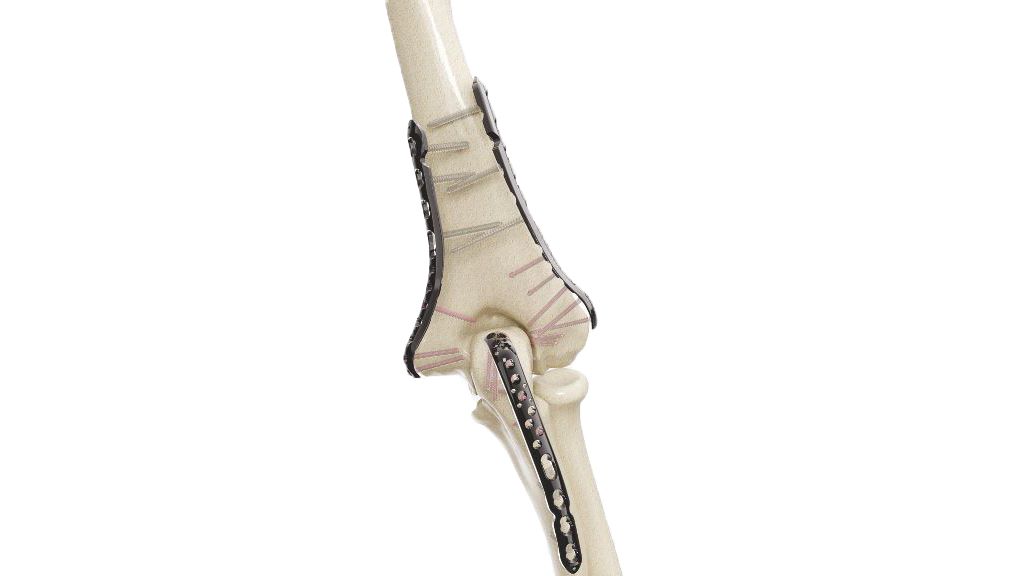
Pelvic Plate - 3.5 mm Symphyseal
Product Overview
Introducing the 3.5 mm Symphyseal Pelvic Plate , a state-of-the-art orthopedic implant designed for optimal stabilization and fixation of pelvic fractures. Engineered with precision, this implant offers exceptional strength and durability, ensuring reliable support during the healing process. Its innovative design allows for easy surgical application and promotes quicker recovery times for patients. Ideal for use in various pelvic trauma cases, the 3.5 mm Symphyseal Pelvic Plate is the trusted choice for orthopedic surgeons seeking high-quality, effective solutions for pelvic injuries.
