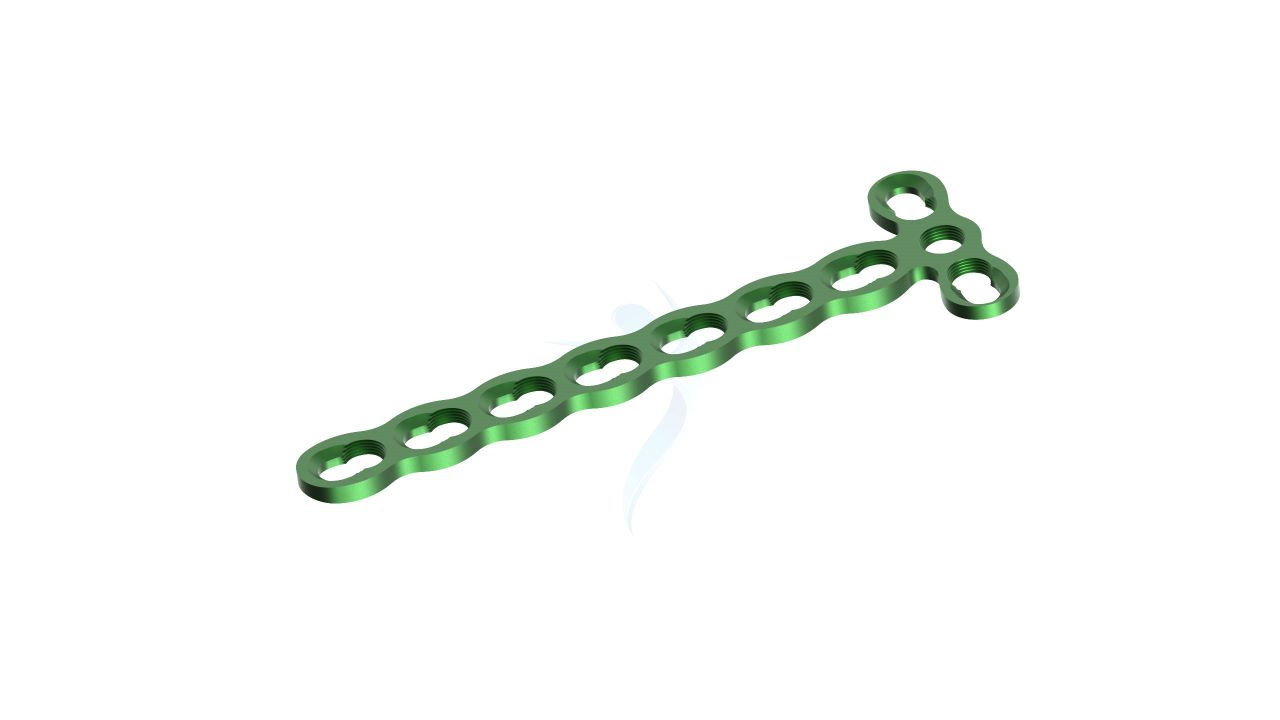
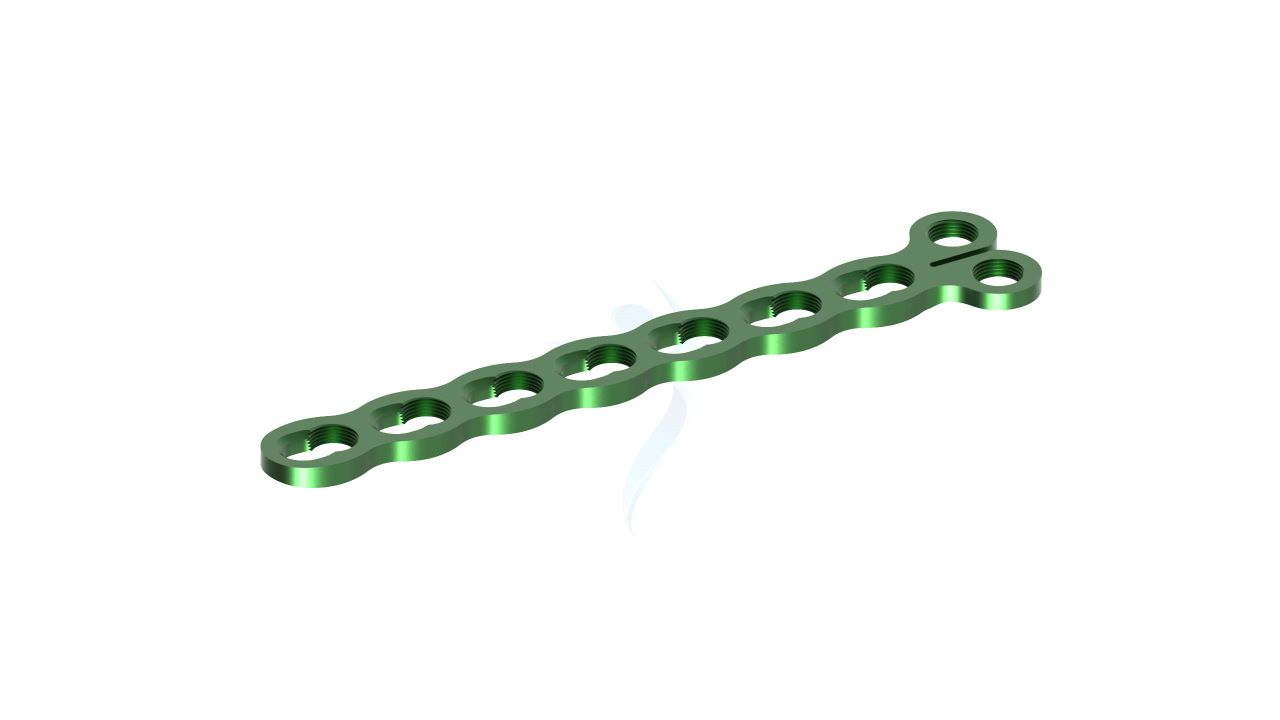
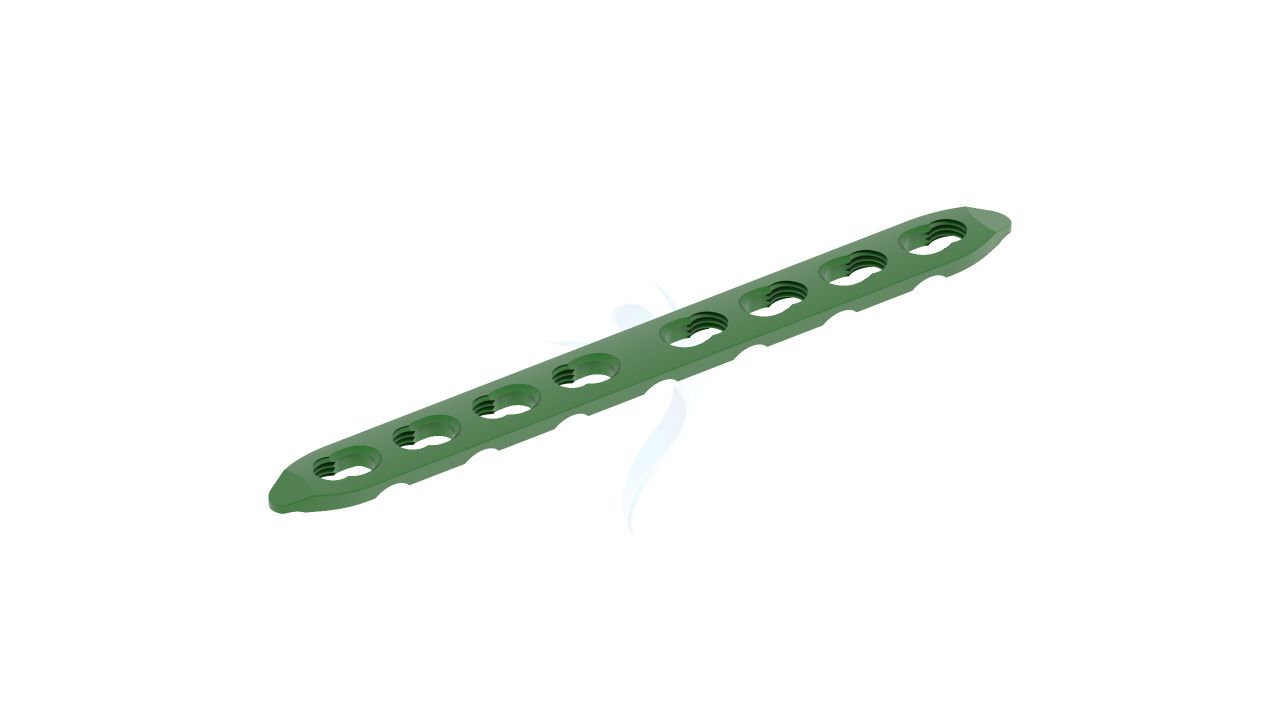
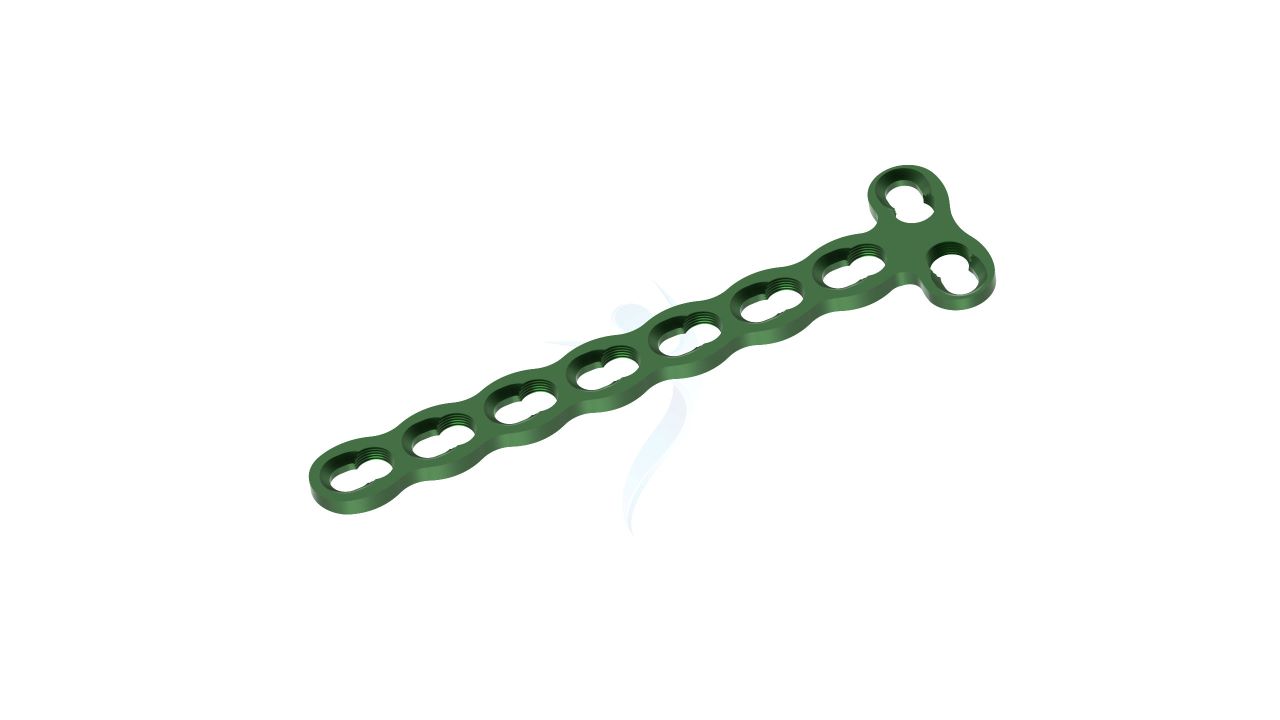
Compact Hand Plates - ASLP 2.4 Y Adaption Plate
Product Overview
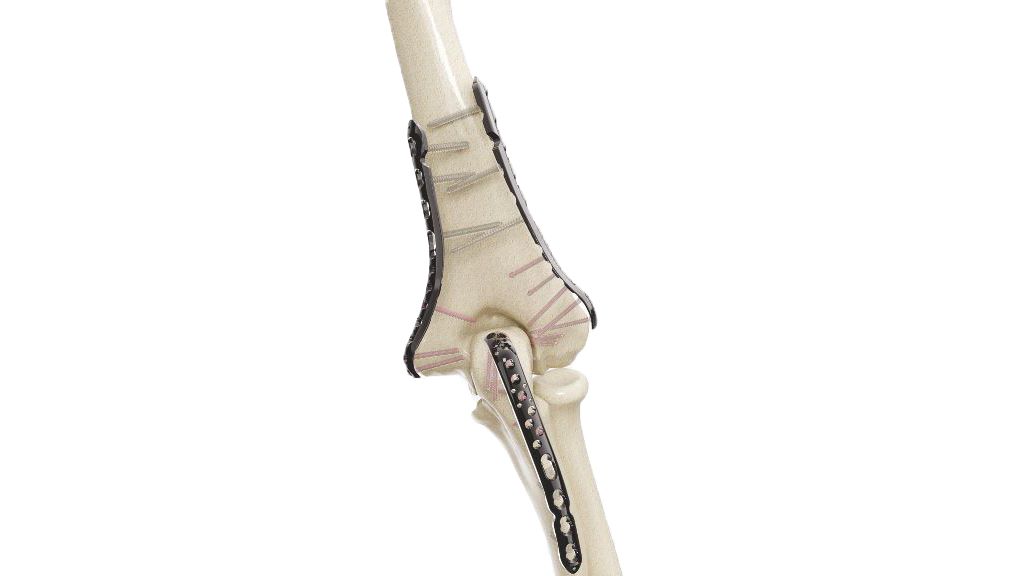
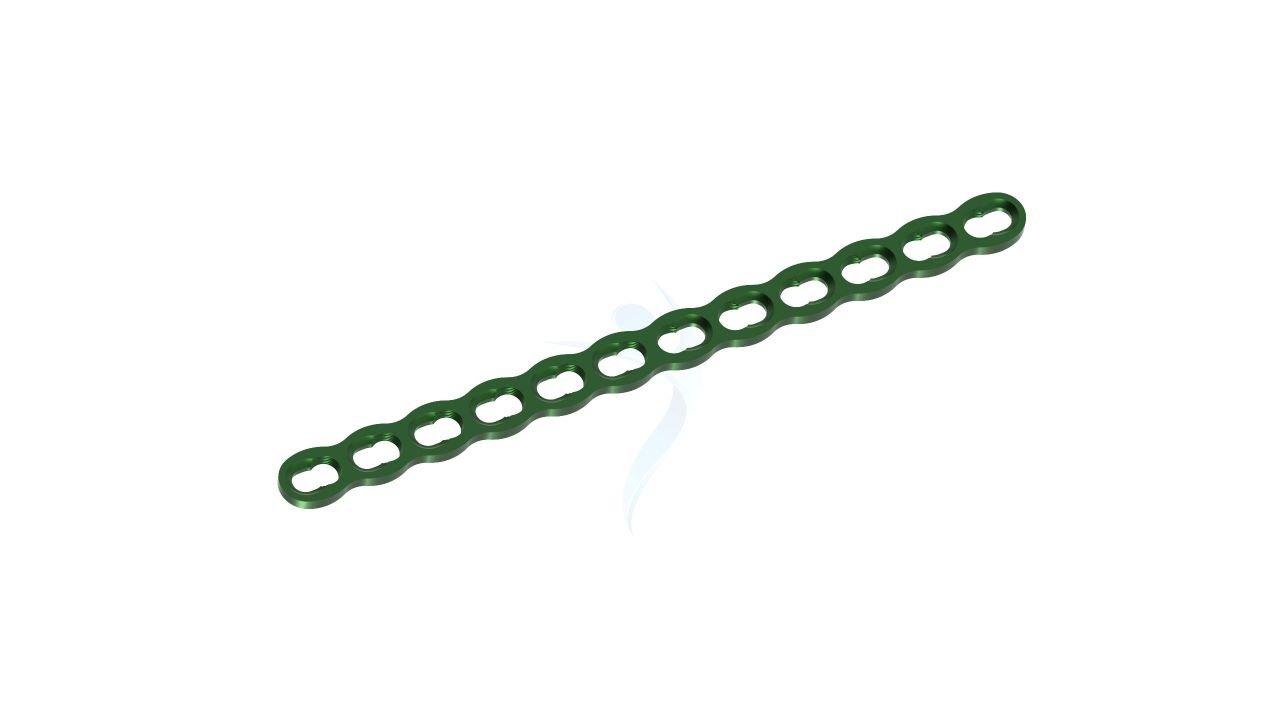
The 2.4 mm Y Adaption Plate is a precision-crafted orthopedic implant designed to address various hand and finger conditions, providing stability and support for optimal healing and functional recovery. Its unique Y-shaped design allows for versatile use in a wide range of hand and finger surgical procedures, including fracture fixation, malunion correction, non-union fracture management, bone deformity correction, joint fusion, and more. The plate's variable hole spacing and 2.4 mm hole diameter ensure compatibility with a variety of orthopedic screws, enabling surgeons to tailor their approach to each patient's unique needs. The 2.4 mm Y Adaption Plate exemplifies precision and adaptability.
