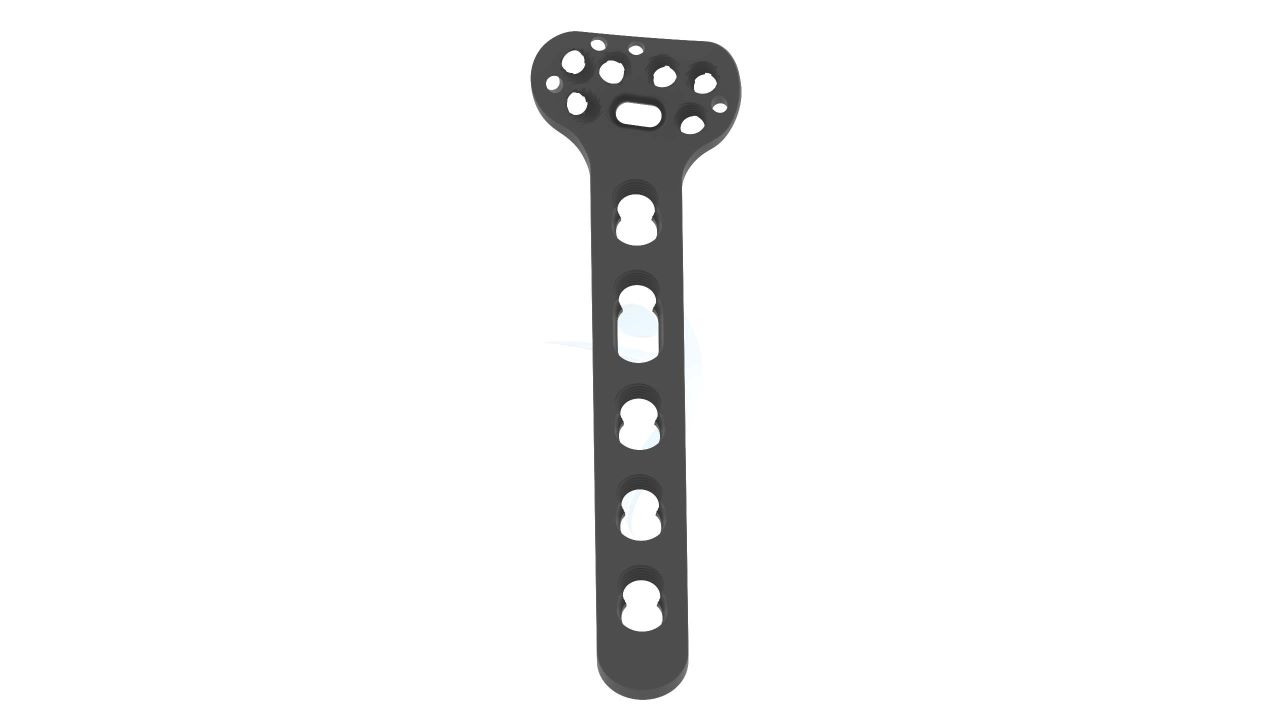
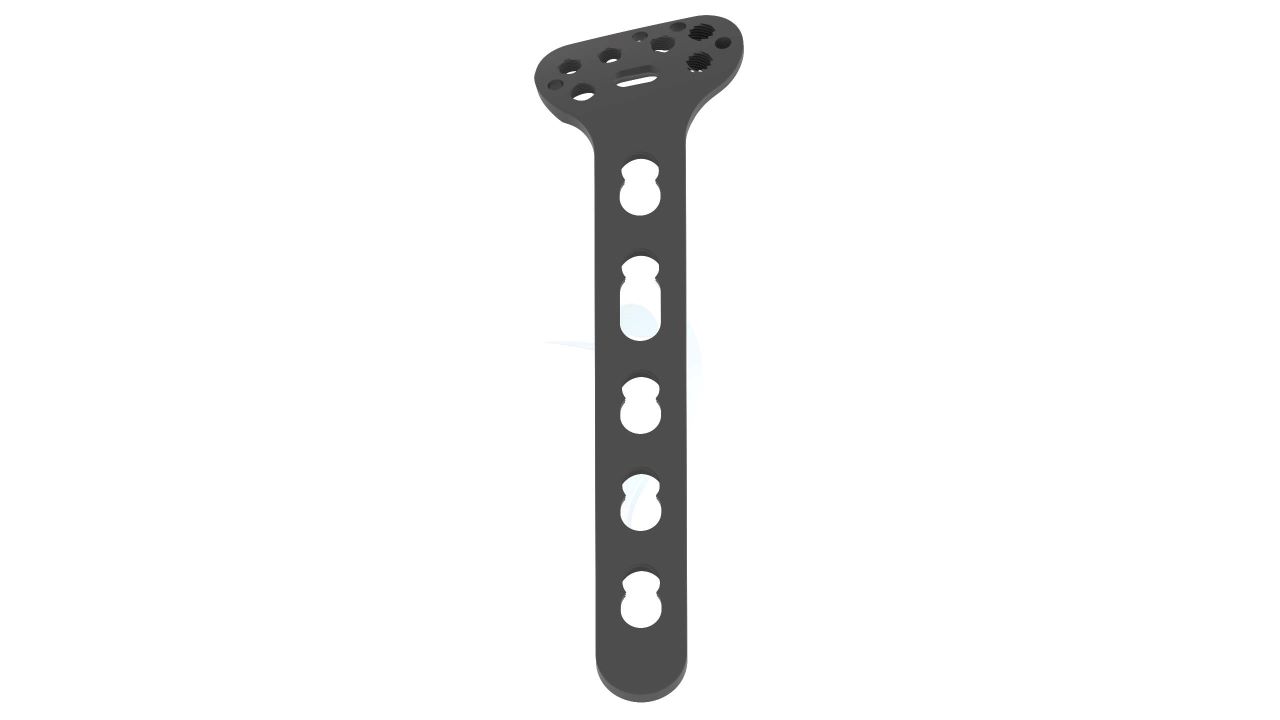