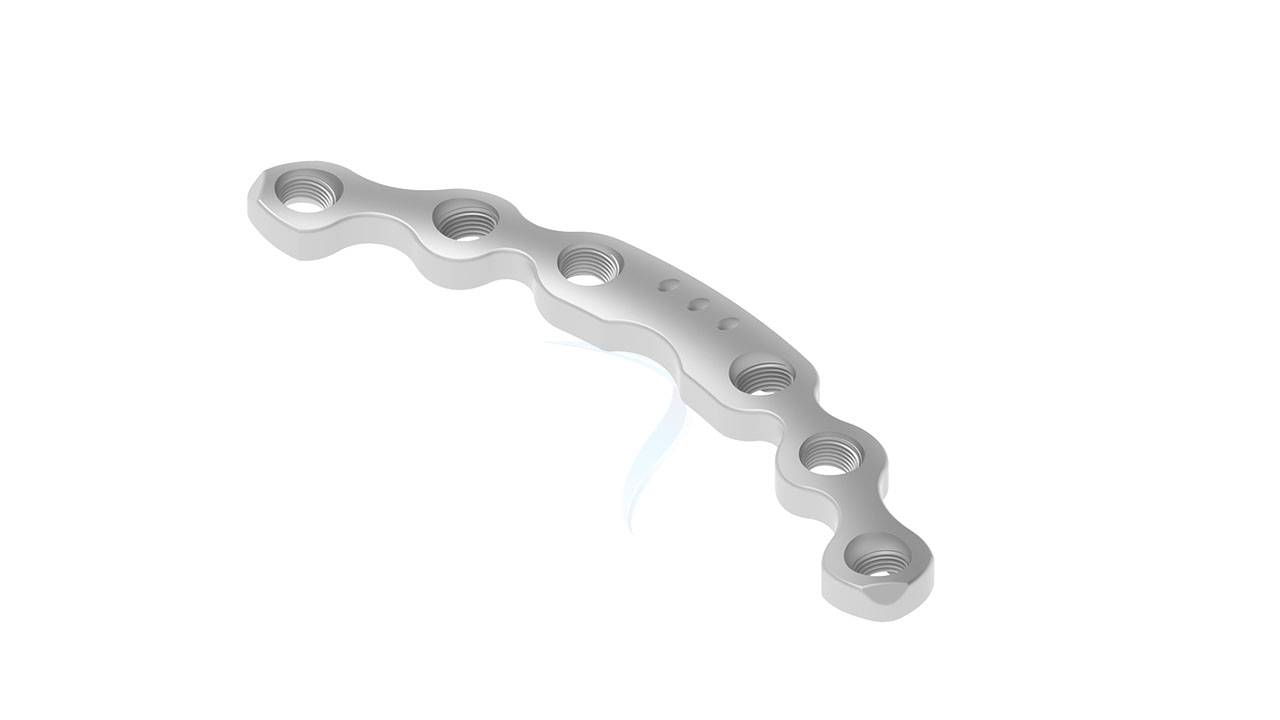
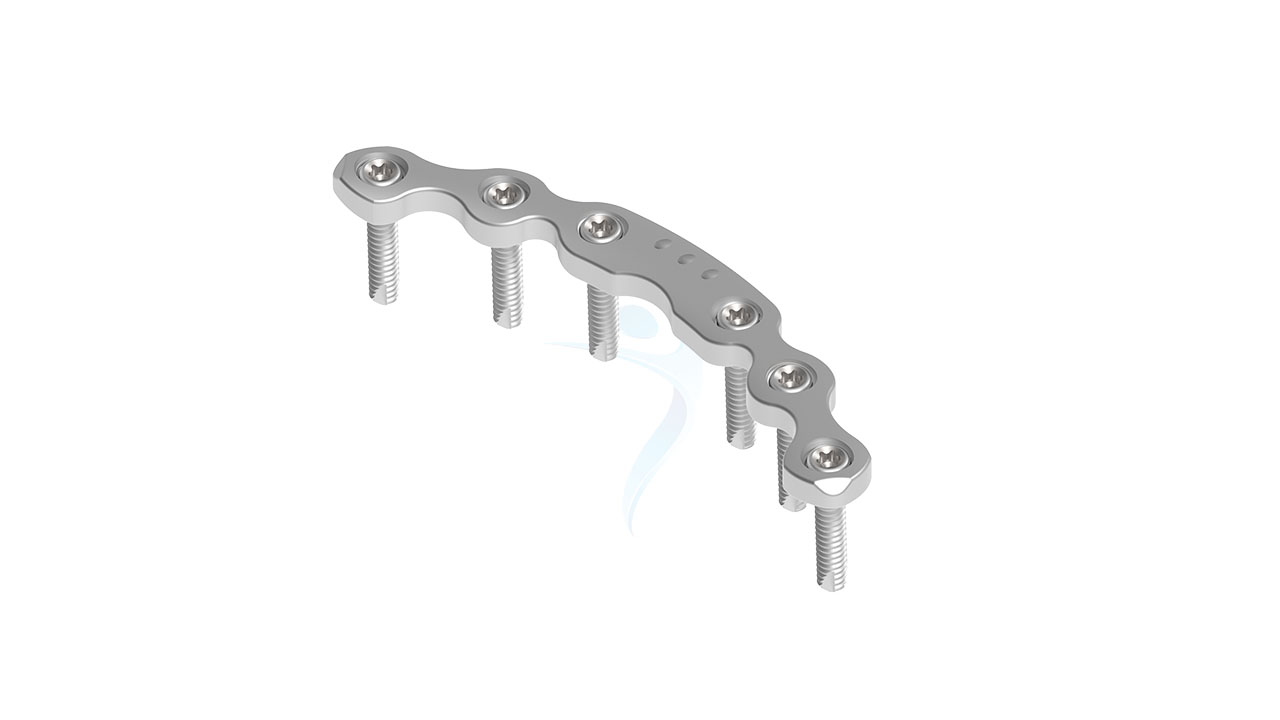
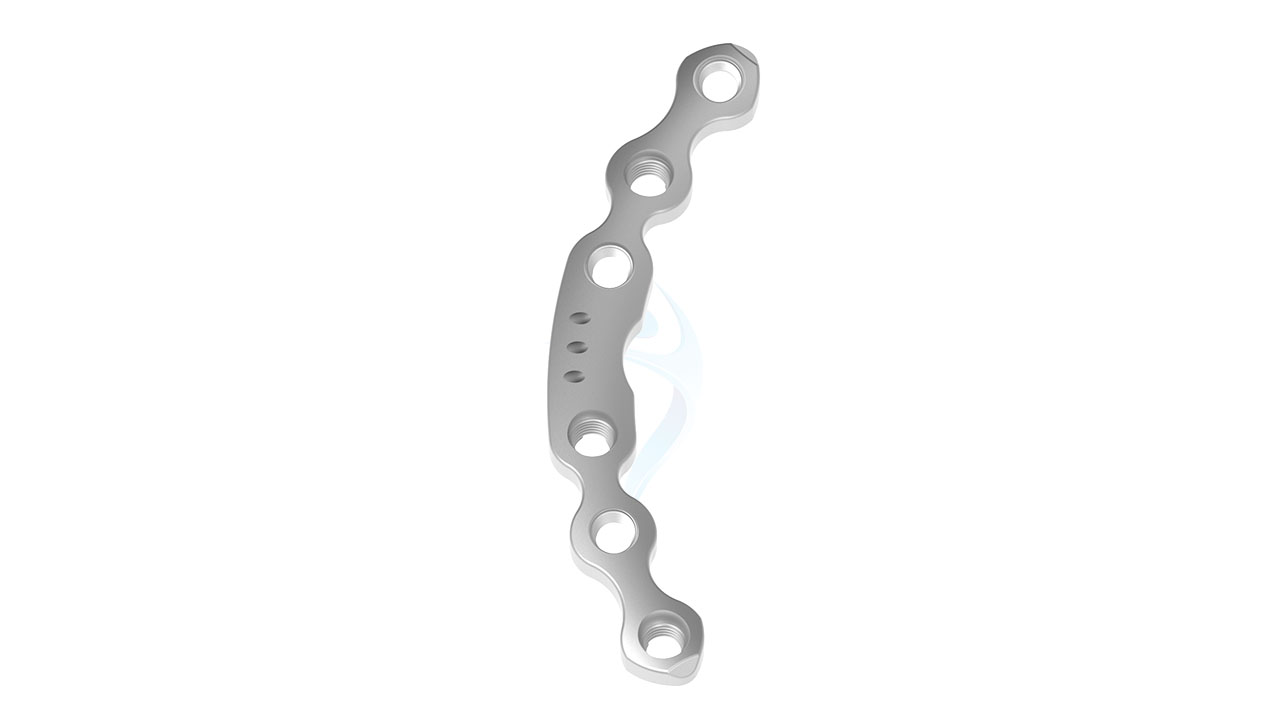
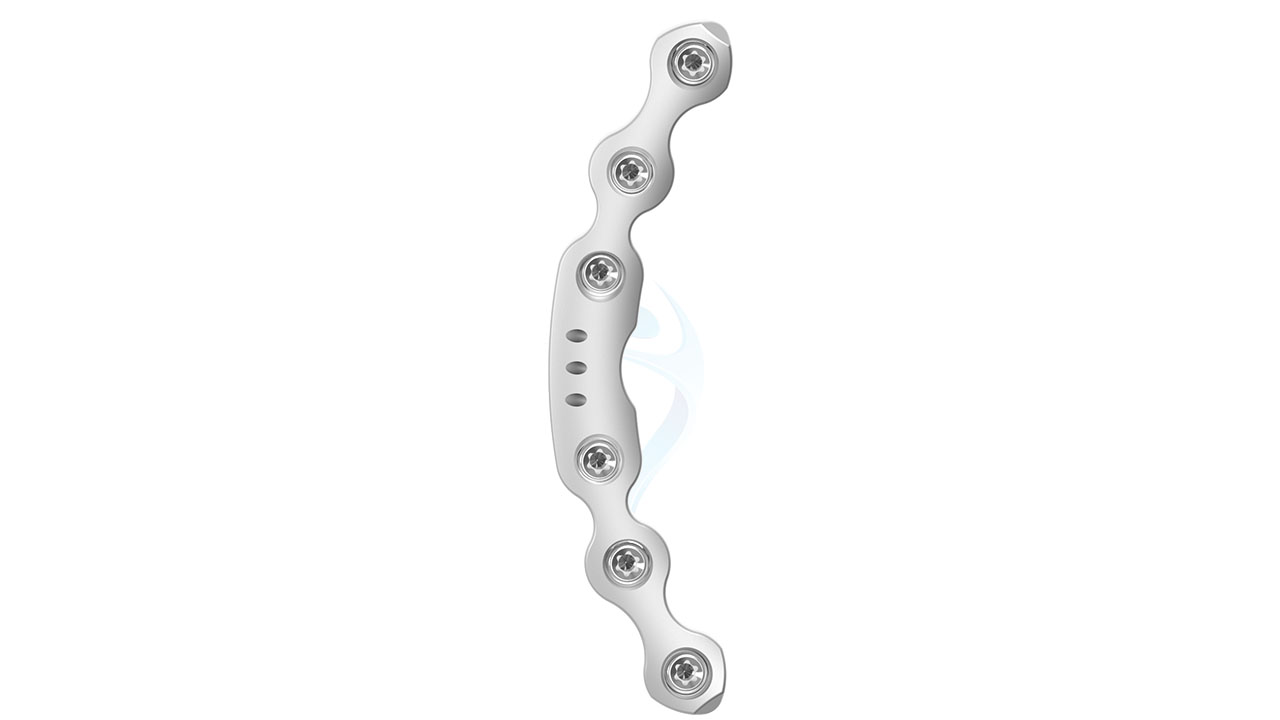
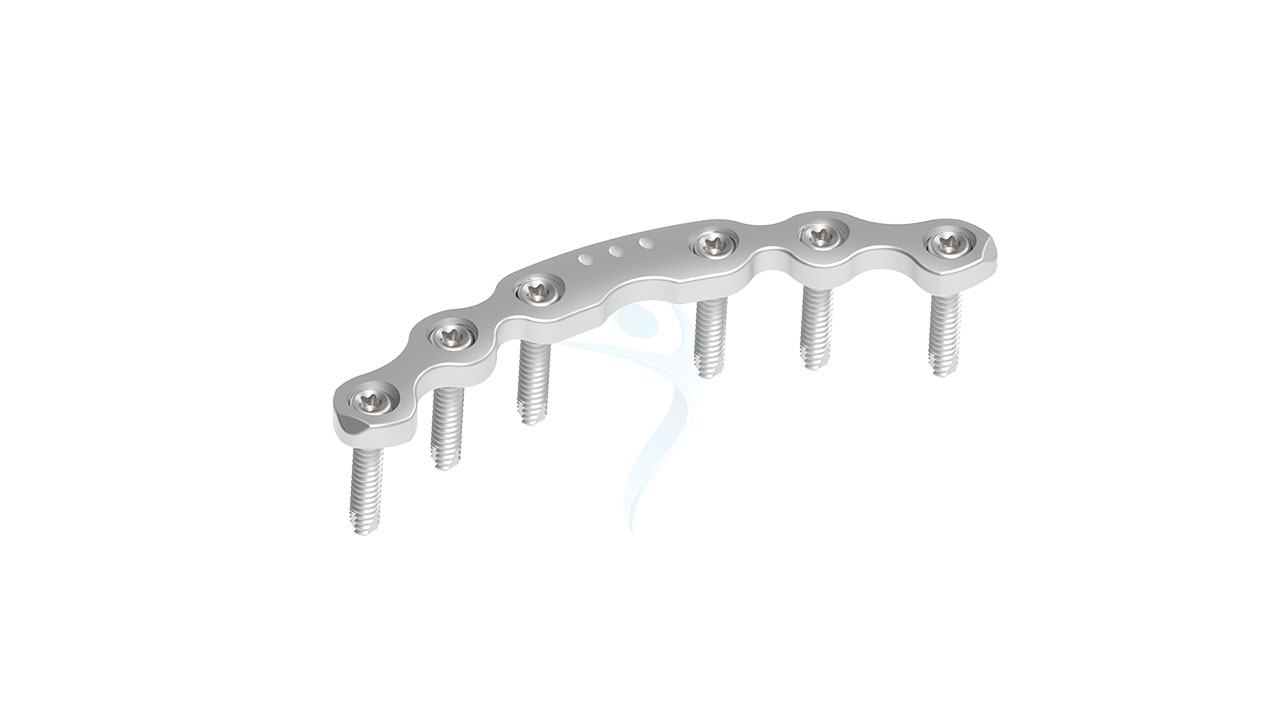
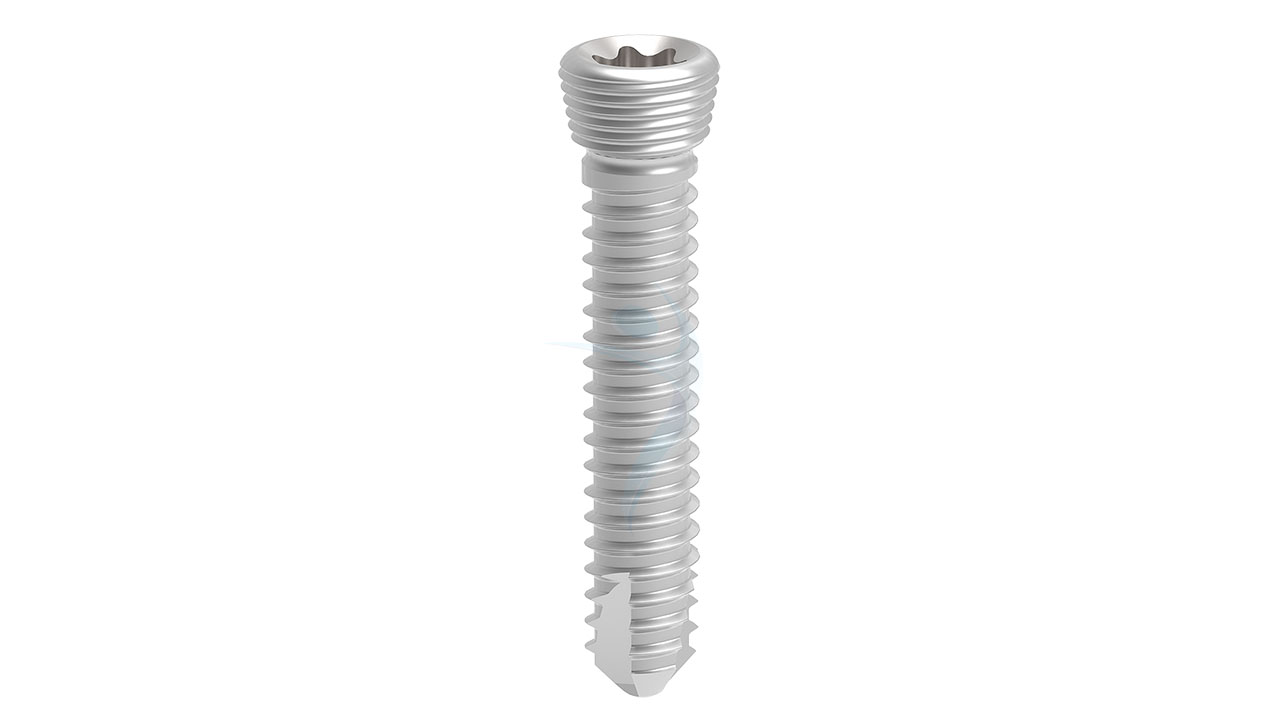





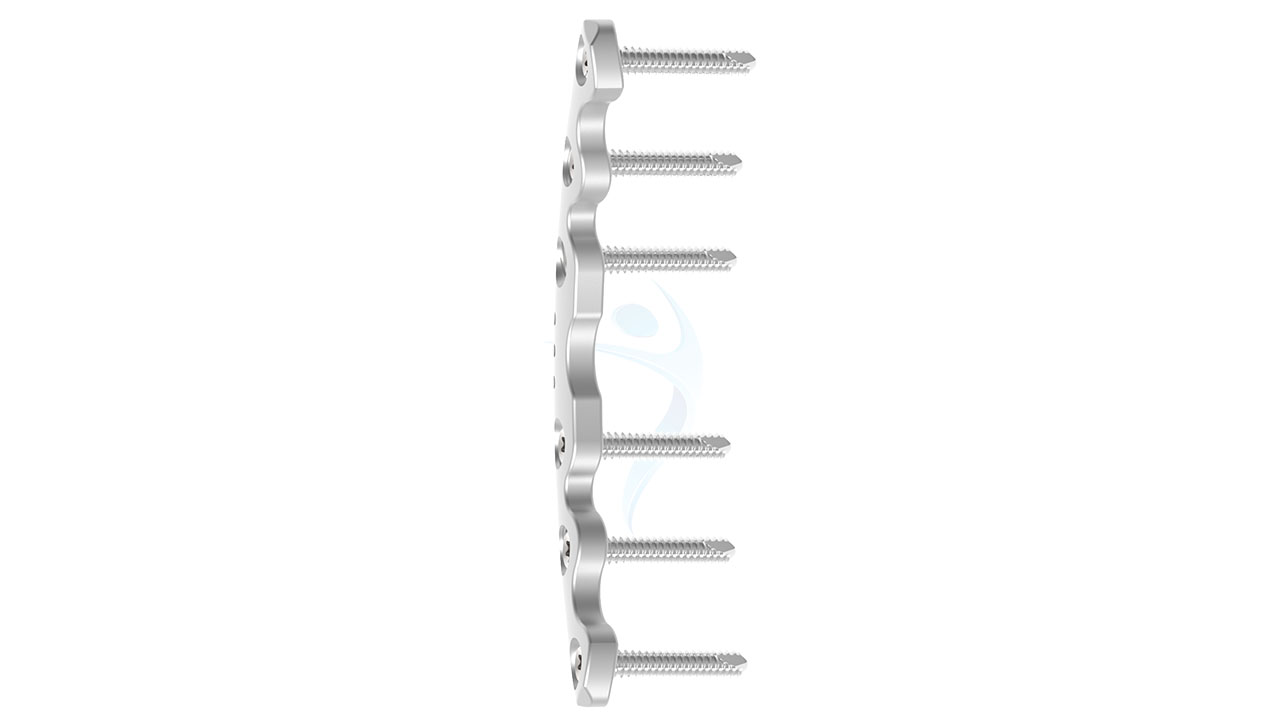

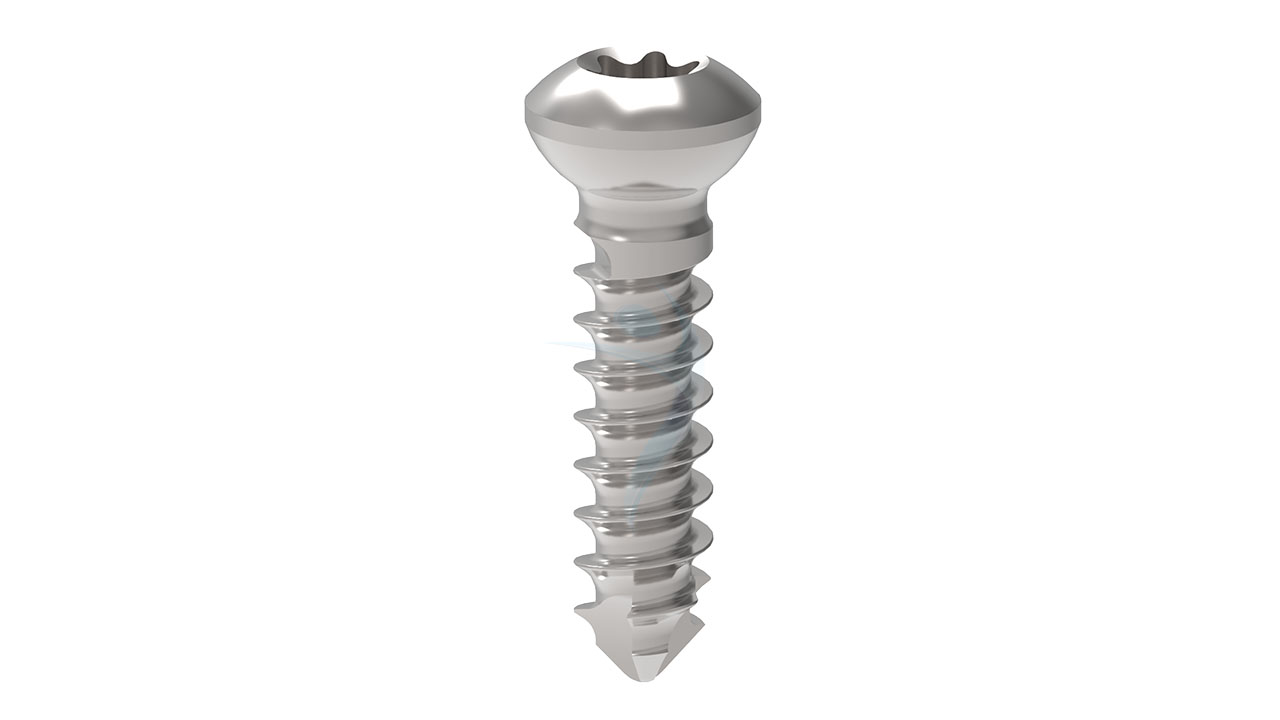
Product Uses
- Symphyseal Diastasis : It is commonly used in the surgical treatment of symphyseal diastasis, a condition where there is a separation or widening of the pubic symphysis, often caused by trauma or childbirth.