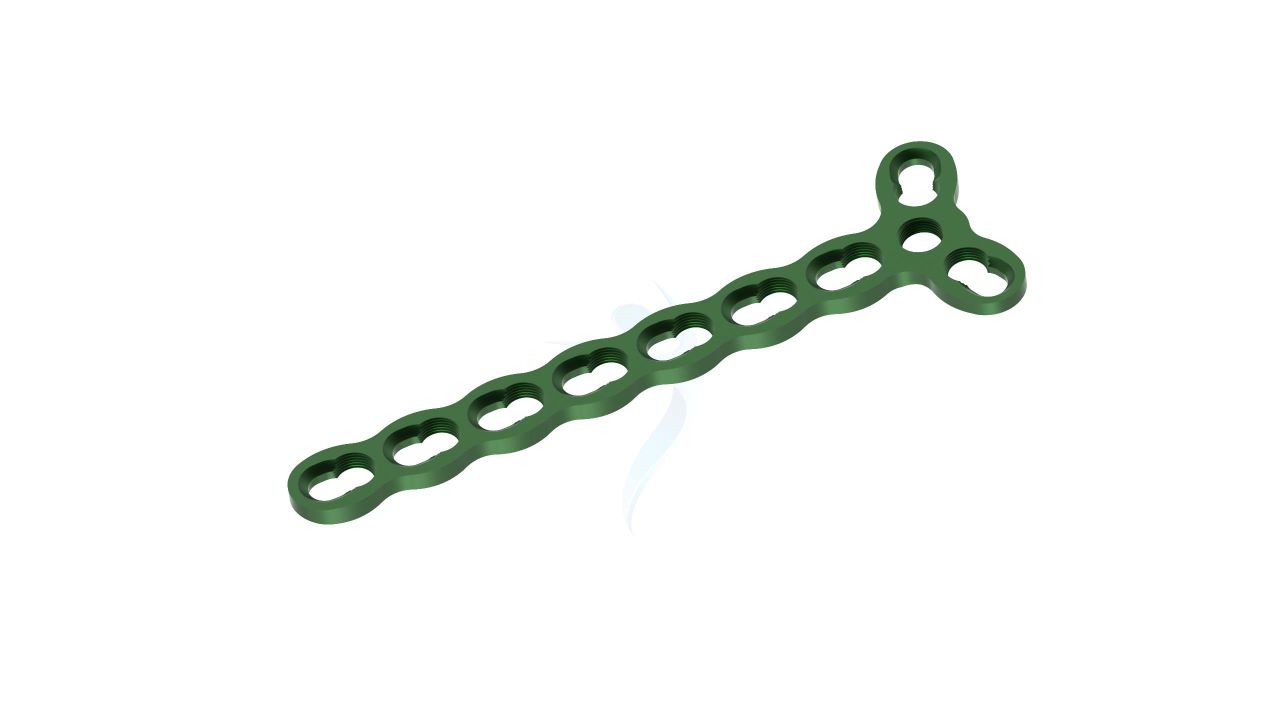
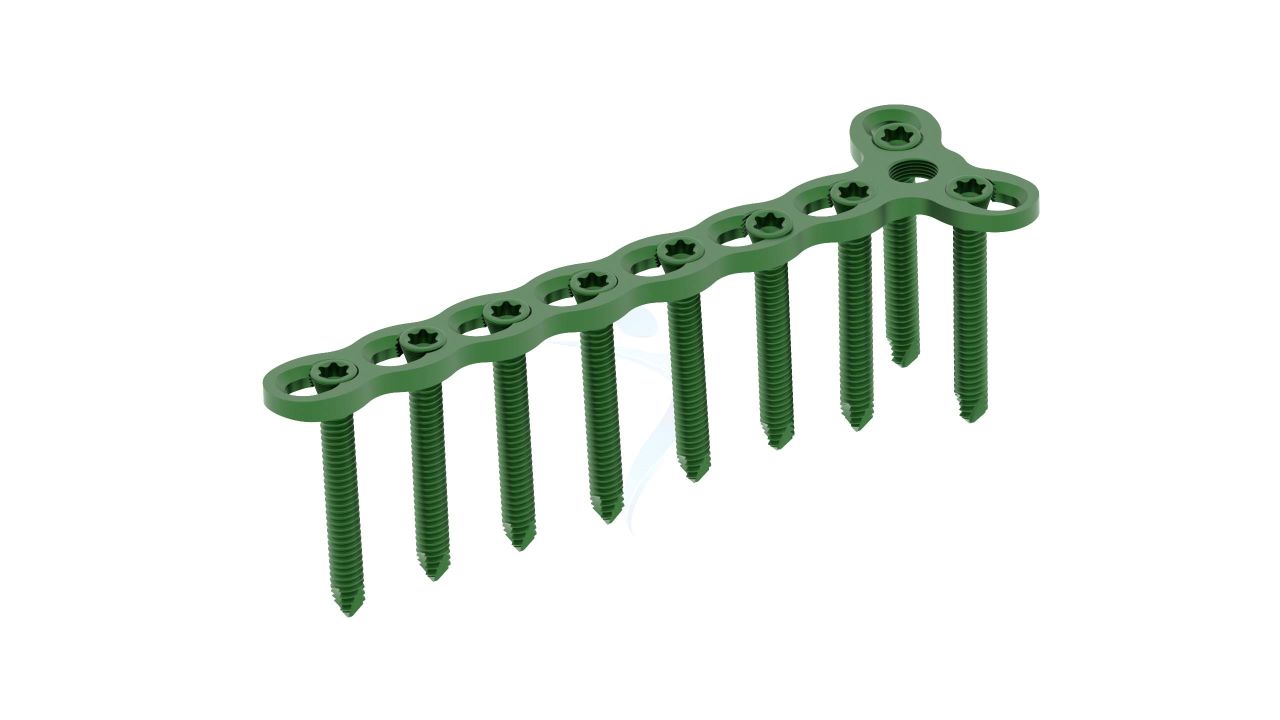
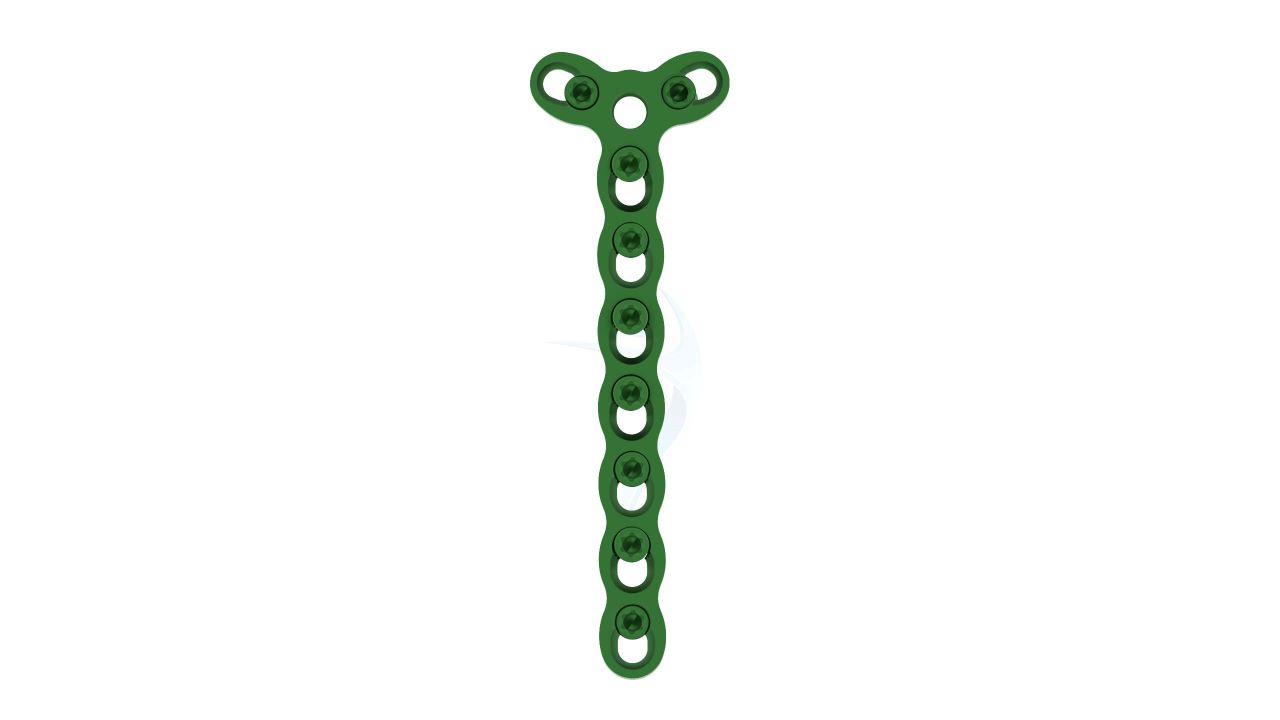
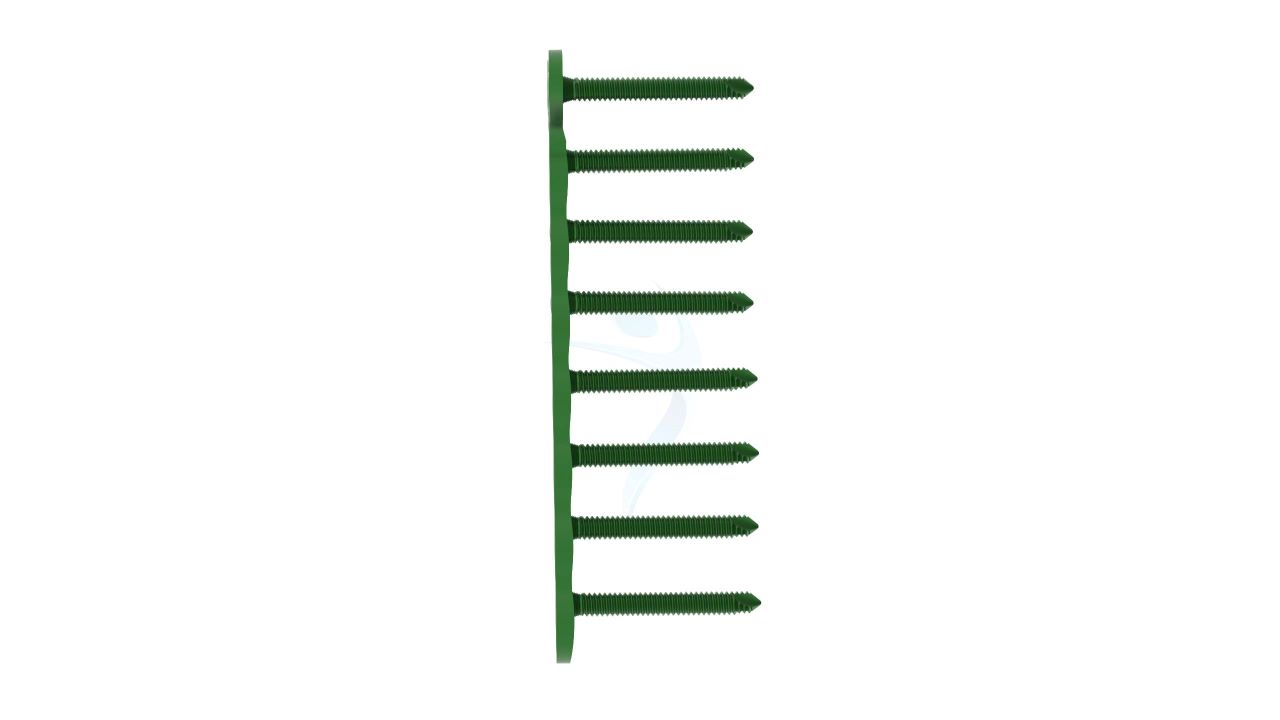
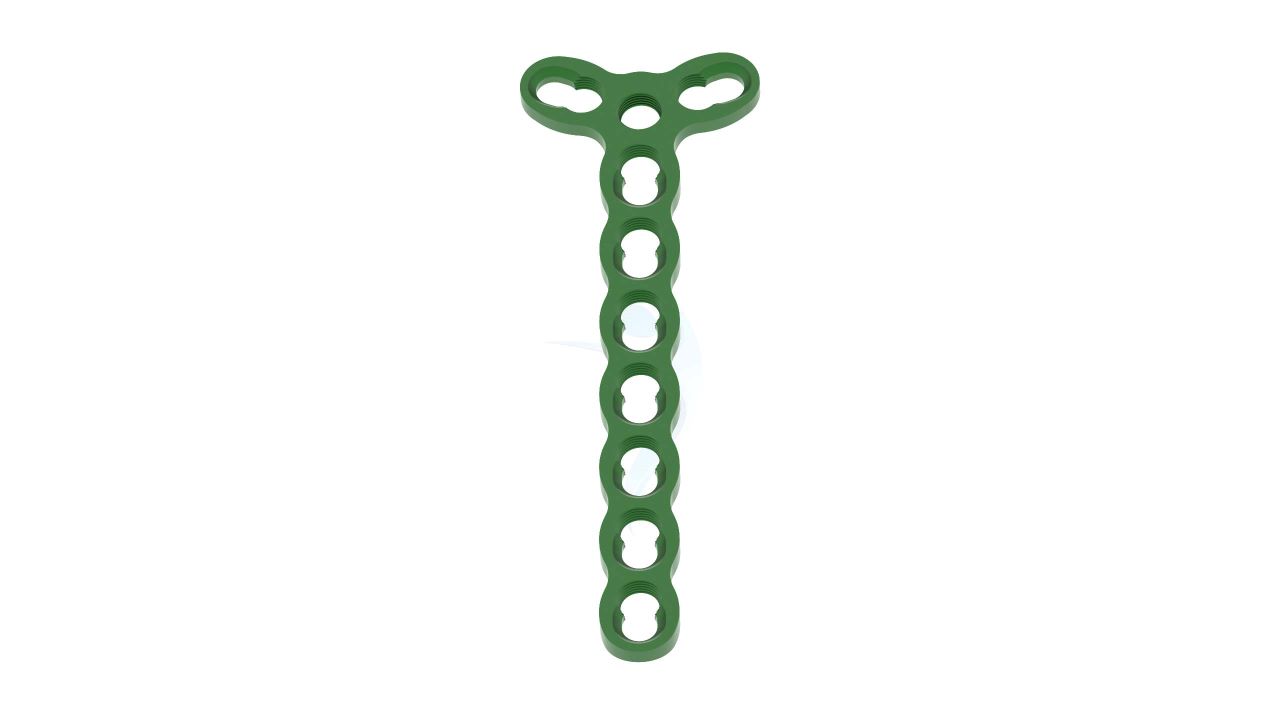