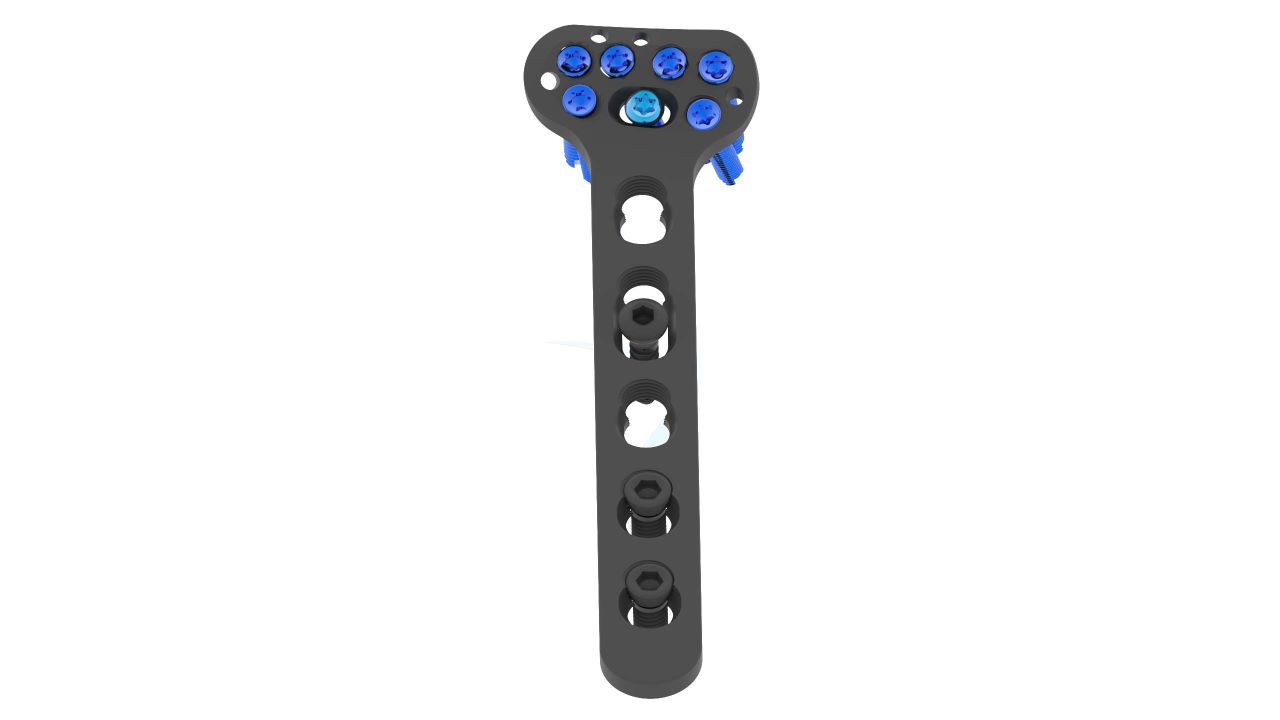
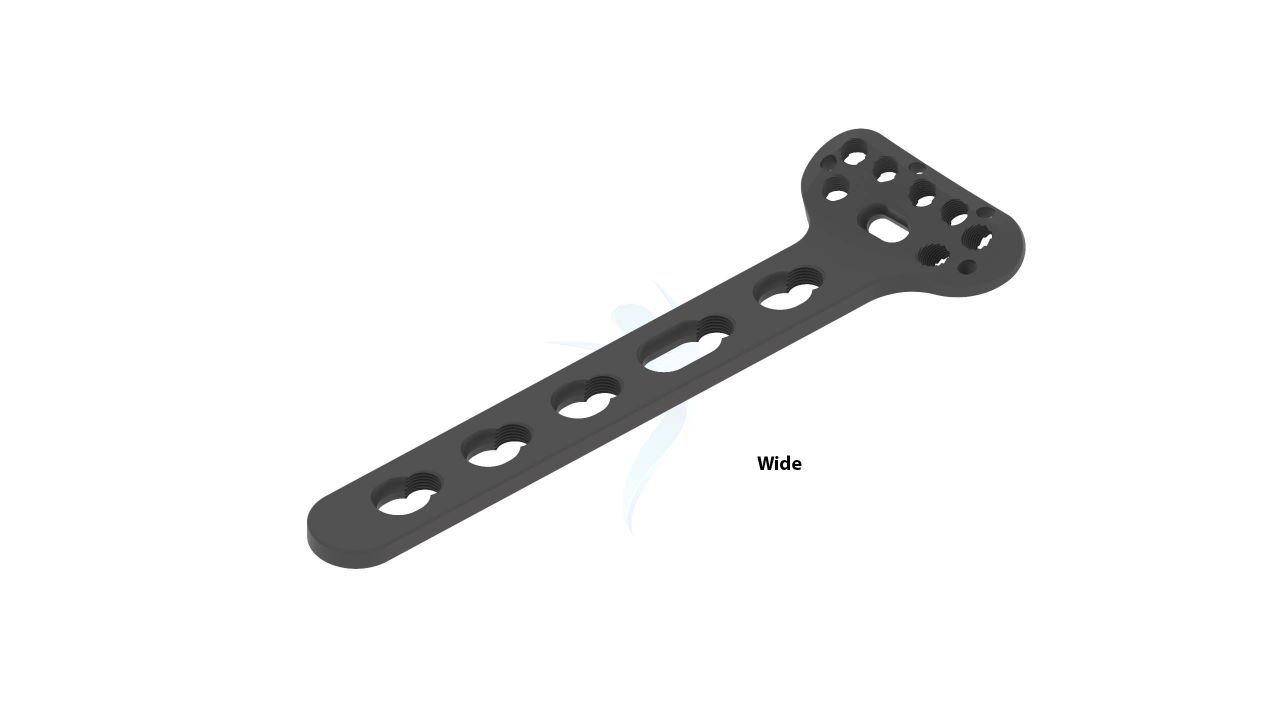
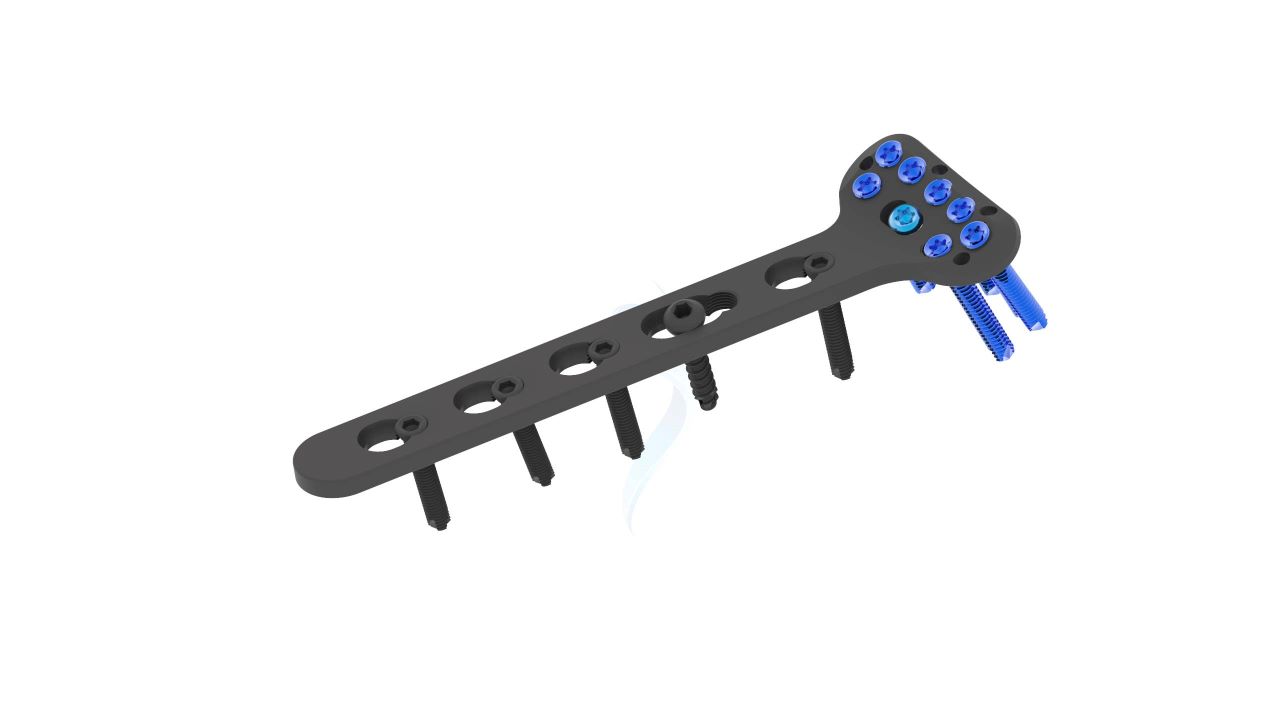