- Pelvic Ring Fractures : This plate is crucial in the stabilization of pelvic ring fractures. These fractures can result from high-energy trauma like car accidents or falls from significant heights.
- Acetabular Fractures : Although primarily designed for the pubic symphysis, it can also be part of a comprehensive fixation strategy for acetabular fractures involving the anterior column of the pelvis.
- Osteotomy Procedures : In cases where pelvic osteotomy is performed to correct deformities or address hip dysplasia, the 3.5 mm Symphyseal Pelvic Plate can provide necessary stabilization post-surgery.
- Non-Union or Mal-Union Corrections : It is useful in revision surgeries where there has been a non-union or mal-union of the pelvic bones, providing the required stability for proper healing.
Product Specification
- Material : Medical-grade stainless steel or titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V).
- Thickness : 3.5 mm.
- Width : Varies depending on design, typically between 12-16 mm.
- Length : Available in multiple lengths to accommodate various patient anatomies, ranging from 60 mm to 120 mm.
- Curvature : Anatomically contoured to fit the natural curvature of the pelvic anatomy.
- Surface Treatment : Anodized or coated to enhance biocompatibility and reduce the risk of corrosion.
- Sterilization : Supplied sterile, typically using gamma radiation or ethylene oxide (ETO) sterilization methods.