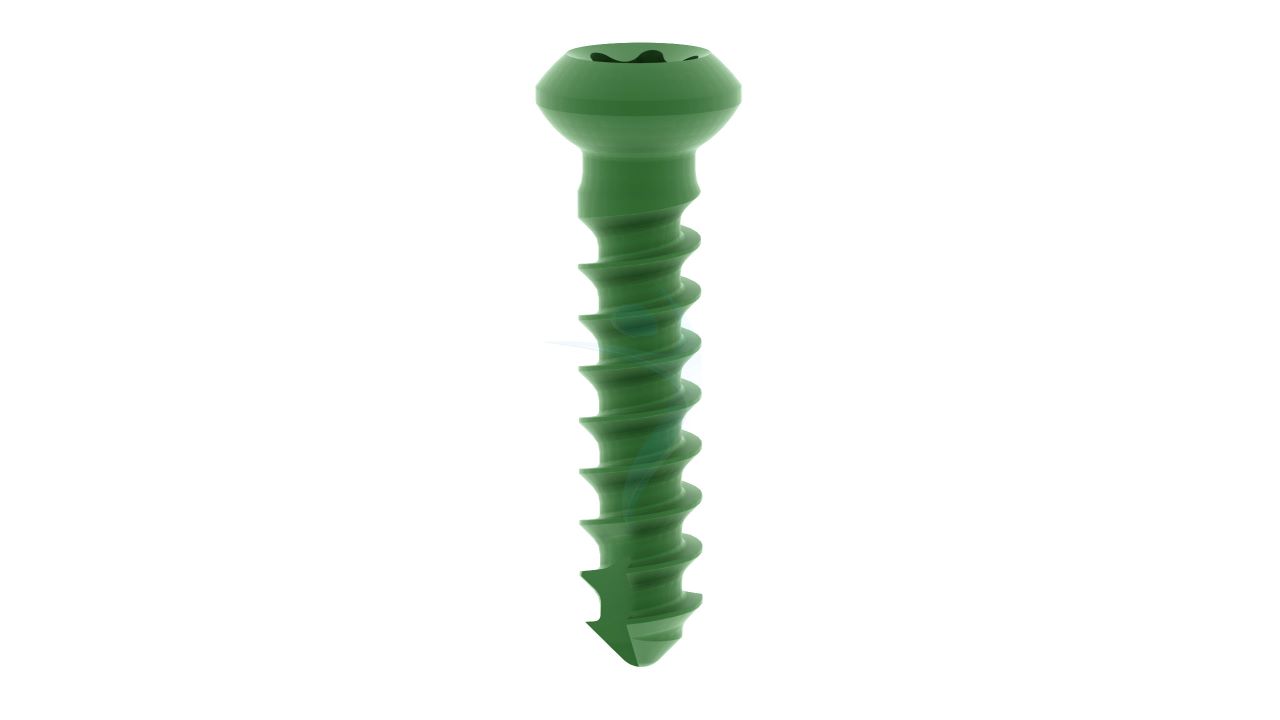
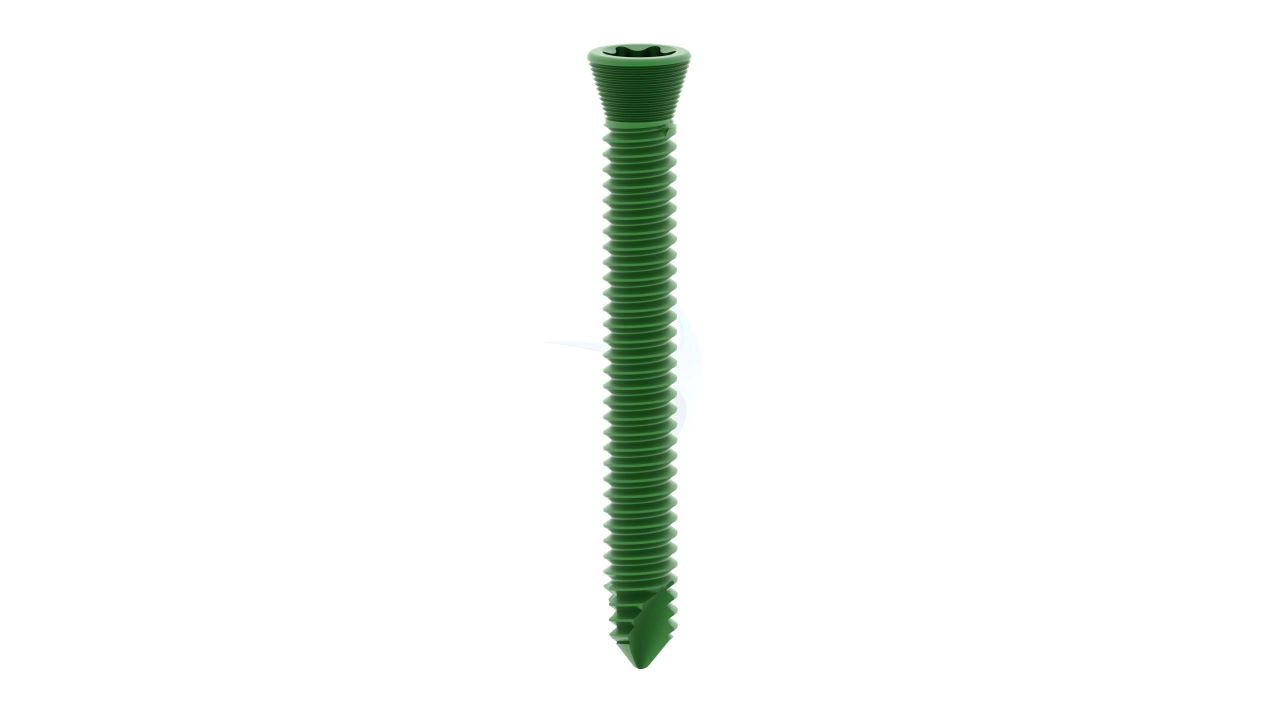







Product Uses
- Fracture Fixation : Used to stabilize and support fractured bones in the hand and fingers, facilitating proper healing.
- Malunion Correction : Employed to correct malunions, where bones have healed in improper alignment.
- Non-Union Fractures : Aids in the treatment of non-union fractures by providing stability and promoting bone fusion.
- Bone Deformity Correction : Utilized to correct bone deformities, such as angular or rotational deformities in the hand and fingers.
- Bone Graft Fixation : Secures bone grafts or bone fragments during reconstructive surgeries.
