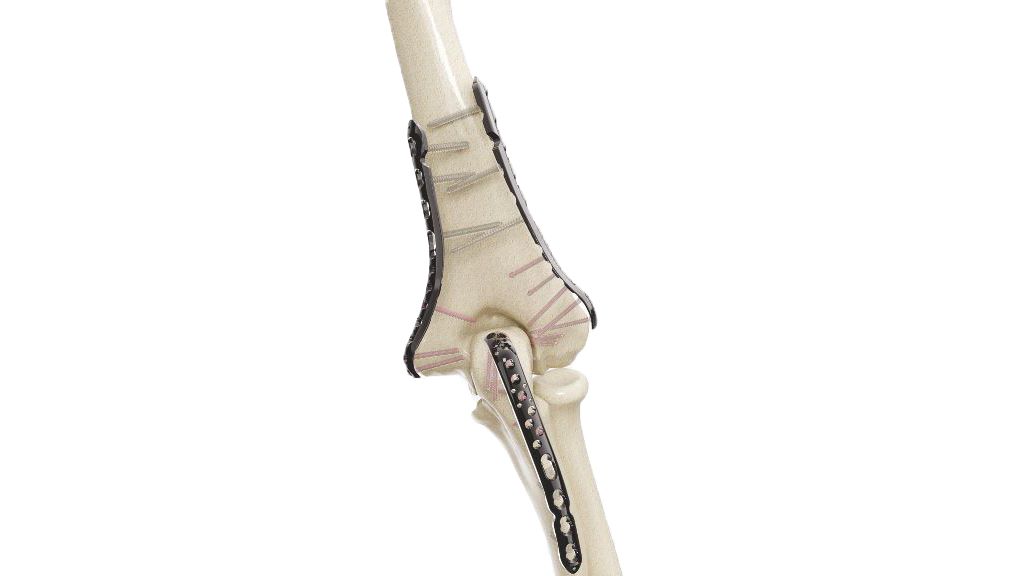
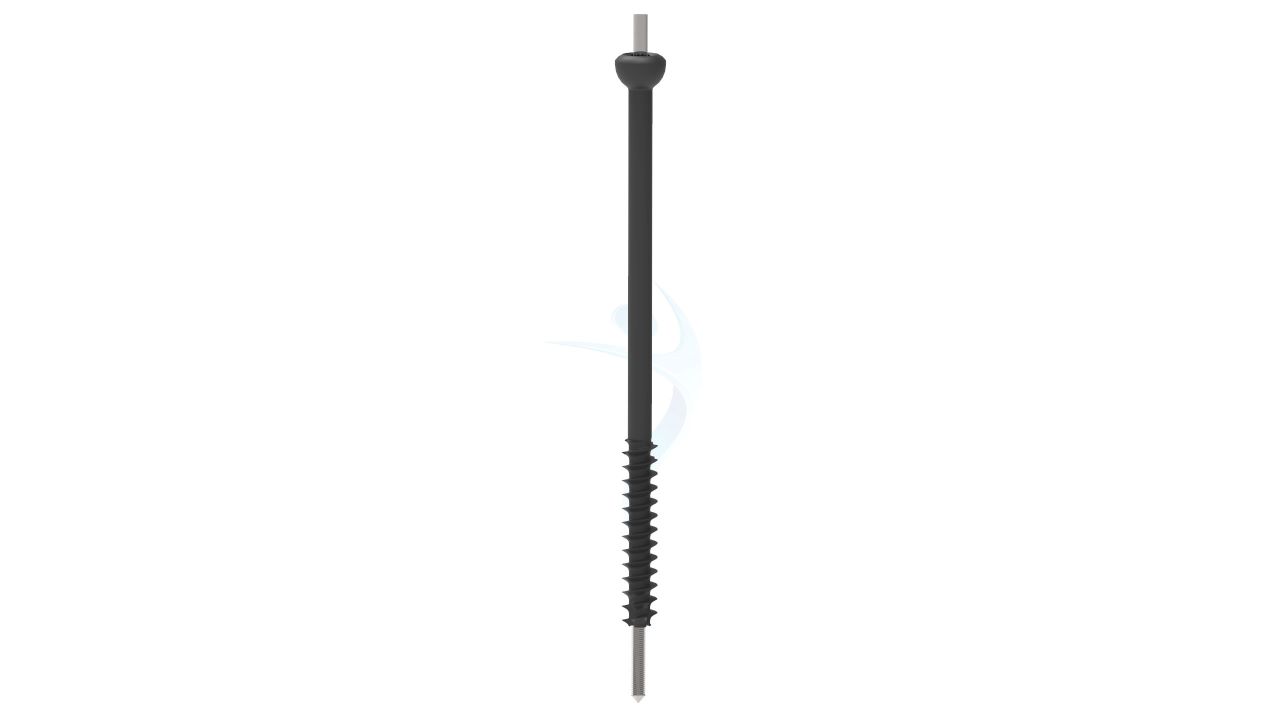
Partially Threaded Cannulated Cancellous Screw - 4.0 mm
Product Overview
The 4.0 mm Partially Threaded Cannulated Cancellous Screw is a premium orthopedic implant designed for enhanced stability and secure fixation in cancellous bone. Its partially threaded design ensures optimal anchoring, while the cannulated structure allows for precise placement over a guide wire. Ideal for use in various orthopedic procedures, this screw offers reliable performance and durability, making it a trusted choice for surgeons seeking high-quality implants for complex bone repairs and reconstructions.





Product Uses
- Fracture Fixation : Securely stabilizes fractures in cancellous bone, such as those in the pelvis, femur, and tibia.
- Bone Reconstruction : Provides reliable fixation for bone grafts or reconstruction procedures, enhancing healing and alignment.
- Spinal Surgery :Assists in spinal fixation and stabilization, particularly in lumbar and sacral regions.
- Joint Surgery : Utilized in repairing or stabilizing joint fractures, including those around the knee or shoulder.
- Trauma Surgery :Essential for treating traumatic injuries involving bone fragmentation or displacement.
Product Specification
- Diameter : 4.0 mm
- Thread Type : Partially threaded for optimal purchase in the bone, allowing for compression and stability.
- Partially Threaded : Threads extend partially along the shaft, promoting optimal compression and stability in cancellous bone.
