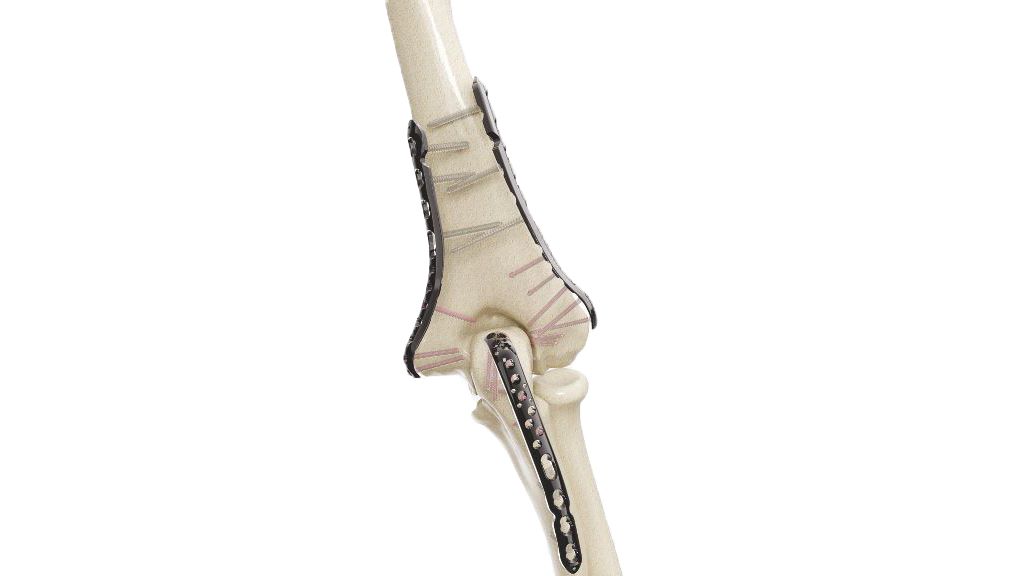
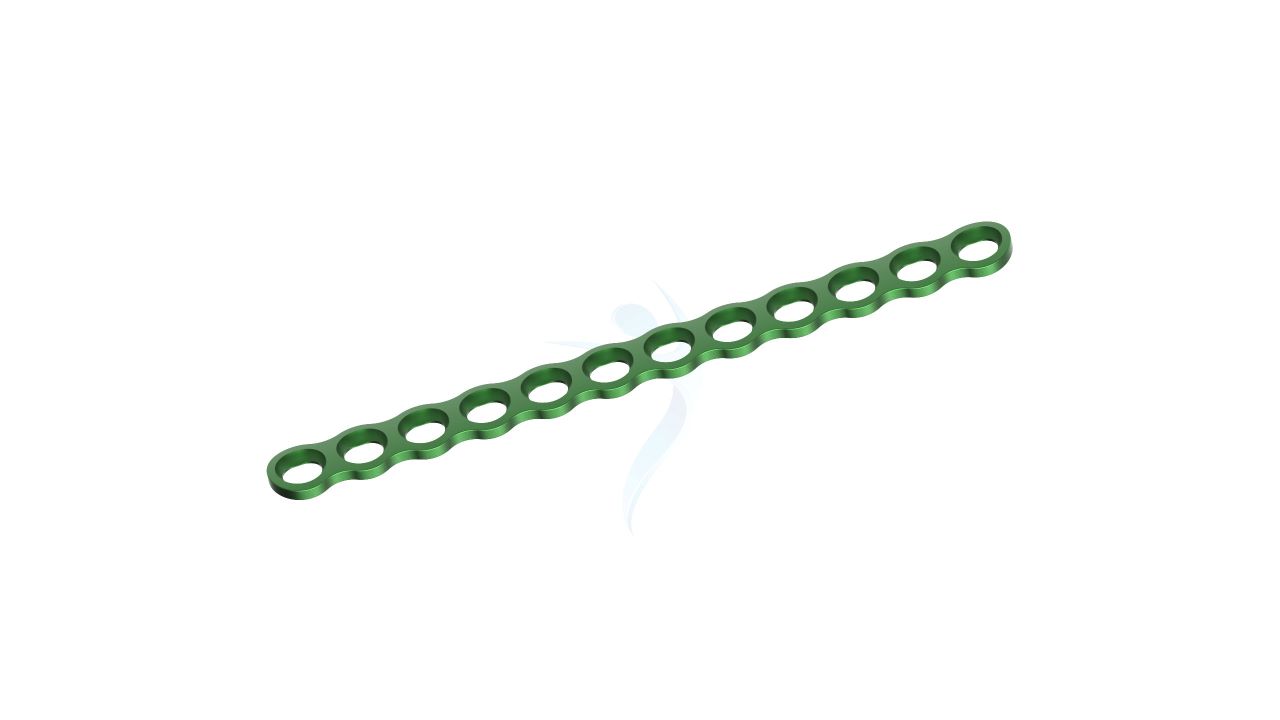
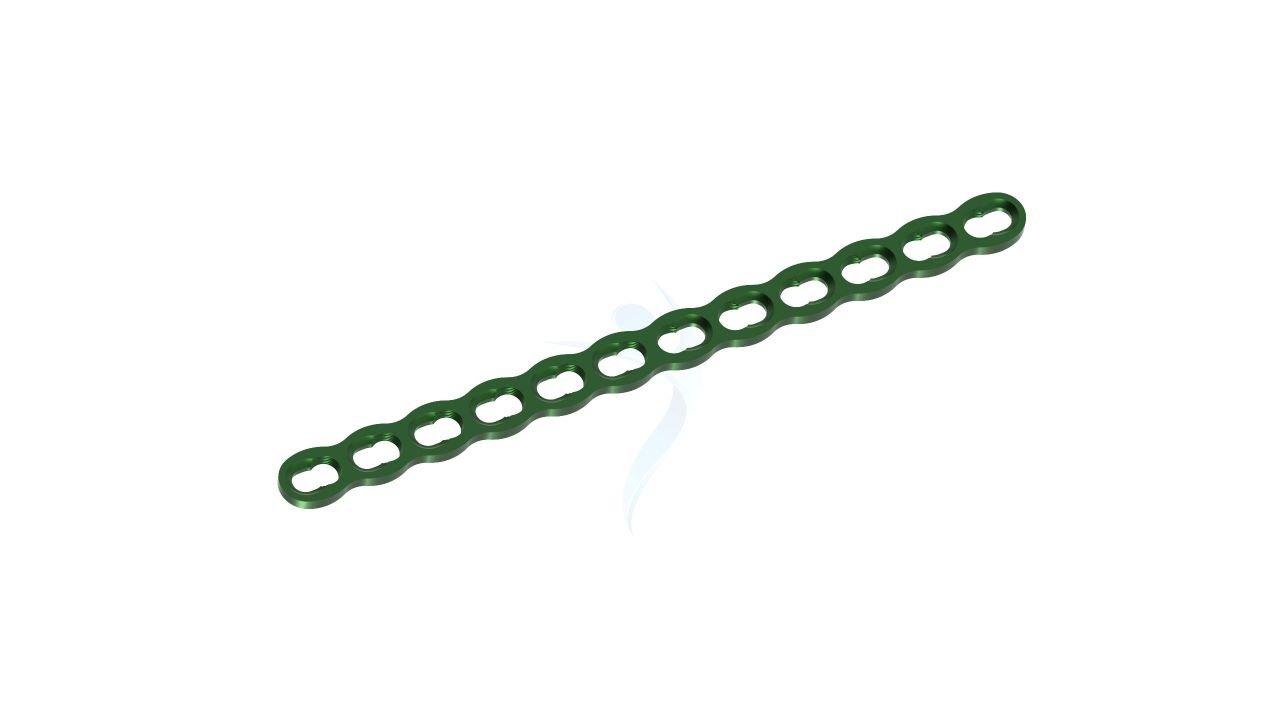
Compact Hand Plates - 2.4 mm Straight
Product Overview
The 2.0 mm Straight Compact Hand Plate is a specialized orthopedic implant designed for delicate hand and finger surgeries. It is a small, low-profile plate made from biocompatible materials, providing stability and support during procedures to treat fractures, deformities, and other orthopedic conditions in the hand and fingers. This implant is valued for its precision and versatility, aiding orthopedic surgeons in restoring functionality and reducing pain in patients' hands and fingers.
