Compact Hand Plates - 2.4 mm Adaption
Product Overview
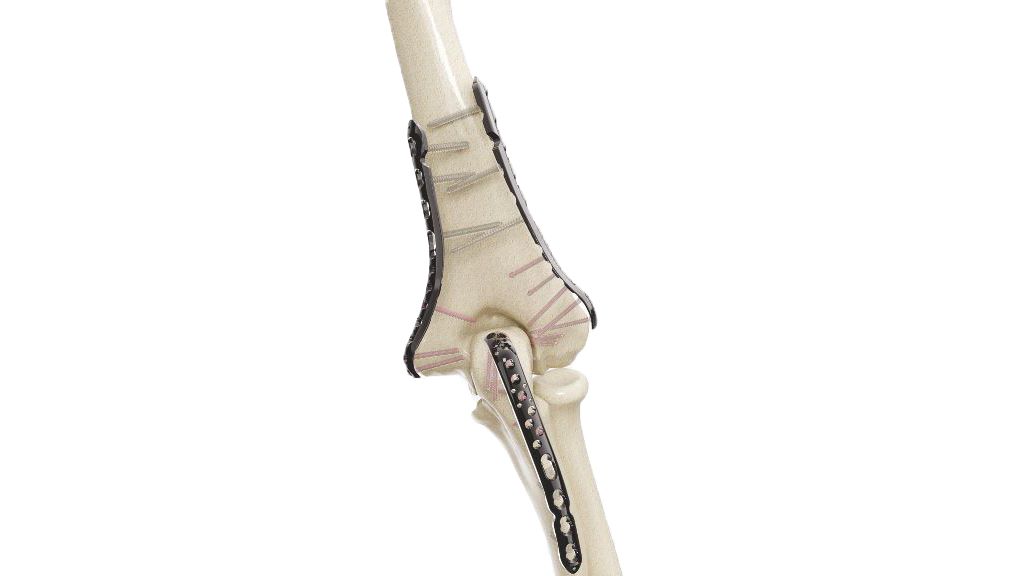
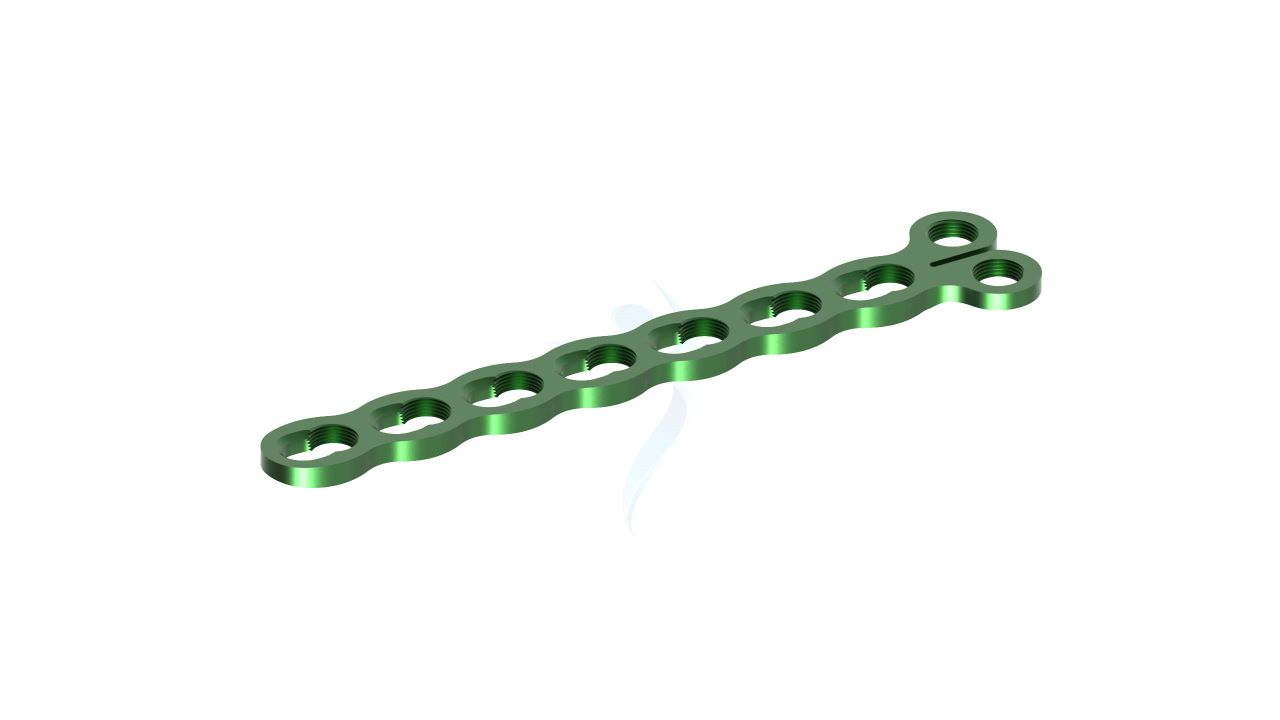
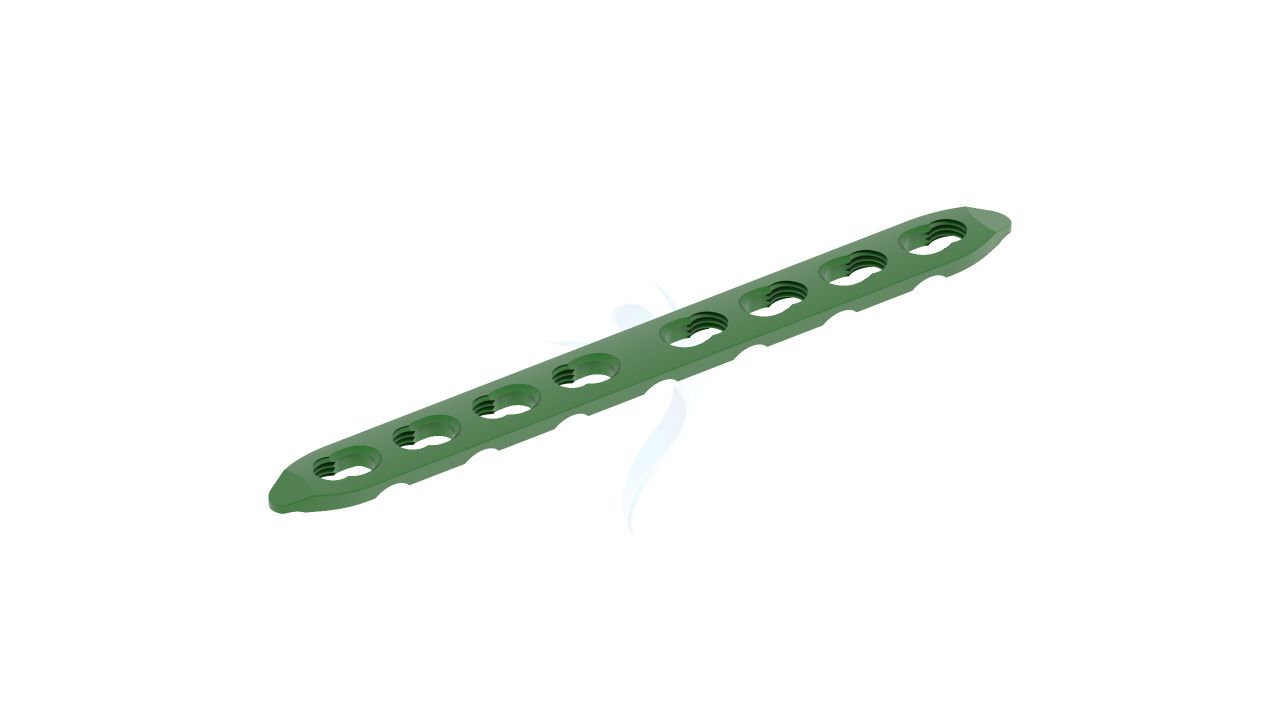
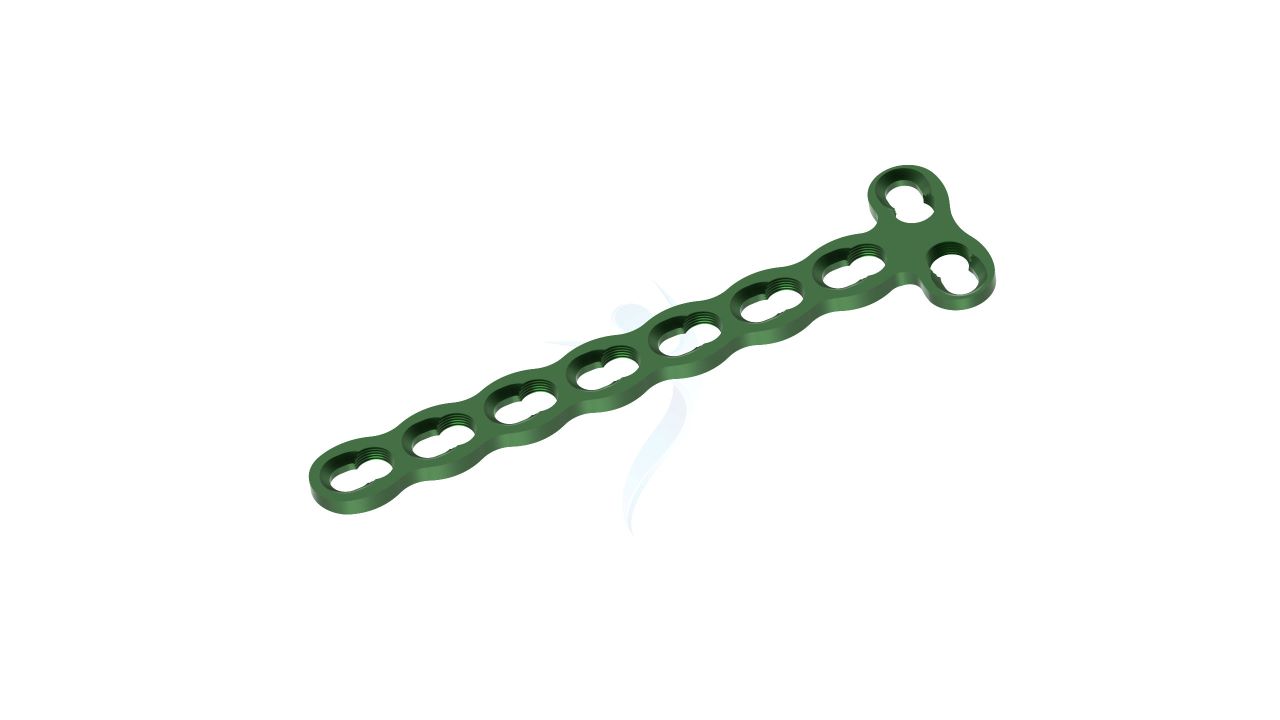