Pelvic Plate - 3.5 mm Symphyseal Sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Pelvic Plate - 3.5 mm Symphyseal
- Patient Evaluation : Assess the patient's medical history, including any previous pelvic injuries, surgeries, or medical conditions. Conduct a physical examination to evaluate pelvic stability, range of motion, and soft tissue condition.
- Surgical Planning : Review the imaging studies to develop a surgical plan, including the selection of the appropriate plate size and configuration. Ensure availability of necessary instruments, implants, and equipment for the procedure.
- Patient Preparation : Provide the patient with pre-operative instructions, including fasting guidelines and medication management. Obtain informed consent from the patient after discussing the risks, benefits, and alternatives of the surgery.
- Informed Consent : Obtain informed consent from the patient after discussing the risks, benefits, and alternatives of the surgery. Address any questions or concerns the patient may have about the procedure or the implant.
- Medical Clearance : Coordinate with other healthcare providers, such as primary care physicians or specialists, to ensure the patient is medically optimized for surgery.
- Anesthesia : Administer anesthesia based on the patient's condition and surgical requirements. Options include general anesthesia or regional anesthesia techniques such as spinal or epidural anesthesia.
- Patient Positioning : Position the patient supine on the operating table with appropriate padding to support the back and limbs. Ensure proper exposure of the pelvic area while maintaining stability and alignment.
- Surgical Approach : Make an appropriate incision based on the location and nature of the pelvic injury, typically using a midline or bikini incision for access to the symphysis pubis.
- Plate Placement : Select the optimal size and configuration of the 3.5 mm Symphyseal Pelvic Plate based on pre-operative planning and intraoperative assessment.