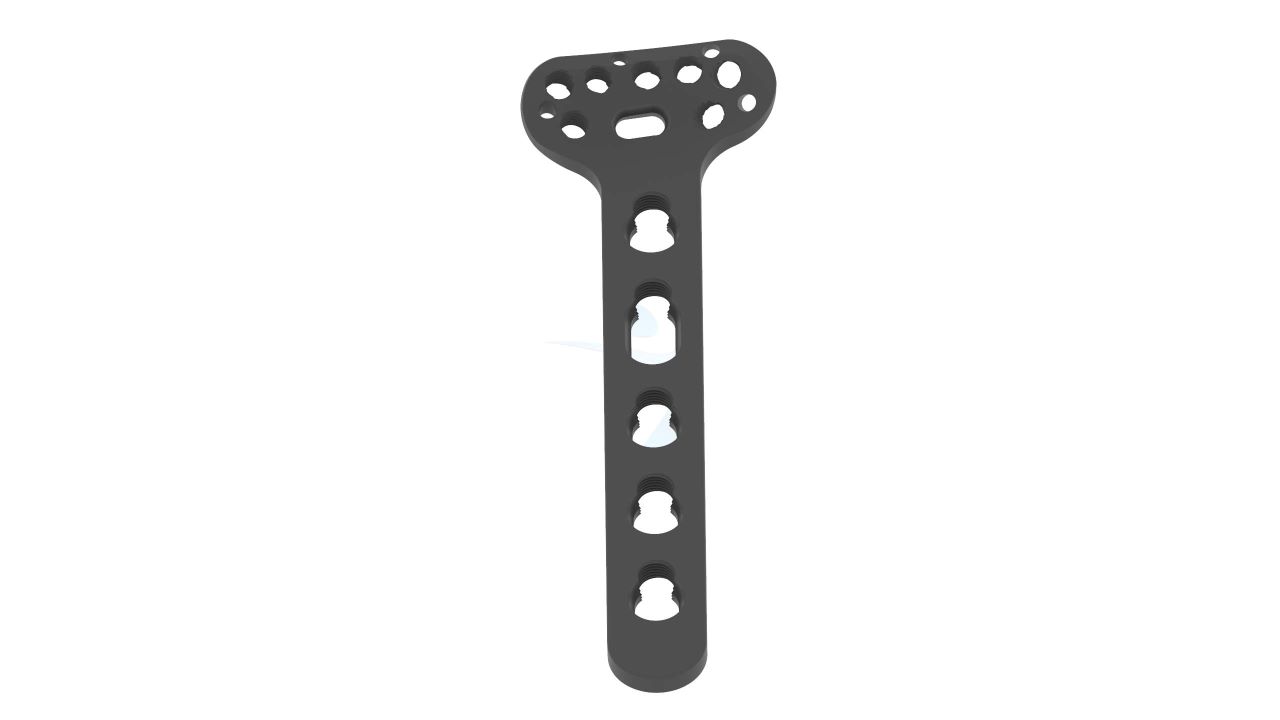
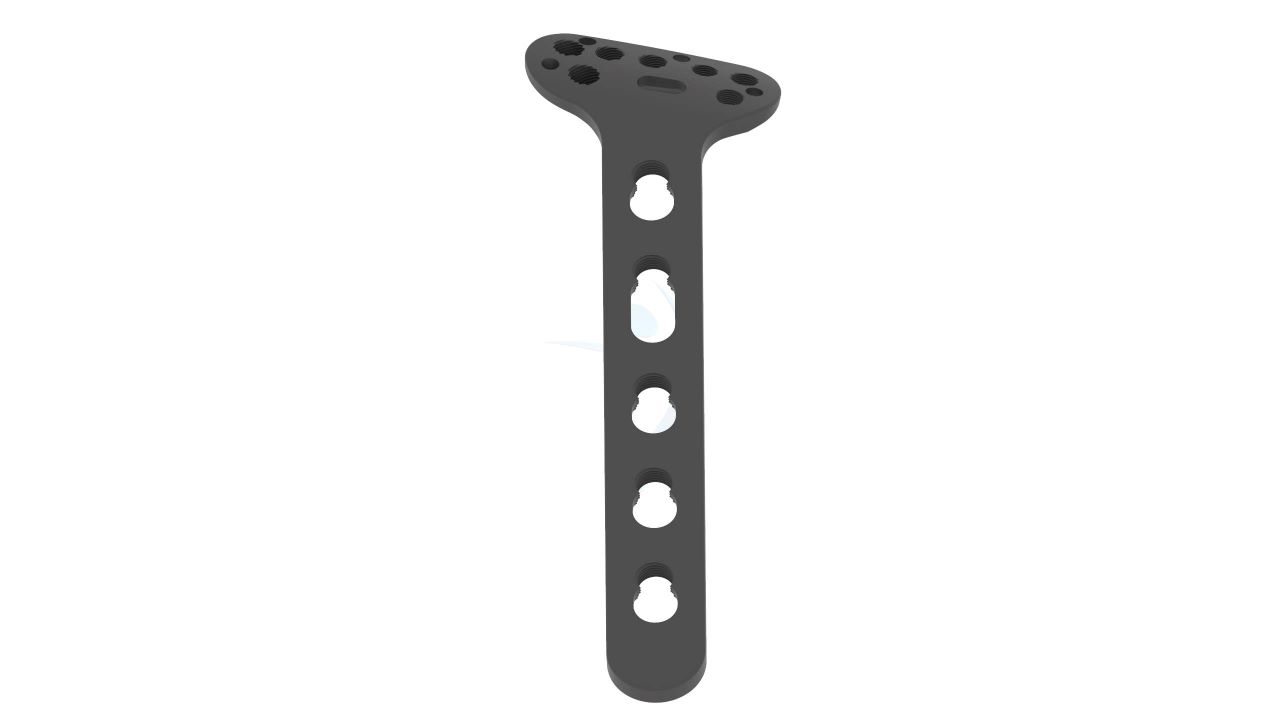