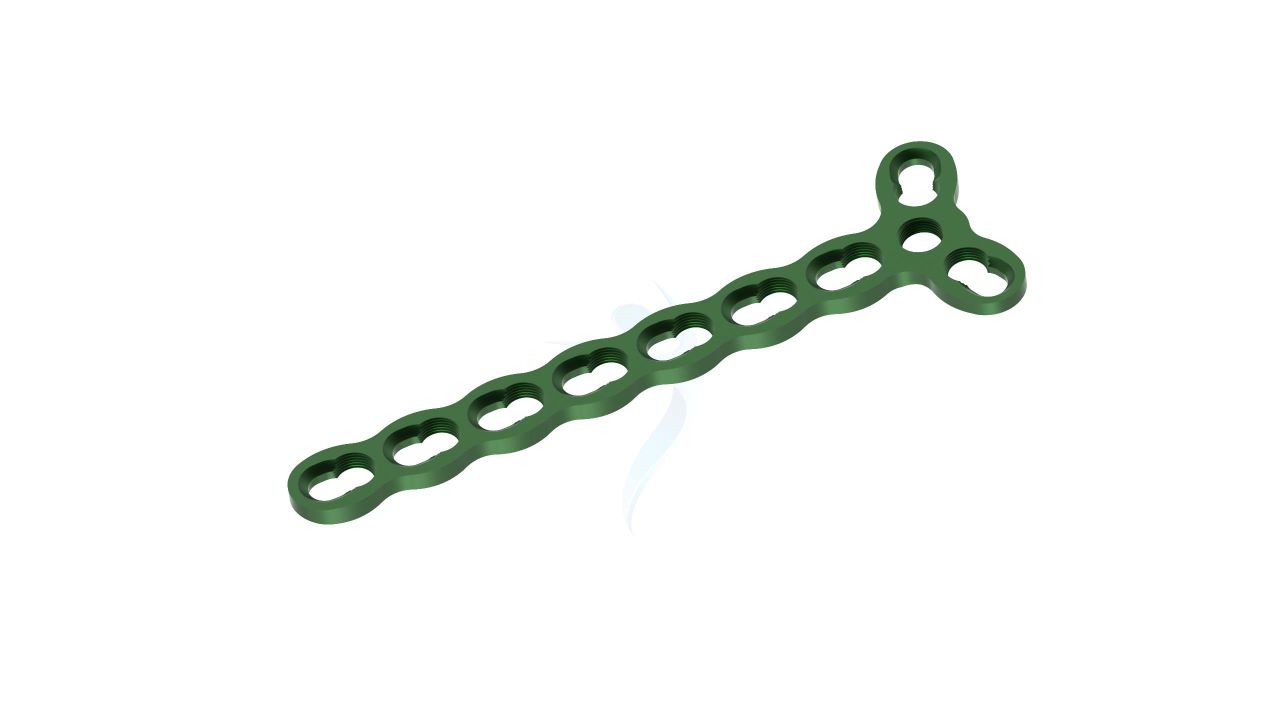
The 2.4 mm Adaption Compact Hand Plate is a specialized orthopedic implant designed for precision and versatility in hand and finger surgeries. This implant provides reliable stability and support