- Head Design : Self-tapping or non-self-tapping head for secure fixation, with a hexagonal or slot drive for ease of insertion.
- Surface Treatment : Passivated and optionally coated with Hydroxyapatite for improved osseointegration.
Partially Threaded Cannulated Cancellous Screw - 4.0 mm sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Partially Threaded Cannulated Cancellous Screw - 4.0 mm
- Patient Assessment : Review the patient’s medical history, including any conditions that could affect the surgery or healing process (e.g., diabetes, osteoporosis).Obtain and analyze relevant imaging (e.g., X-rays, CT scans) to assess the bone quality and the exact location for screw placement.
- Surgical Planning : Confirm the appropriate length and type of screw based on the surgical plan and the patient’s anatomy.Ensure all necessary instruments and the implant (4.0 mm Partially Threaded Cannulated Cancellous Screw) are available and sterile.
- Patient Preparation : Obtain informed consent from the patient after discussing the procedure, risks, and expected outcomes.Position the patient on the operating table to provide optimal access to the surgical site.
- Site Preparation : Clean and sterilize the surgical site with an antiseptic solution. Drape the area with sterile coverings to maintain a sterile field.
- Incision : Make an incision over the targeted area to expose the bone where the screw will be inserted. Minimize soft tissue damage.
- Screw Insertion : Using a screwdriver, carefully insert the screw into the bone. Ensure it is properly aligned and not over-tightened.Confirm the screw is securely engaged with the bone and positioned correctly.