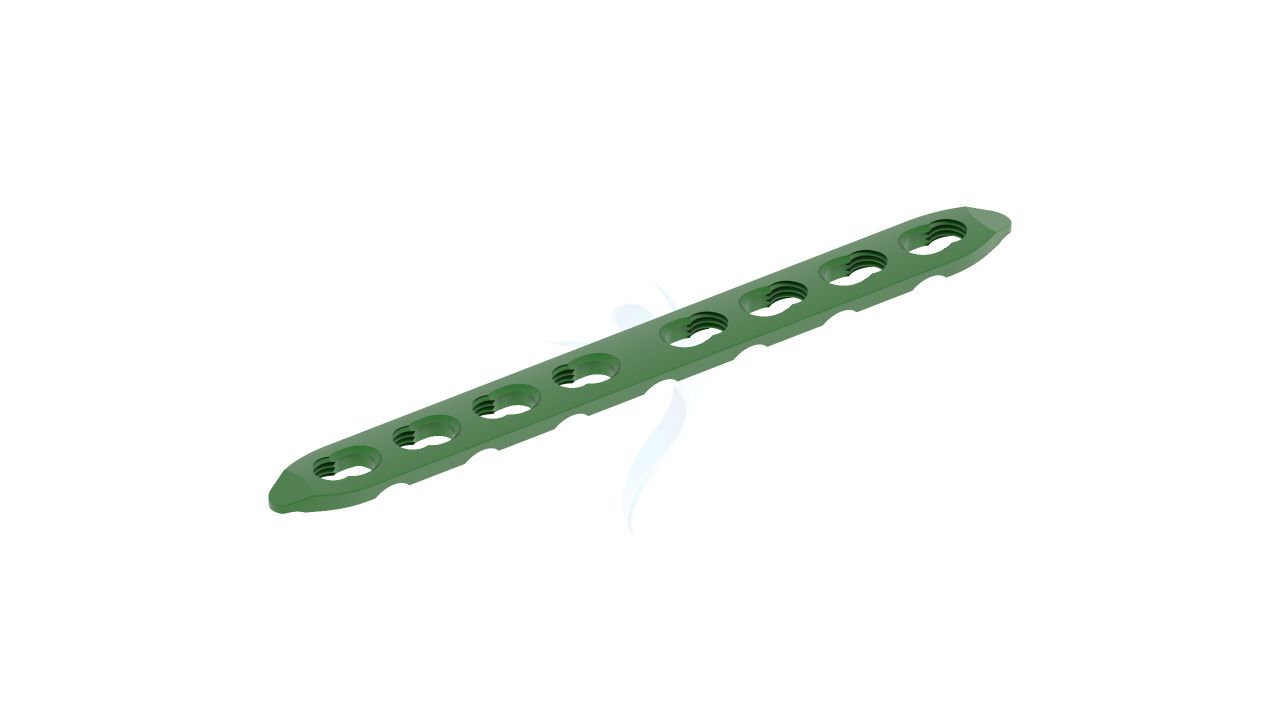
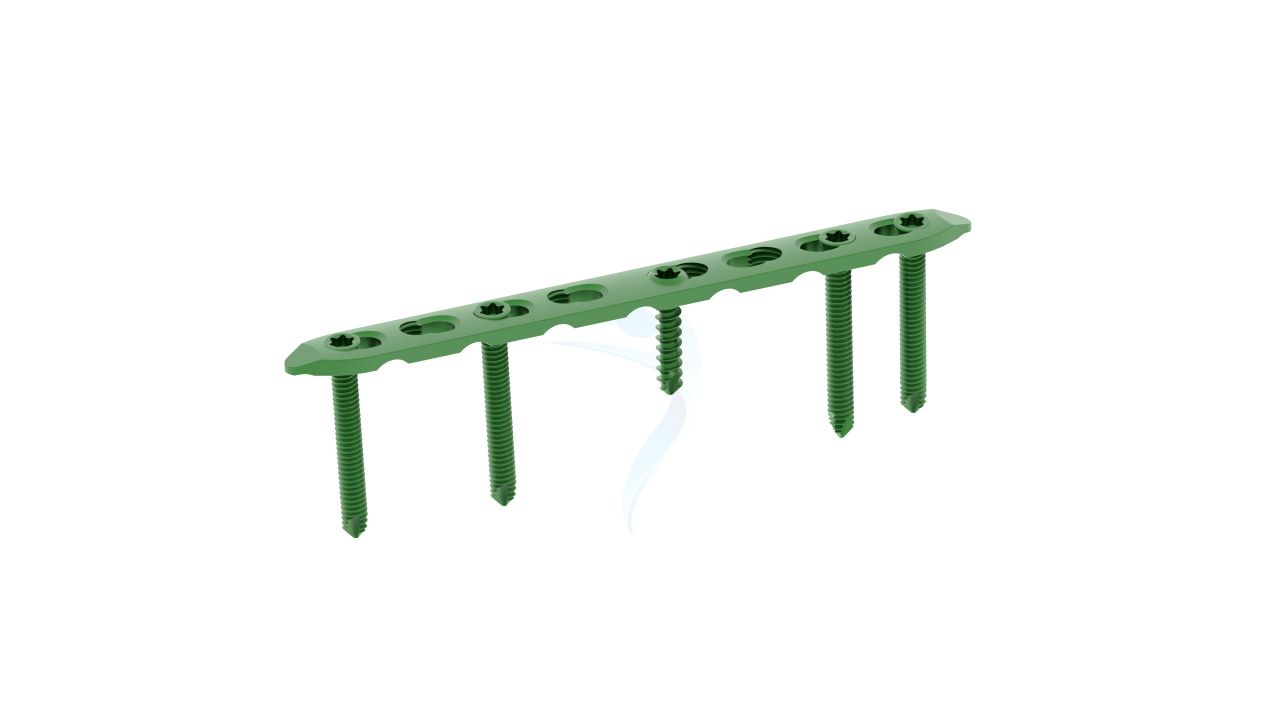
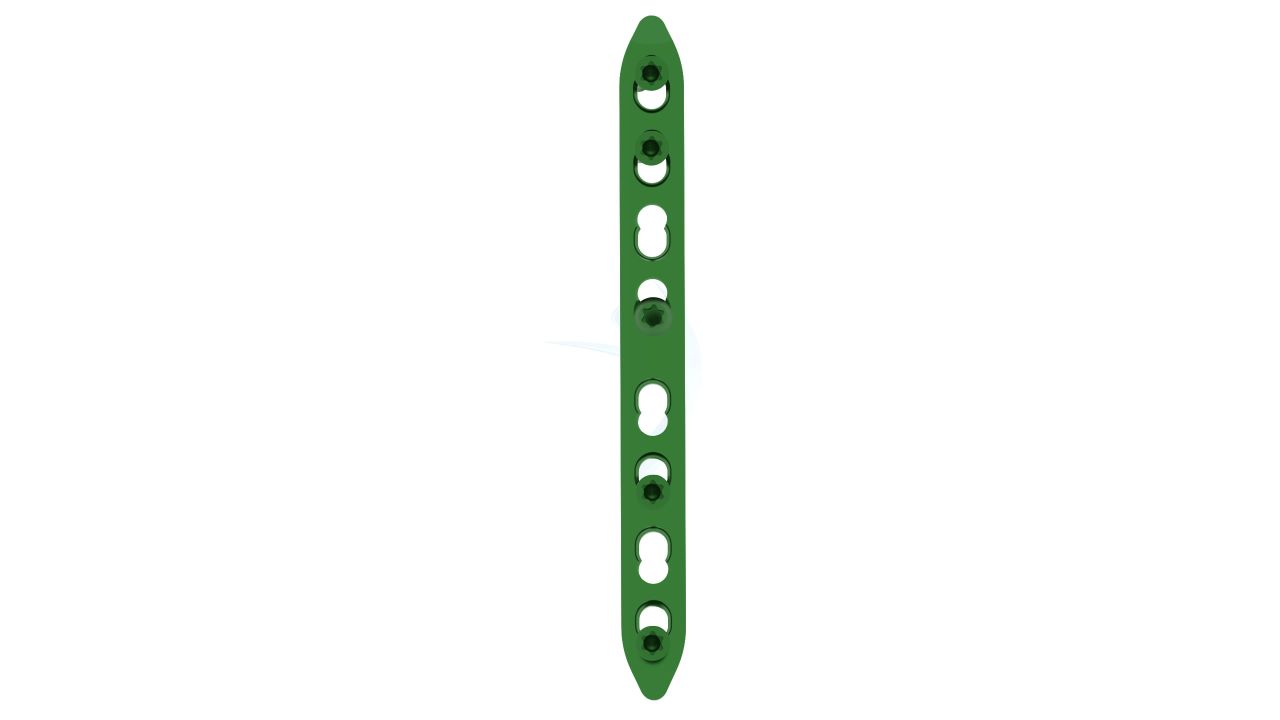