during procedures to address fractures, deformities, and other orthopedic conditions affecting the hand. Its compact yet robust design allows orthopedic surgeons to achieve precise outcomes, ultimately enhancing patients' hand function and comfort. Trust in the 2.4 mm Adaption Compact Hand Plate for effective solutions in hand surgery.
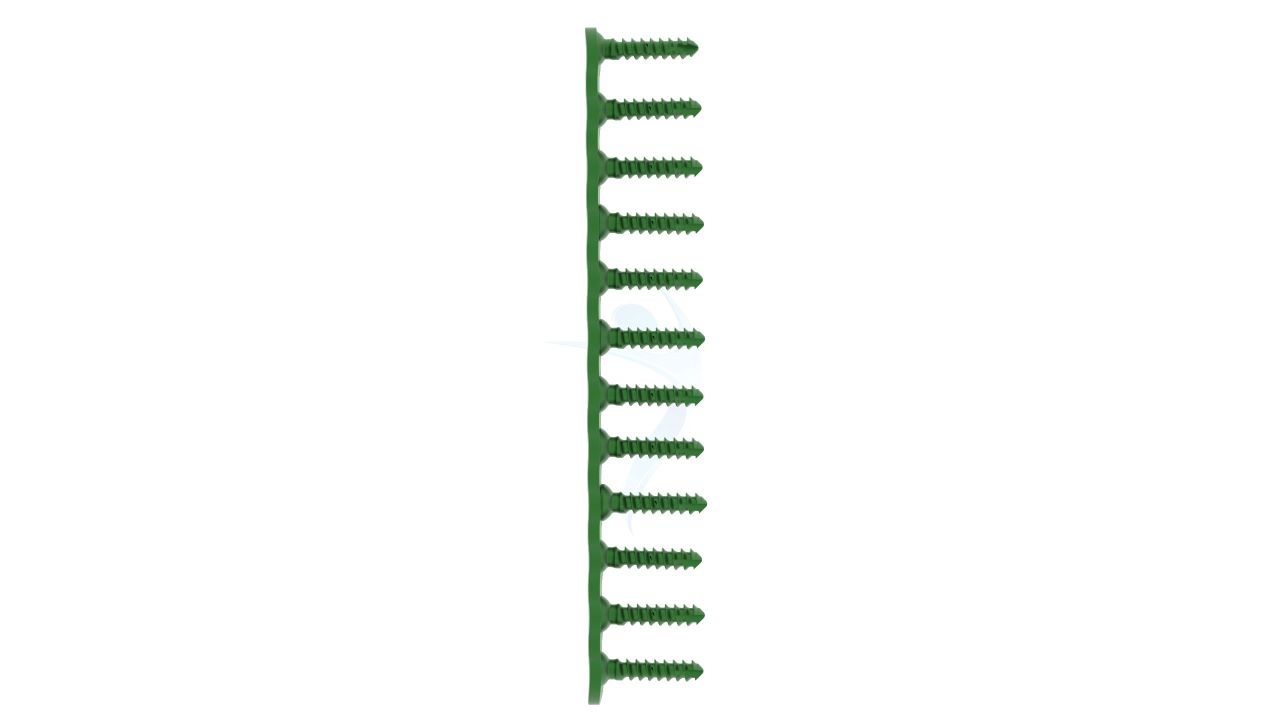
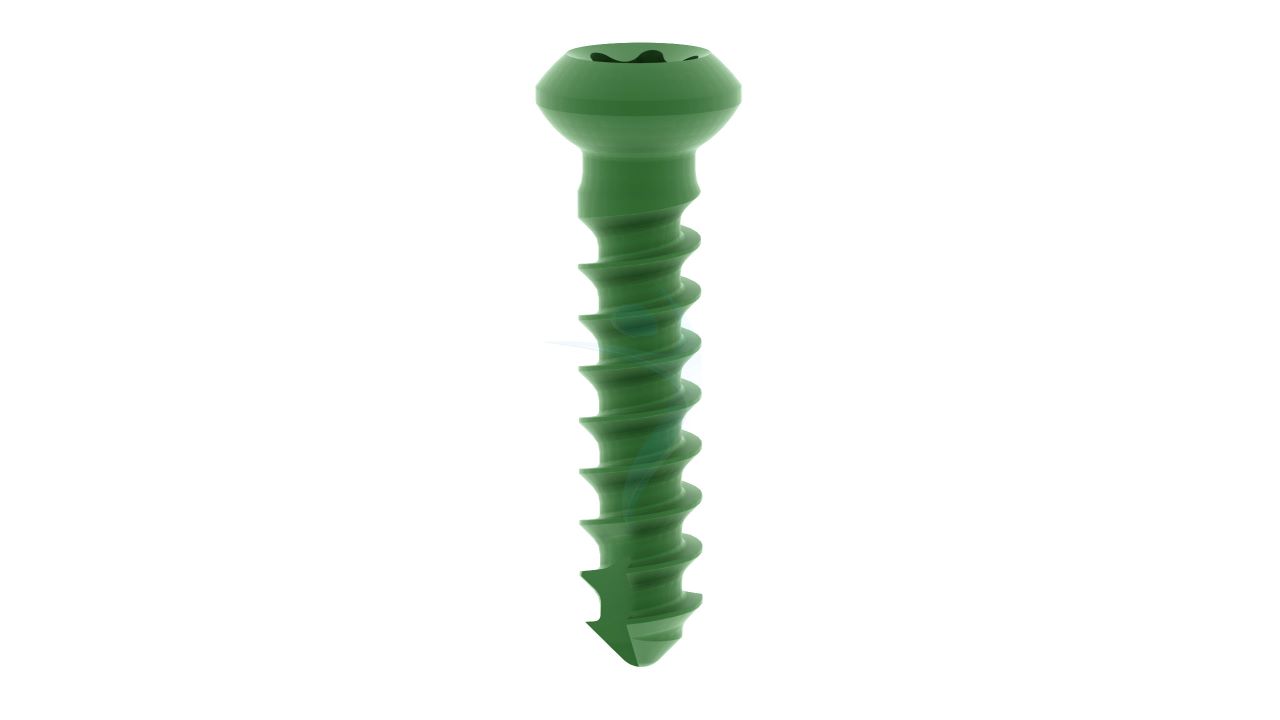
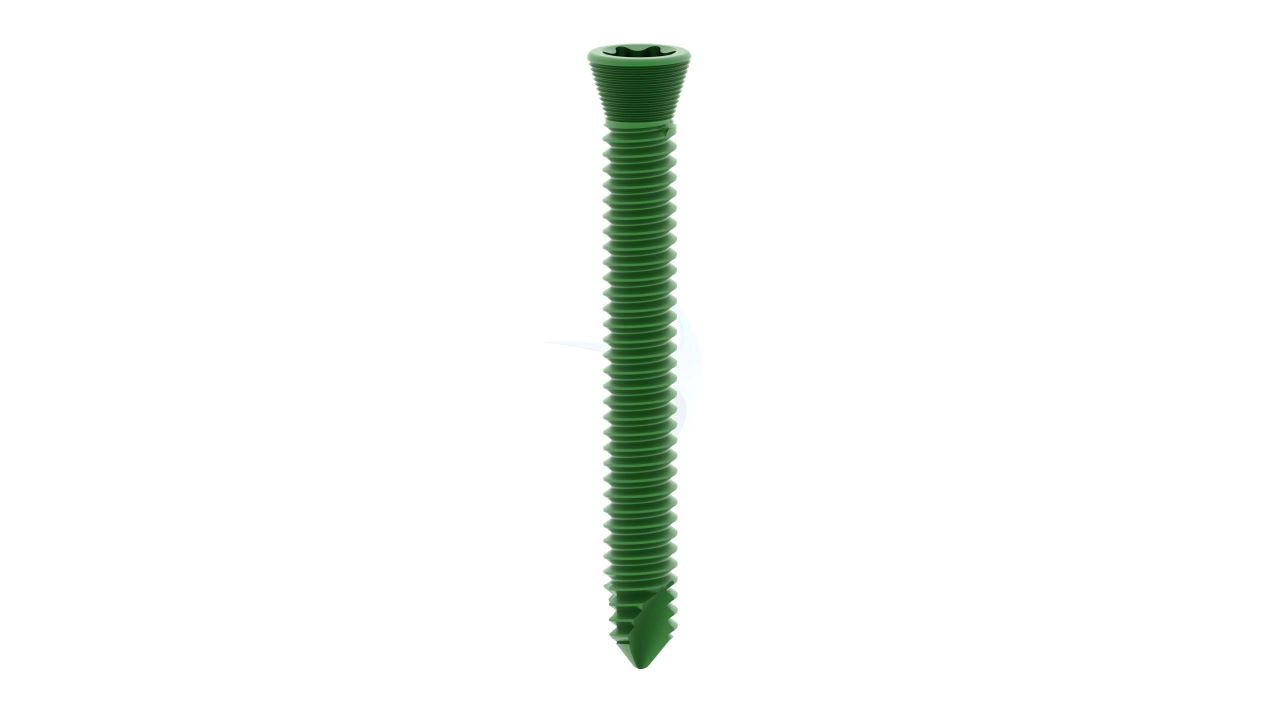