Product Specification
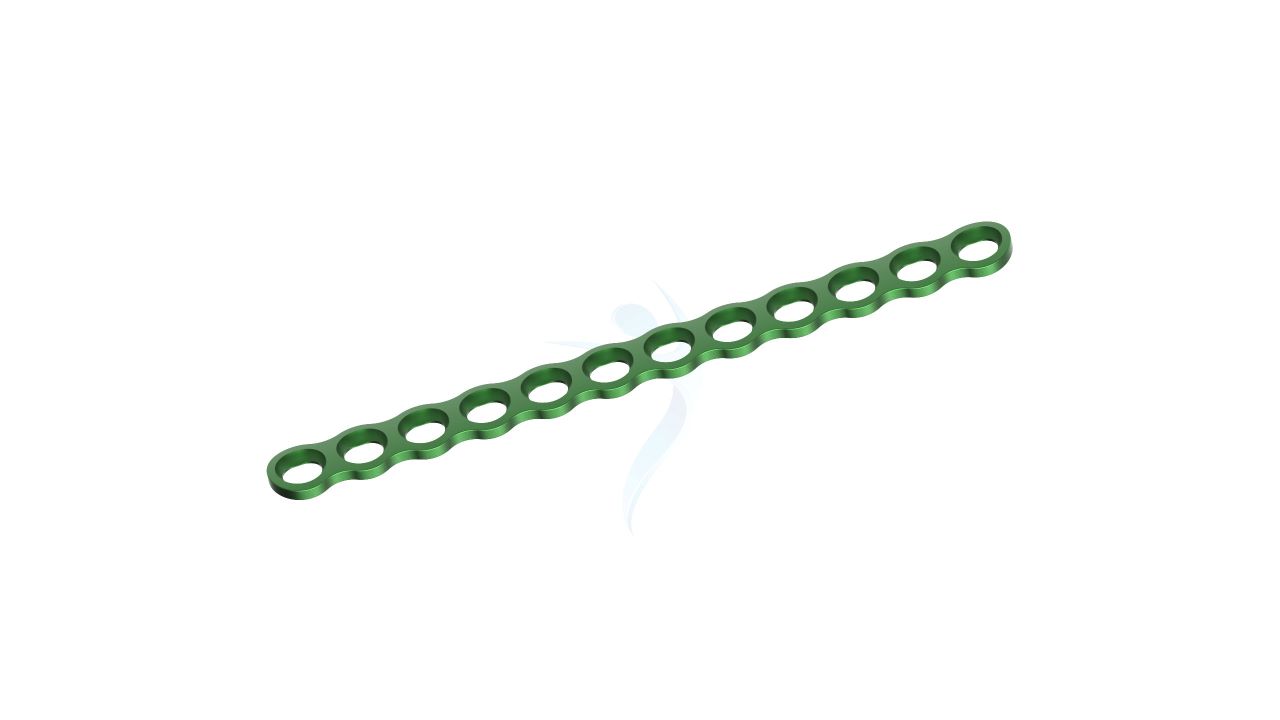
- Plate Hole Diameter :Designed to accommodate 2.4 mm orthopedic screws.
- Plate Hole Spacing : Variable hole spacing for accommodating different surgical needs.
- Design : Unique Y-shaped design for versatile applications in hand and finger surgeries.
- Surface Finish :Smooth and polished to minimize tissue irritation and promote efficient healing.
- Compatibility : Compatible with a variety of orthopedic screws and instruments commonly used in hand and finger surgeries.
- Manufacturer :Produced by reputable medical implant manufacturers, adhering to strict quality and regulatory standards.
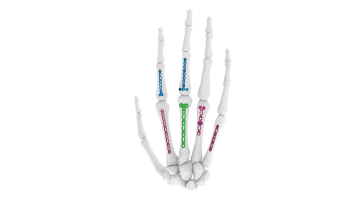
Compact Hand Plates - ASLP 2.4 mm Y Adaption Plate Sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Compact Hand Plates ASLP 2.4 Y Adaption Plate
- Patient Evaluation: Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history, hand condition, and diagnostic imaging (such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI) to assess the need for surgery and the suitability of the ASLP 2.4 mm Y Adaption Plate.
- Informed Consent: Obtain informed consent from the patient, explaining the surgical procedure, potential risks, benefits, and expected outcomes.
- Anesthesia Planning: Collaborate with the anesthesia team to determine the most appropriate anesthesia type (local, regional, or general) based on the patient's health and surgical requirements.
- Surgical Team Readiness: Ensure the surgical team, including the surgeon, nurses, and technicians, is fully prepared with the necessary instruments and equipment.
- Incision: Make a precise incision over the affected hand or finger area, exposing the fractured or deformed bone.
- Fracture Reduction (If Applicable): In cases of fractures, carefully realign the bone fragments to their correct anatomical position.
- Plate Selection: Choose the appropriate size and configuration of the ASLP 2.4 mm Y Adaption Plate based on the surgical requirements and patient anatomy.
- Plate Placement: Secure the selected plate onto the bone surface using orthopedic screws, ensuring proper alignment and fixation.
- Screw Insertion: Carefully insert orthopedic screws through the plate holes and into the bone to provide stable fixation. Ensure screws are tightened to the desired tension.
- Dressing and Bandaging: Apply a sterile dressing and bandage to the surgical site to protect it and absorb any post-operative drainage.
- Immobilization:Depending on the procedure and surgeon's recommendation, immobilize the hand or finger using a splint, cast, or brace to facilitate proper healing.
- Pain Management: Prescribe pain medications and provide instructions for pain management to ensure patient comfort during the initial recovery period.
- Physical Therapy: Recommend or provide guidance for physical therapy to assist the patient in regaining hand and finger mobility and strength. This may include gentle range-of-motion and strengthening exercises.
- Rehabilitation: Provide ongoing support and rehabilitation recommendations to ensure the best possible functional outcome for the patient's hand or finger.







.png)