- Imaging : Perform intraoperative imaging if needed to verify screw placement and alignment.
- Closure : Close the incision with sutures or staples as appropriate. Ensure the wound is properly aligned to minimize scarring and promote healing.
- Recovery : Observe the patient in the recovery room for any immediate postoperative issues such as bleeding or adverse reactions to anesthesia.Administer pain relief as needed and monitor the patient’s response to medication.
- Patient Instructions : Advise the patient on weight-bearing limits and movement restrictions to protect the implant site during the healing process.
- Follow-Up : Perform follow-up imaging if necessary to ensure the screw is in place and the bone is healing as expected.
- Rehabilitation : Recommend physical therapy or rehabilitation exercises to improve range of motion, strength, and function as appropriate.
- Complications Management : Manage any issues related to the screw, such as loosening or misalignment, and address them during follow-up visits.
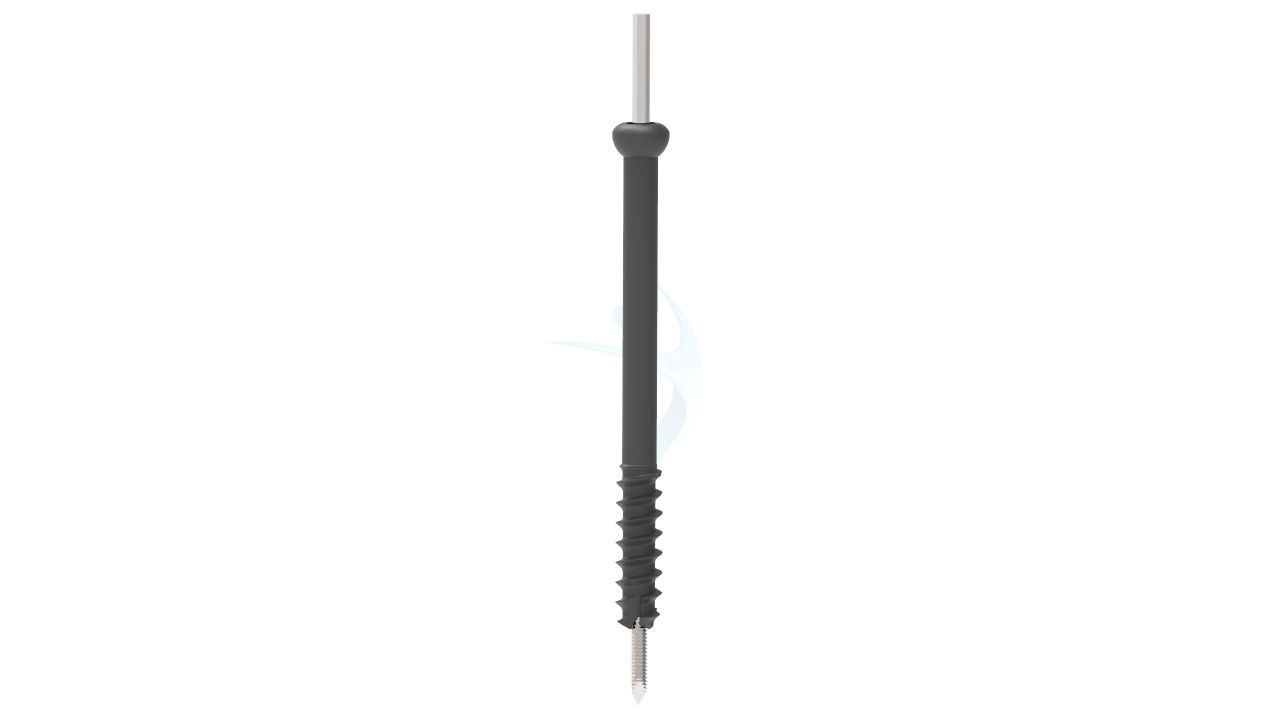






.png)