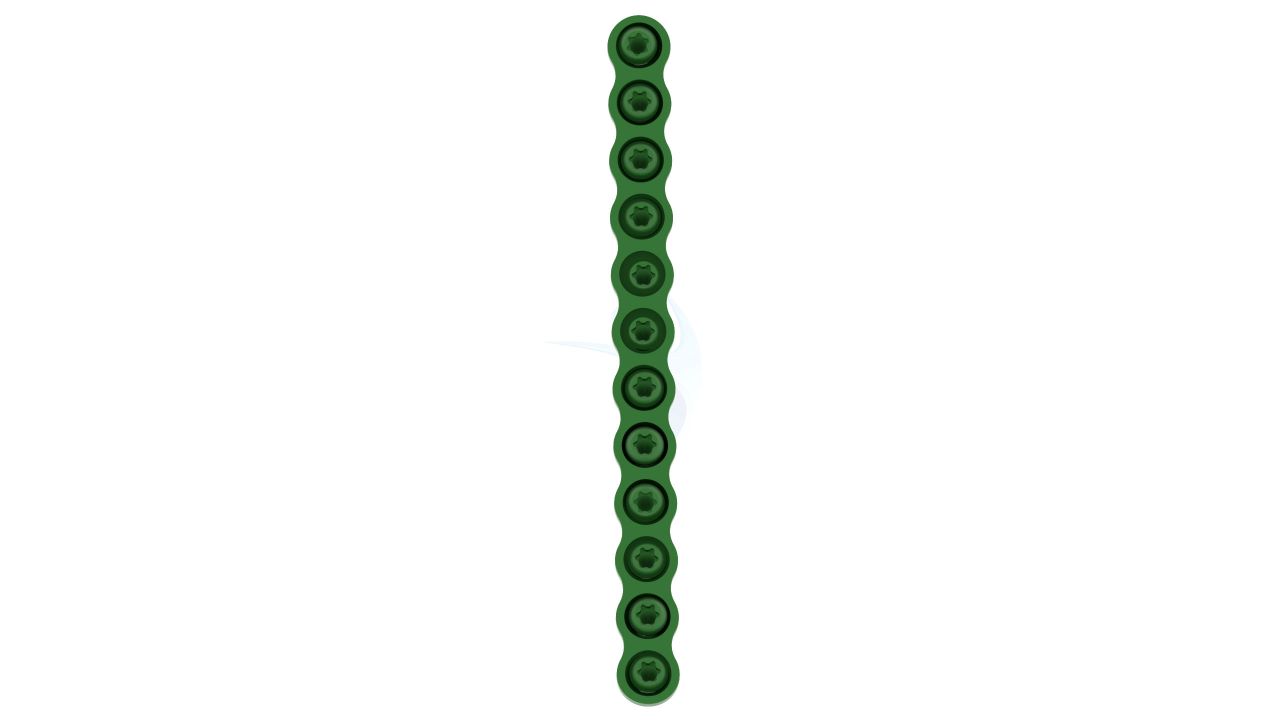

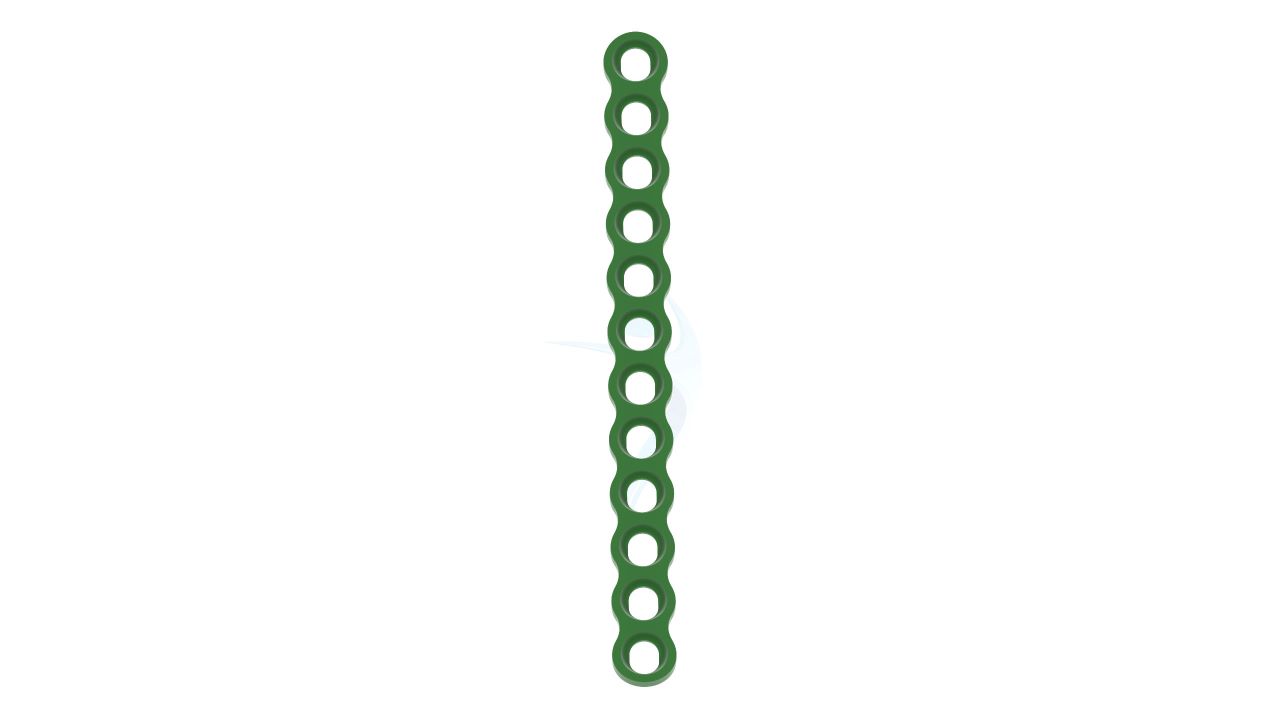


Product Uses
- Fracture Fixation : Stabilizing and immobilizing fractures of the hand and fingers, including metacarpal and phalangeal fractures.