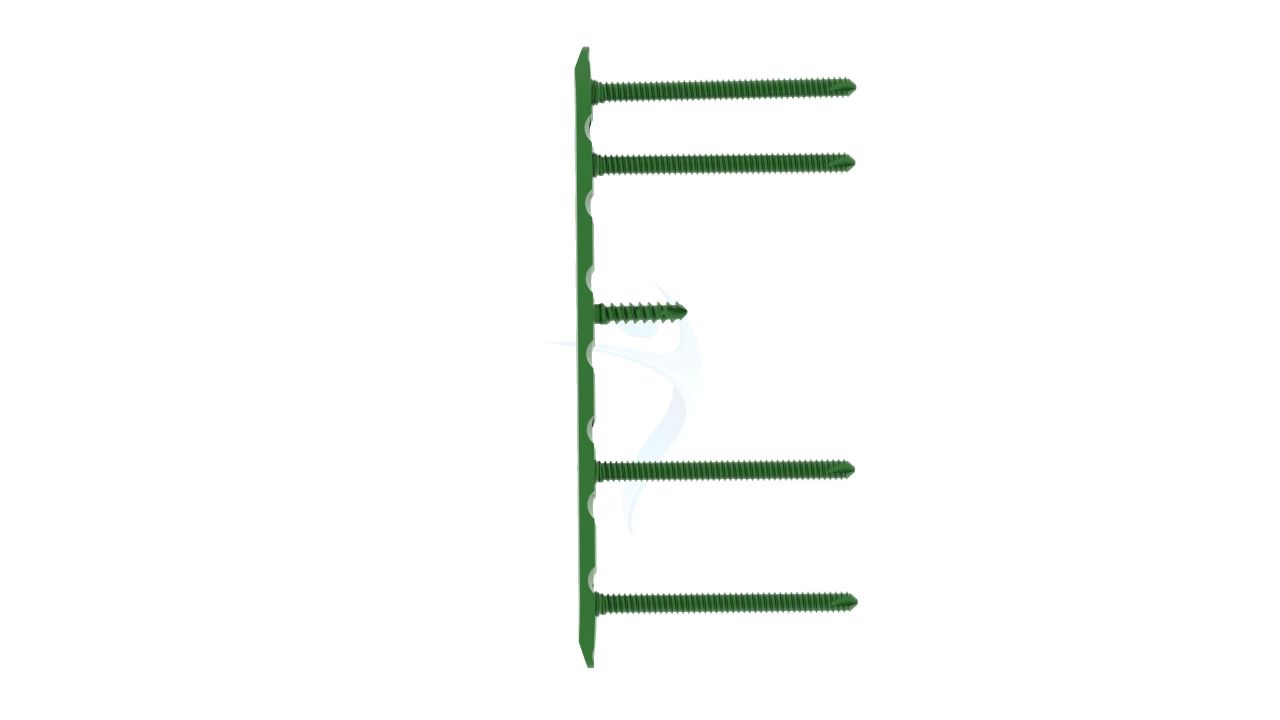
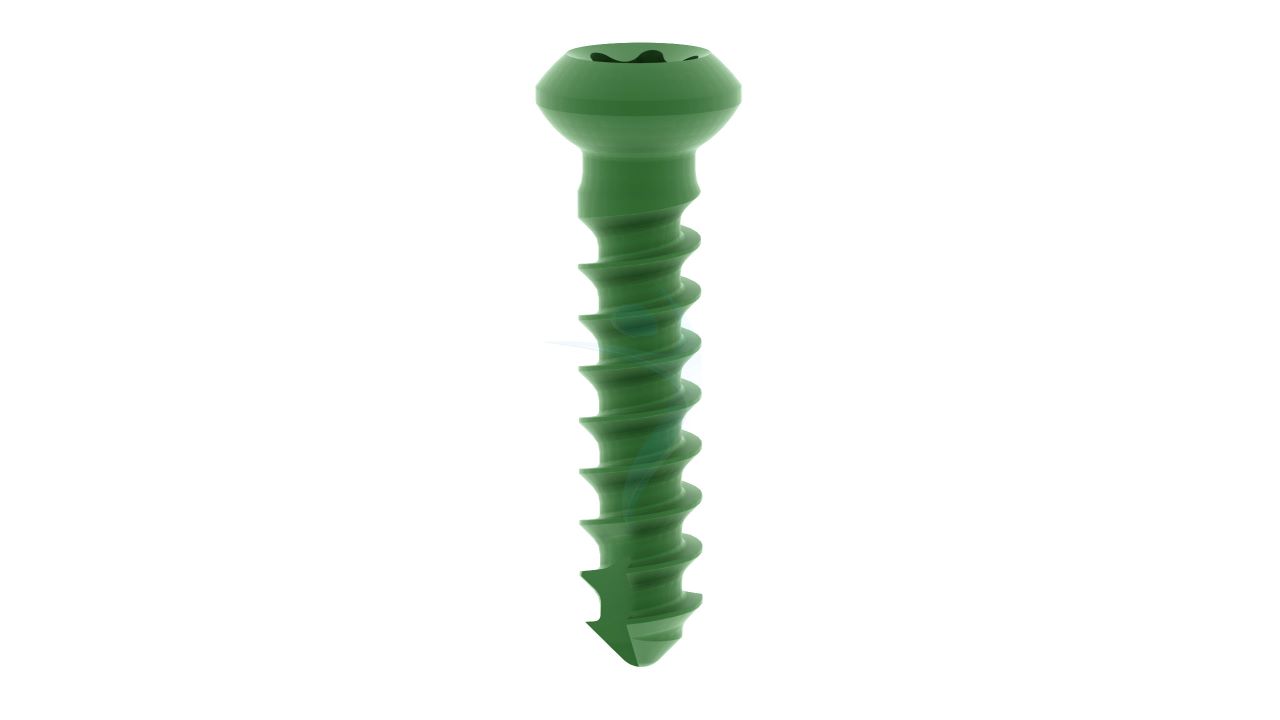