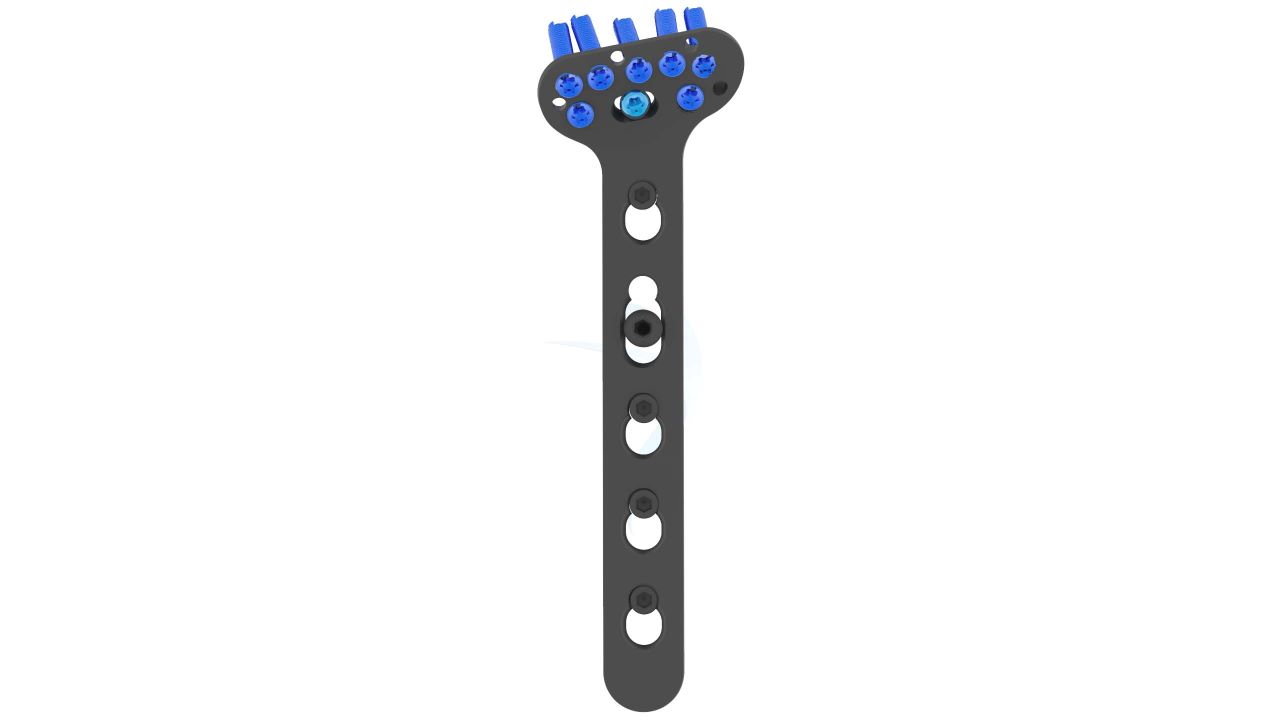
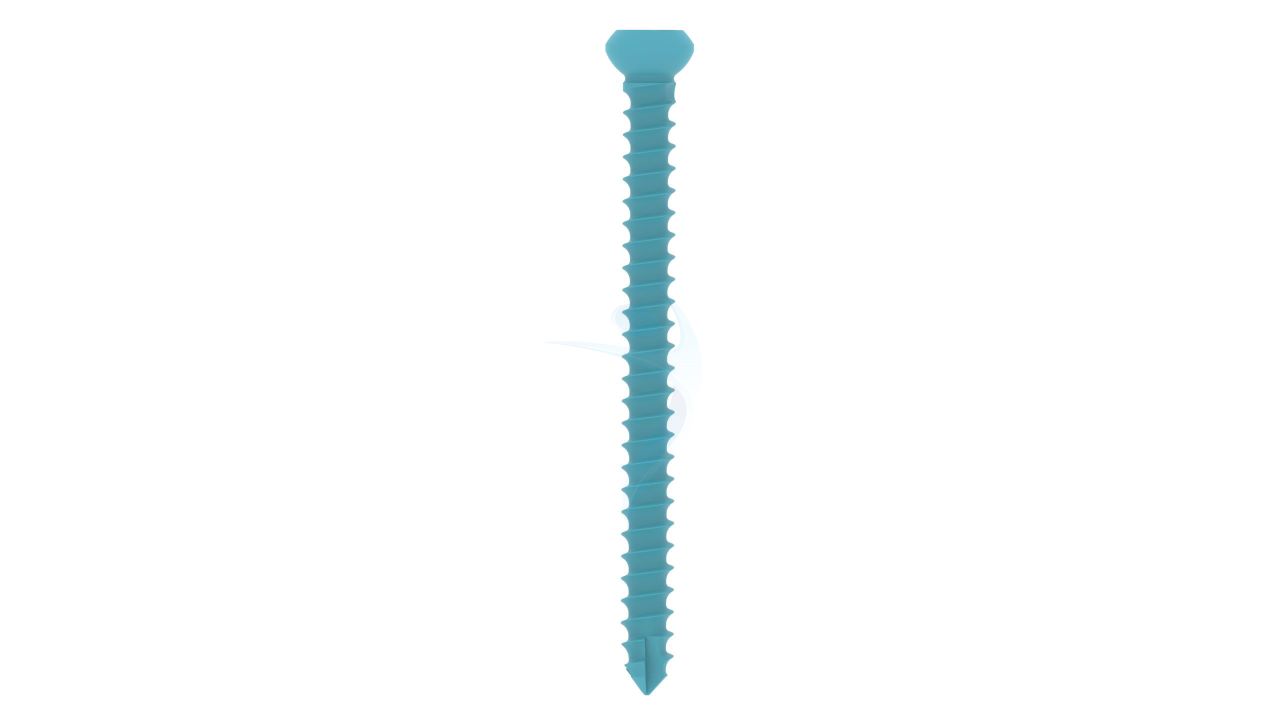