- Malunion Correction : Correcting malunions, where a bone has healed in an incorrect position or alignment.
- Non-Union Fractures : Assisting in the treatment of non-union fractures by providing stability and promoting bone healing.
- Bone Deformity Correction : Addressing bone deformities, including angular or rotational deformities in the hand and fingers.
- Arthrodesis (Joint Fusion) : Immobilizing joints to promote fusion, often used in cases of severe arthritis or instability.
- Complex Hand Trauma : Addressing complex hand trauma involving multiple fractures or significant soft tissue damage.
Product Specification
- Material : The plate should be made of medical-grade titanium alloy or stainless steel for biocompatibility and strength.
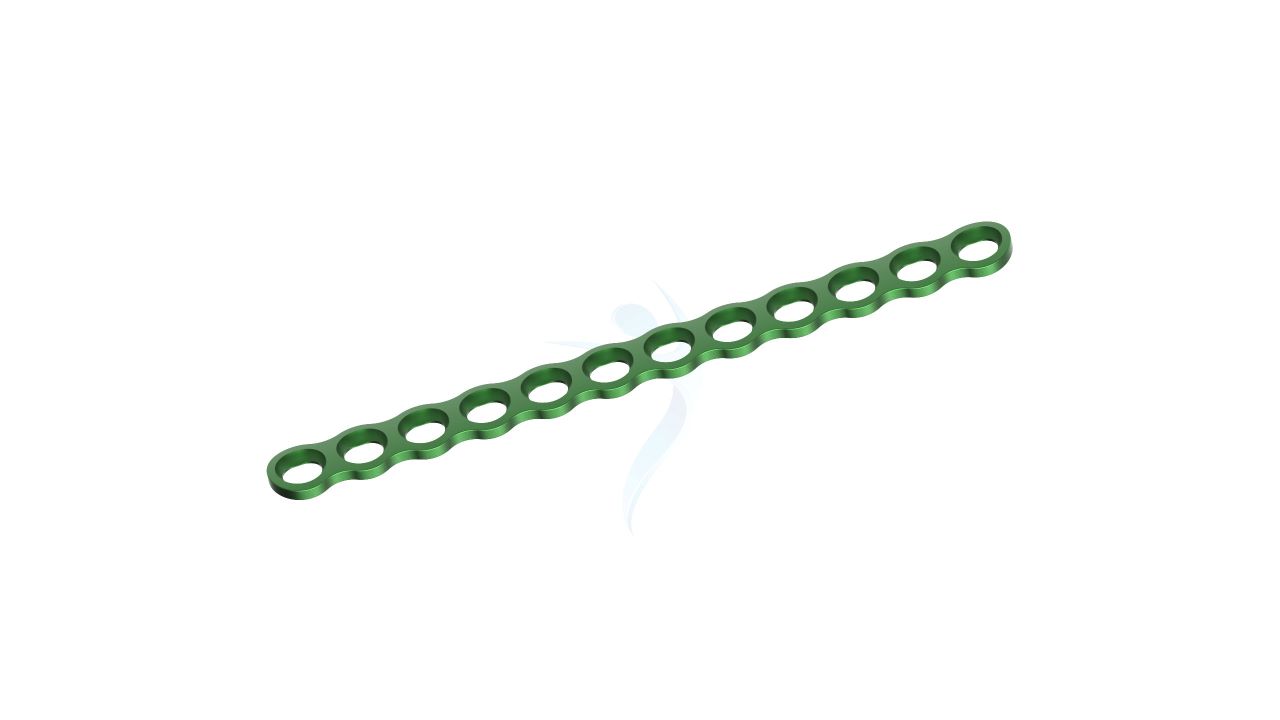