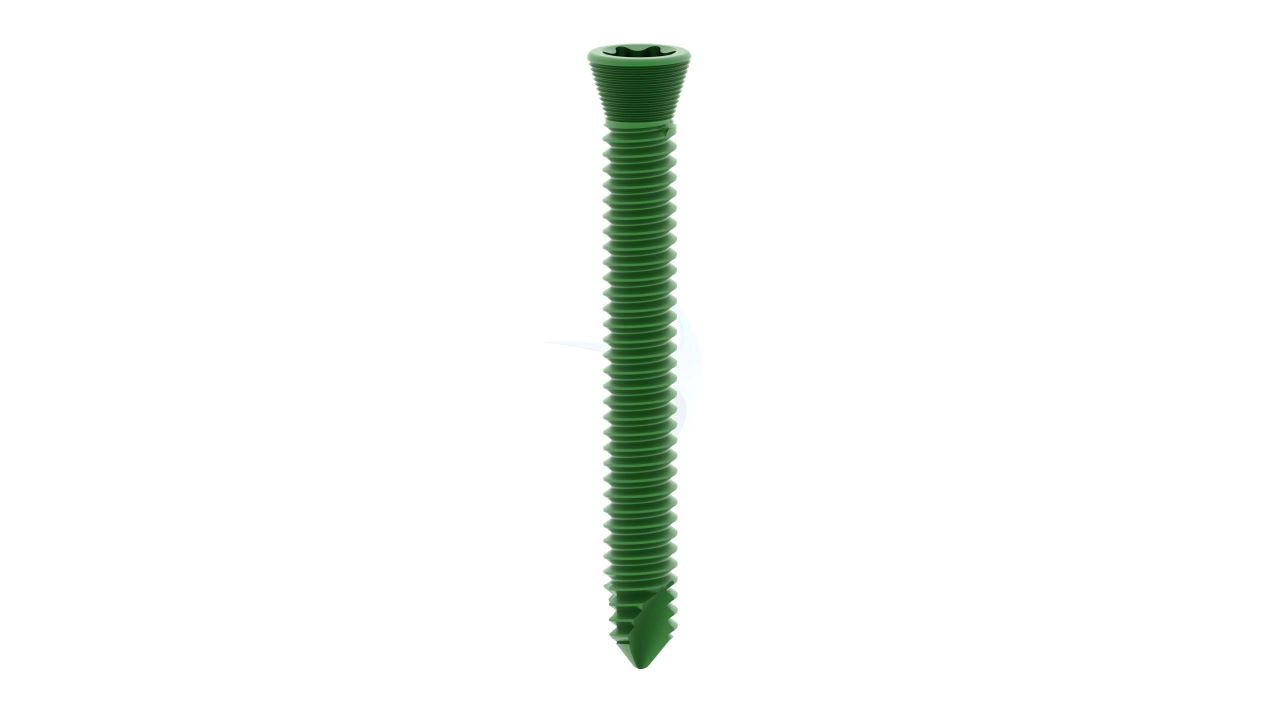


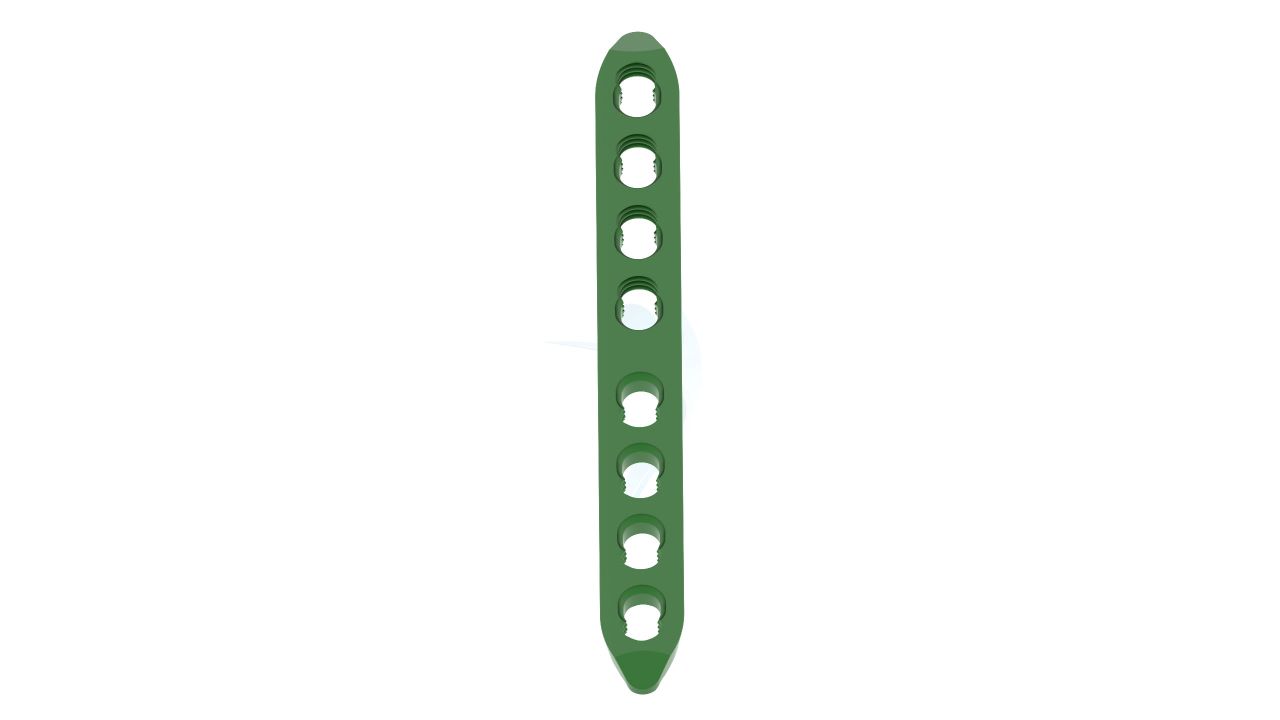




Product Uses
- Hand Fractures : The 2.0 mm straight Compact Hand Plate may be used to stabilize and fix fractures of the hand, including metacarpal fractures, phalangeal fractures, and fractures of the finger or thumb bones.