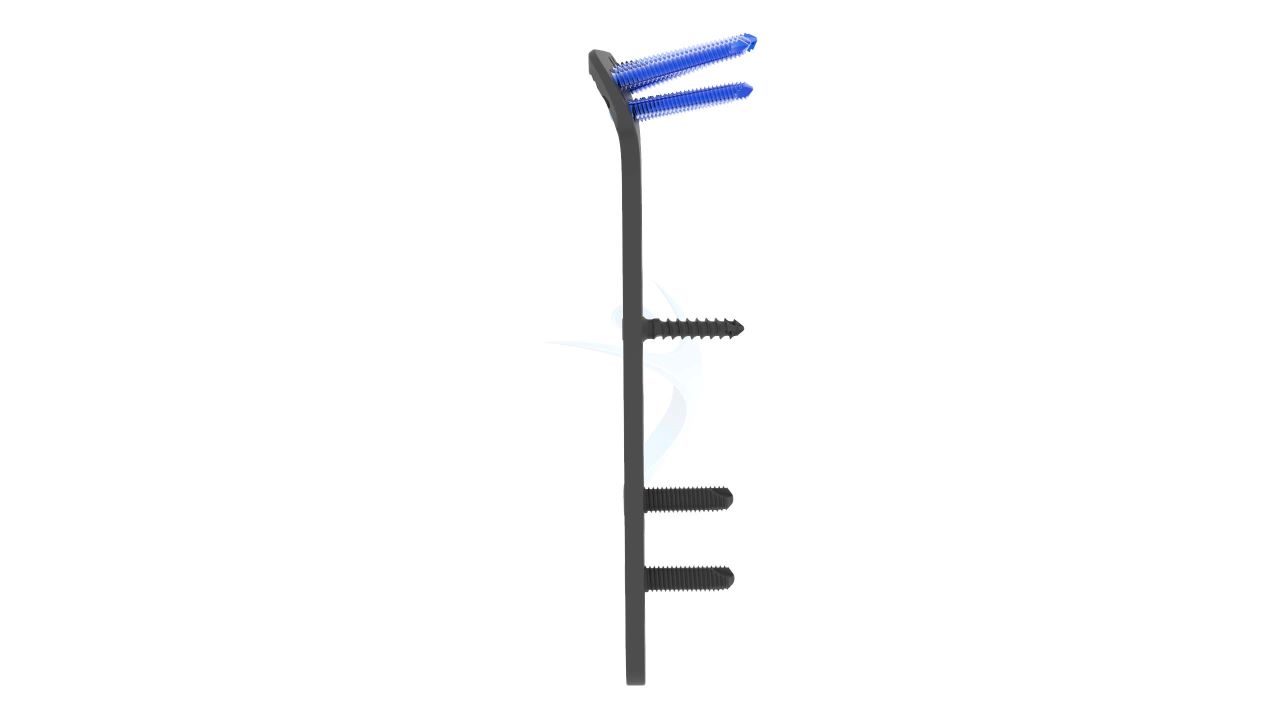





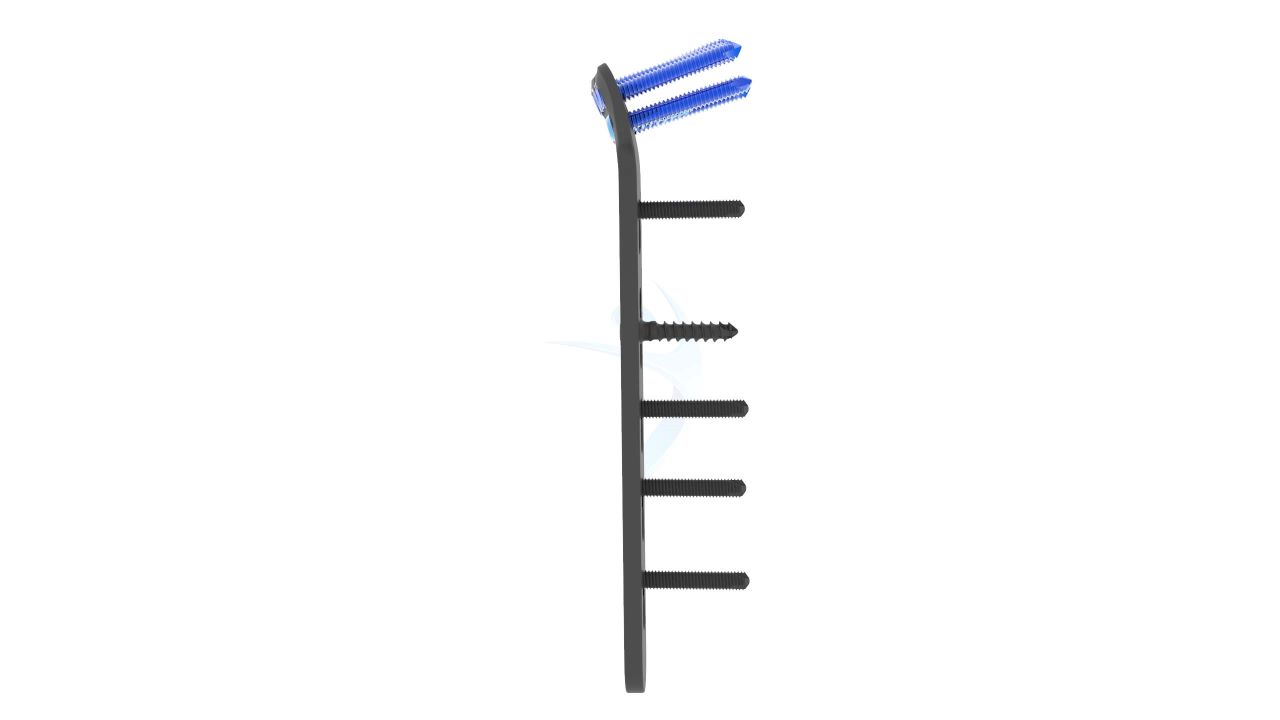




Product Uses
- Fracture Fixation : The Volar Distal Radius Plate ASLP is primarily used for the fixation of distal radius fractures, providing stable support to the fractured bone during the healing process.