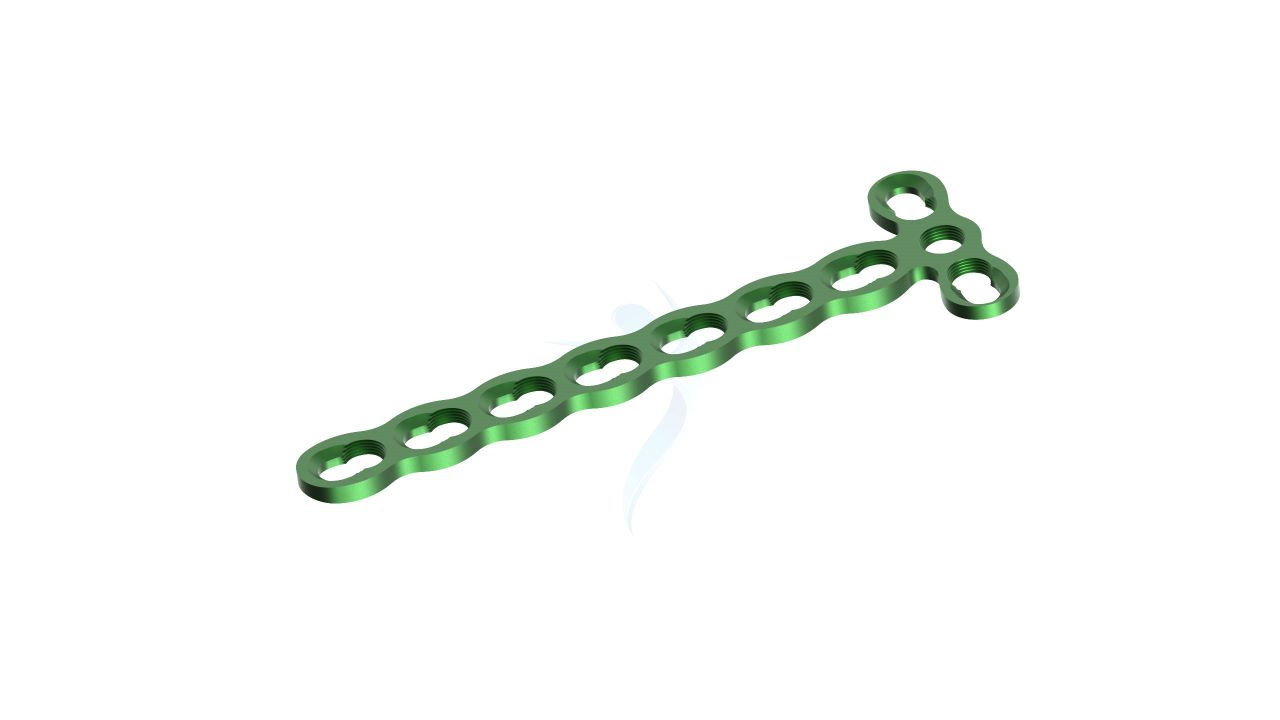
- Design : The plate should have a low-profile, compact design suitable for hand surgeries, ensuring minimal interference with surrounding tissues and bones.
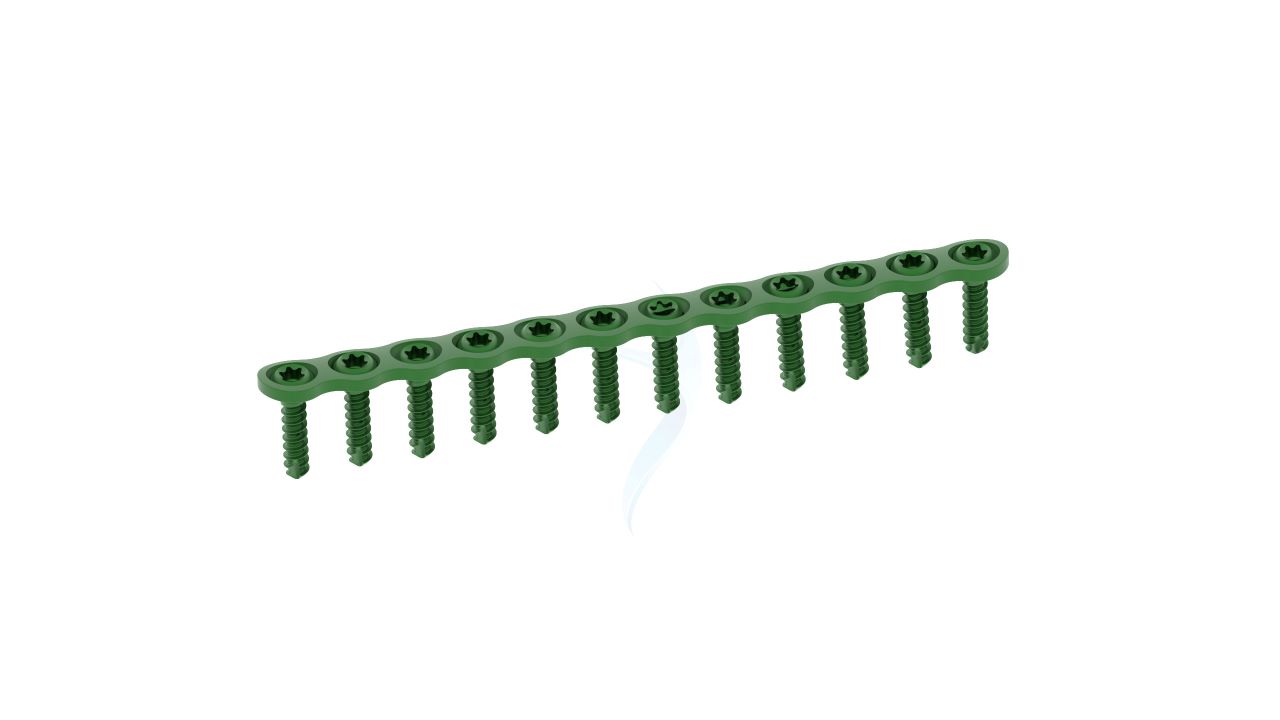
- Screw Holes : The plate should have a pattern of screw holes designed for secure fixation to the bone. These holes should accommodate 2.4mm screws.
- Surface Finish :The surface of the plate should be smooth to minimize tissue irritation and facilitate tissue integration.
- Modularity : The plate is modular, allowing for intraoperative adjustments in length and shape to accommodate variations in patient anatomy and surgical needs.
- Interoperability : Engineered for seamless compatibility with standard orthopedic instruments and established surgical techniques.