- Screw Fixation : Drill pilot holes through the plate and into the pelvic bones using appropriate drill guides and depth stops. Insert cortical screws through the plate holes and into the bone, achieving stable fixation while avoiding penetration of neurovascular structures.
- Immediate Post-operative Care : Transfer the patient to the recovery area for monitoring of vital signs and neurovascular status. Provide appropriate pain management and post-operative instructions to the patient and caregivers.
- Early Mobilization : Encourage early mobilization and ambulation as tolerated, with the assistance of physical therapy as needed. Use supportive devices such as crutches or a walker to facilitate mobility while protecting the surgical site.
- Monitoring and Follow-up :Monitor the patient for signs of infection, wound healing, and implant stability during follow-up appointments. Schedule regular imaging studies to assess the progression of bone healing and the integrity of the implant fixation.
- Rehabilitation : Implement a comprehensive rehabilitation program tailored to the patient's specific needs and functional goals. Focus on strengthening exercises, range of motion activities, and gait training to promote full recovery and return to pre-injury activities.
- Long-term Management : Educate the patient about long-term considerations such as activity modification, potential hardware removal, and the importance of maintaining pelvic stability to prevent future injuries.
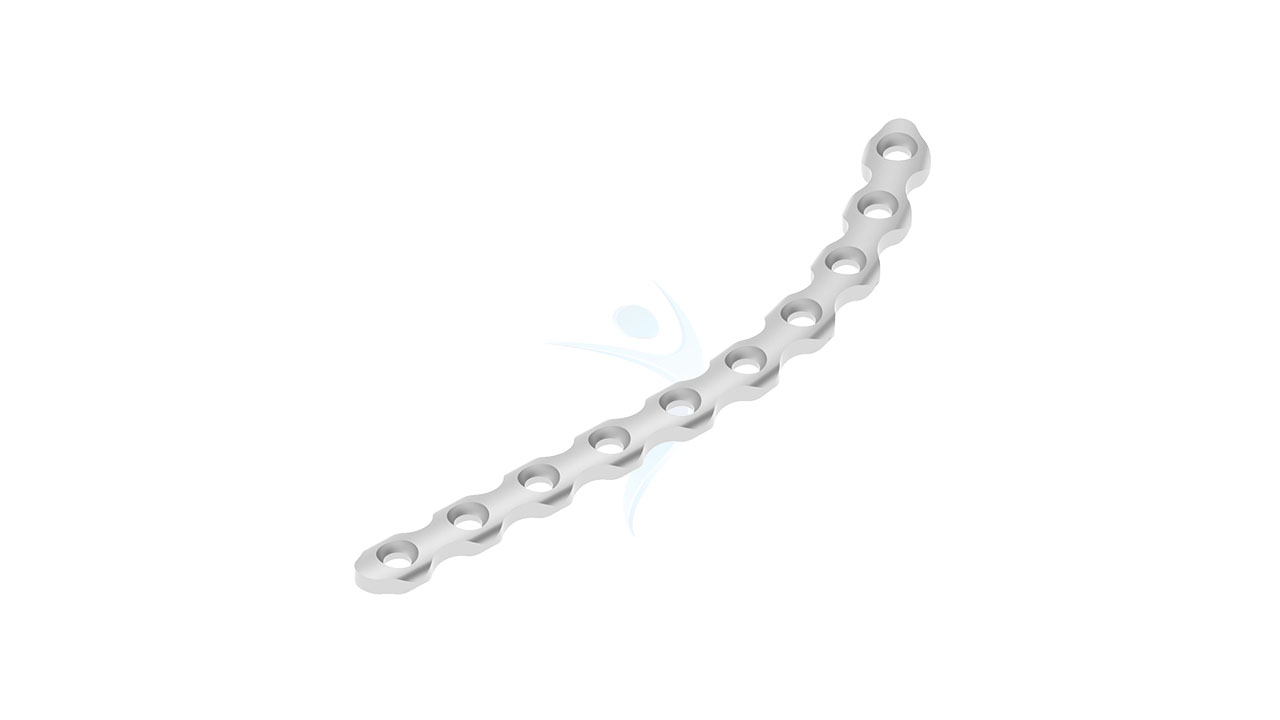







.png)