- Orthopedic Surgery : Surgeons utilize this plate in orthopedic surgical procedures to accurately align and stabilize the fractured distal radius, aiding in proper bone healing.
- Angle-Stable Locking : With its advanced angle-stable locking technology, the ASLP plate ensures enhanced stability, reducing the risk of implant failure and promoting successful fracture healing.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures : The ASLP plate can be used in minimally invasive surgical techniques, offering a less invasive approach while providing reliable fixation for distal radius fractures.
- Bone Alignment : The plate helps maintain optimal bone alignment, facilitating the restoration of normal bone function and strength after the injury.
Product Specification
- Material : Titanium - The plate is made from high-quality titanium, known for its strength, biocompatibility, and resistance to corrosion.
- Design : Anatomical Design - The plate is designed with anatomical contours to closely match the shape of the volar (palm-side) aspect of the distal radius bone, promoting better fit and stability.
- Locking Mechanism : Angle-Stable Locking - The plate incorporates angle-stable locking technology, ensuring secure fixation and minimizing the risk of implant failure.
- Screw Holes : Multiple Screw Holes - The plate features multiple holes of various sizes to accommodate locking screws, allowing for versatile fixation options based on the patient's specific needs.
- Thickness : Uniform Thickness - The plate maintains a uniform thickness, providing consistent strength and stability along its entire length.
Volar Distal Radius Plate - (ASLP) Sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Volar Distal Radius Plate - (ASLP)
- Patient Evaluation : Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history, physical condition, and any pre-existing health issues that may affect the surgery or recovery process.
- Imaging Studies : Review X-rays, CT scans, or other imaging studies to assess the extent and nature of the distal radius fracture. This will help in determining the appropriate plate size and configuration for the patient's specific anatomy.
- Informed Consent : Schedule a detailed consultation with the patient to discuss the procedure, potential risks, benefits, and expected outcomes. Obtain informed consent from the patient to proceed with the surgery.
- Pre-Operative Instructions : Provide the patient with clear pre-operative instructions, which may include fasting guidelines and medication protocols. Following these instructions diligently is crucial to minimize potential risks and complications during the surgery.
- Operating Room Preparation : Ensure that the operating room is well-equipped with the necessary instruments, implants, and advanced technology to facilitate a smooth and efficient surgical procedure.
- Anesthesia : Administer the appropriate anesthesia to ensure the patient's comfort and pain control during the surgery. General or regional anesthesia may be used based on the patient's condition and the surgeon's preference.
- Patient Positioning : Position the patient supine on the operating table with the affected arm placed on an arm table or hand table. Ensure proper padding and positioning to prevent pressure points.
- Surgical Approach : Make an incision over the volar aspect of the distal radius to access the fracture site. The length and location of the incision will depend on the fracture pattern and the surgeon's preference.
- Fracture Reduction : Gently manipulate the fractured bone fragments to restore proper alignment and anatomical position. Use fluoroscopy or image intensification to verify the reduction accuracy.
- Plate Placement : Select the appropriate size and configuration of the Volar Distal Radius Plate ASLP based on pre-operative planning and the patient's anatomy. Carefully position the plate on the volar aspect of the distal radius, ensuring proper alignment with the bone.
- Recovery Area : Transfer the patient to the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) or recovery area for close monitoring during the initial recovery phase.
- Pain Management : Implement a pain management plan to ensure the patient's comfort. Administer prescribed pain medications as needed and adjust the dosage according to the patient's response.
- Wound Care : Monitor the surgical incision site for any signs of infection, redness, or swelling. Keep the wound clean and dry, following the surgeon's instructions for dressing changes.
- Immobilization : Maintain the wrist in a splint or cast as prescribed by the surgeon to protect the surgical site and promote proper bone healing.
- Elevation : Encourage the patient to elevate the affected arm above heart level whenever possible to reduce swelling and enhance circulation.
- Mobility and Rehabilitation : Gradually initiate a personalized rehabilitation program under the guidance of a physical therapist. This may include gentle wrist exercises to improve range of motion and strength.









.png)