Compact Hand Plates - 2.4 mm Adaption Plate Sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Compact Hand Plates 2.4 mm Adaption Plate
- Patient Evaluation : Assess the patient's medical history, including allergies, previous surgeries, medications, and relevant medical conditions. Ensure that the patient is a suitable candidate for the procedure.
- Informed Consent : Obtain informed consent from the patient or their legal guardian after explaining the risks, benefits, and alternatives of the procedure.
- Pre-operative Imaging : Review any pre-operative imaging studies (e.g., X-rays, CT scans) to understand the anatomy and plan the surgery.
- Pre-operative Bloodwork : Perform necessary pre-operative blood tests, such as complete blood count (CBC) and coagulation studies, as directed by the surgeon or anesthesiologist.
- Anesthesia Evaluation : Assess the patient's suitability for anesthesia and discuss the type of anesthesia (e.g., general, regional) with the anesthesia team.
- Instrument Setup : Prepare all necessary surgical instruments and implants, including the 2.4 mm Adaption Compact Hand Plate and associated screws, following the manufacturer's guidelines and ensuring sterility.
- Incision : The surgeon makes an incision at the surgical site to access the affected bone or area of interest. The size and location of the incision depend on the specific procedure and patient's condition.
- Fracture Reduction (if applicable) : If there is a fracture, the surgeon aligns the fractured bone fragments to restore proper anatomical alignment. This may involve manipulation of the bones or the use of reduction clamps.
- Plate Placement : The 2.4 mm Adaption Compact Hand Plate is selected based on the patient's anatomy and the specifics of the case. It is then carefully positioned over the fractured or treated area.
- Screw Placement : Orthopedic screws, typically of a compatible size and type, are inserted through the holes in the plate and into the bone to secure the plate in place. The number and placement of screws depend on the fracture and the surgeon's judgment.
- Incision Closure : The incision is closed using sutures or staples, and the wound is dressed with sterile bandages.
- Post-Operative Recovery :Transfer the patient to the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) for initial recovery and monitoring.
- Pain Management :Administer pain medications as prescribed to manage post-operative pain and discomfort.
- Observation : Monitor the patient for any signs of complications, such as infection, bleeding, or changes in vital signs.
- Wound Care : Instruct the patient or their caregiver on proper wound care, including dressing changes and hygiene.
- Activity Restrictions : Provide the patient with clear instructions regarding activity restrictions, including weight-bearing limitations and the use of assistive devices.


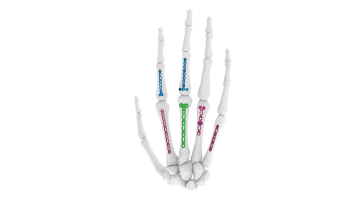

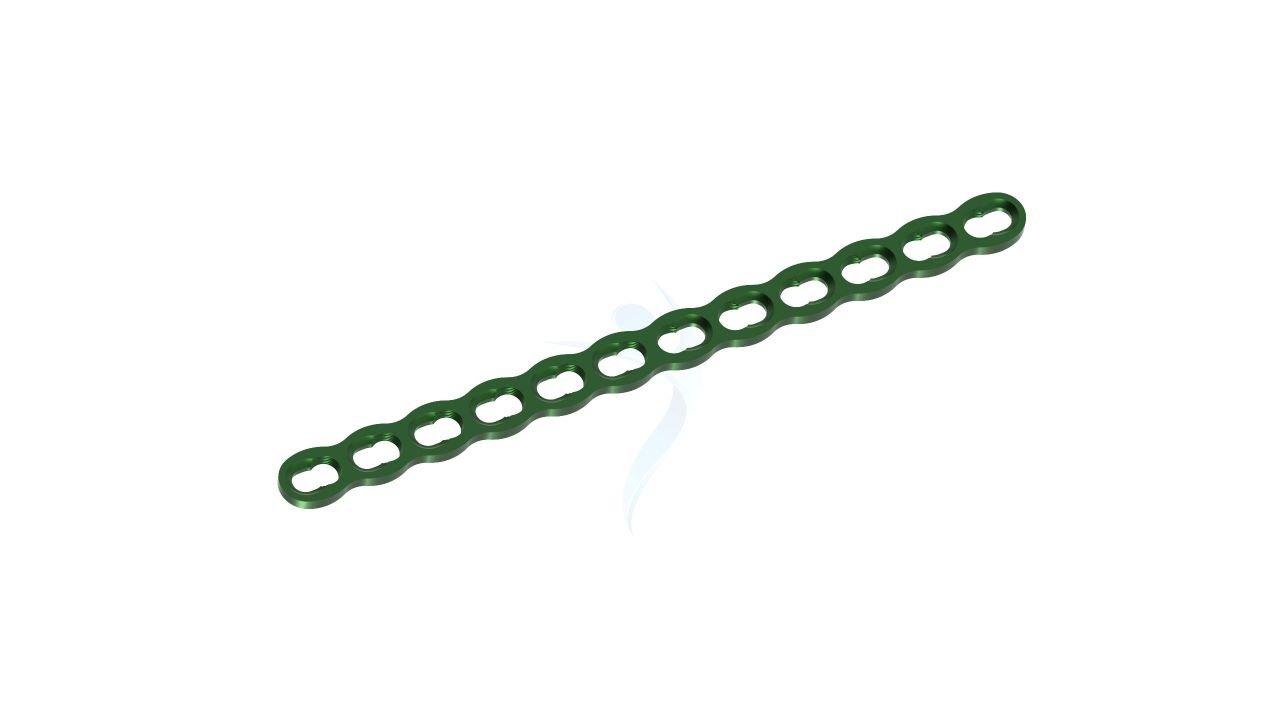





.png)