- Hand and Finger Reconstructive Surgery : This implant can be used in hand and finger reconstructive procedures to correct bone deformities, restore function, or improve hand and finger alignment.
- Thumb Basal Joint (CMC Joint) Arthritis : In cases of thumb basal joint arthritis, the Compact Hand Plate may be used to stabilize the joint, reduce pain, and improve thumb function.
- Non-Union Fracture Treatment : Applied to promote the healing of non-union fractures, facilitating bone union and recovery.
- Non-Union Fractures : Non-union fractures, where a fracture fails to heal properly, may require the use of this plate to provide stability and promote bone healing.
Product Specification
- Size :The Plates have a width of 2.4 mm, providing strength and stability while accommodating the delicate structures of the hand.
- Material : Constructed from high-quality medical-grade titanium alloy, known for its biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength.
- Design : The Plates feature a specialized 2.4 Straight Plate, allowing for seamless integration with the hand's complex anatomy.
- Thickness :The Plates are designed to have a low profile while maintaining structural integrity, contributing to minimally invasive surgical techniques.
- Screw Compatibility : Compatible with orthopedic screws of matching dimensions (2.4mm) for secure fixation.
- Number of Holes : The Plates may have multiple screw holes for secure fixation, and the Straight Plate feature allows for adaptability in screw placement.
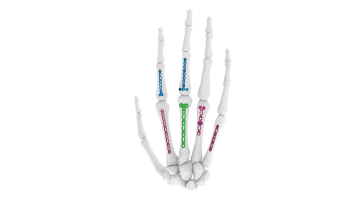
Compact Hand Plates - 2.4 mm Straight Plate Sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Compact Hand Plates 2.4 mm Straight Plate
- Patient Evaluation : Assess the patient's medical history, including allergies, previous surgeries, medications, and relevant medical conditions. Ensure that the patient is a suitable candidate for the procedure.
- Informed Consent : Obtain informed consent from the patient or their legal guardian after explaining the risks, benefits, and alternatives of the procedure.
- Pre-operative Imaging: Review any pre-operative imaging studies (e.g., X-rays, CT scans) to understand the anatomy and plan the surgery.
- Pre-operative Bloodwork :Perform necessary pre-operative blood tests, such as complete blood count (CBC) and coagulation studies, as directed by the surgeon or anesthesiologist.
- Anesthesia Evaluation : Assess the patient's suitability for anesthesia and discuss the type of anesthesia (e.g., general, regional) with the anesthesia team.
- Sterile Environment : Ensure that the operating room is sterile and equipped with all necessary instruments and equipment.
- X-ray Imaging : Use fluoroscopy or other imaging techniques to guide the placement of the plate accurately, especially in cases where alignment is critical.
- Procedure Steps : Follow the surgical plan meticulously, including the precise placement of the Compact Hand 2.4 Straight Plate and any necessary screws. The surgeon should use their expertise to ensure the plate is appropriately positioned and secured.
- Post-Procedure Verification: Verify the stability and proper positioning of the plate and screws, and assess their alignment using imaging if required.
- Wound Closure : Close the surgical incision meticulously using appropriate sutures or wound closure techniques.
- Post-Operative Imaging : Perform post-operative imaging, such as X-rays, to confirm the placement and alignment of the plate and screws.
- Post-Operative Recovery : Transfer the patient to the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) for initial recovery and monitoring.
- Pain Management : Administer pain medications as prescribed to manage post-operative pain and discomfort.
- Observation : Monitor the patient for any signs of complications, such as infection, bleeding, or changes in vital signs.
- Wound Care : Instruct the patient or their caregiver on proper wound care, including dressing changes and hygiene.
- Activity Restrictions :Provide the patient with clear instructions regarding activity restrictions, including weight-bearing limitations and the use of assistive devices.







.png)