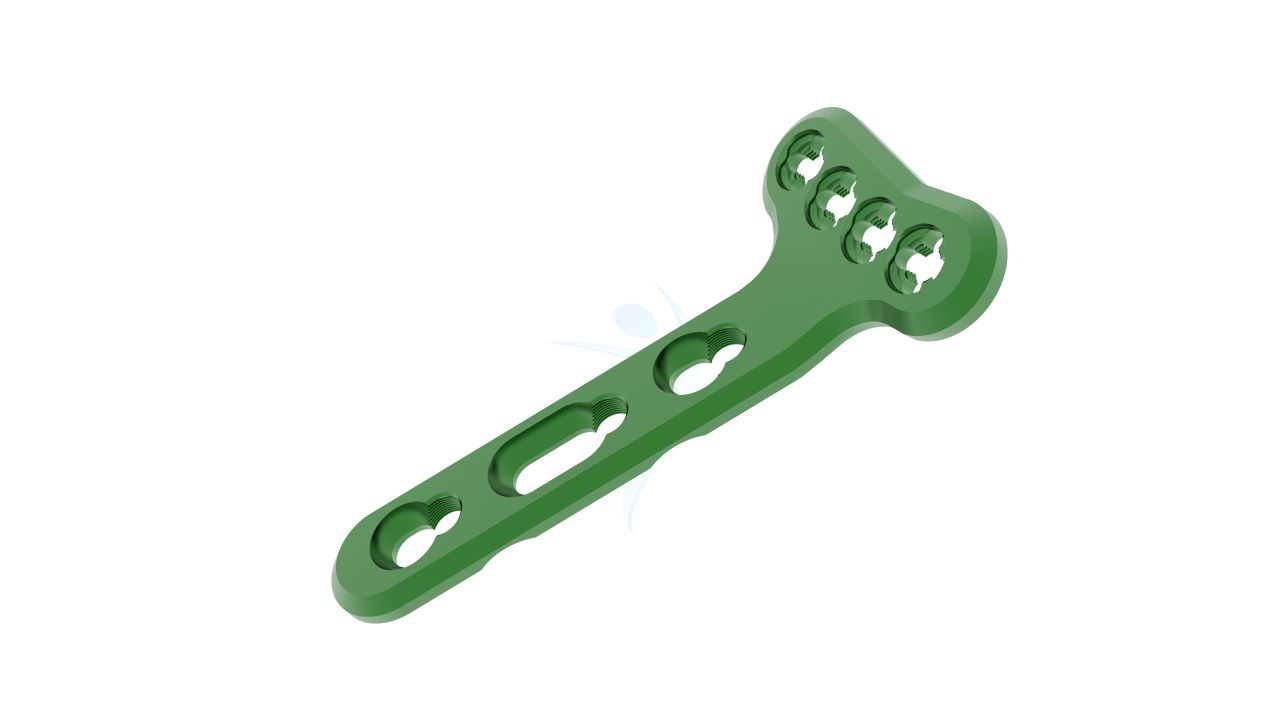
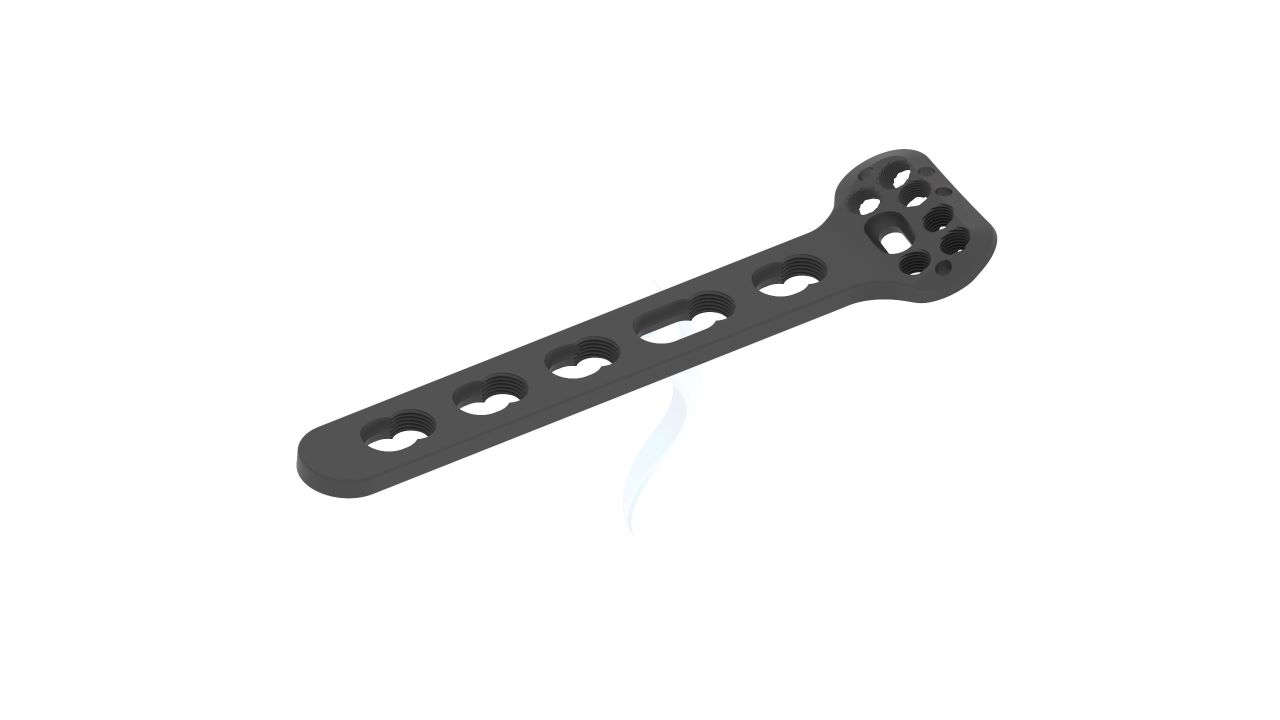
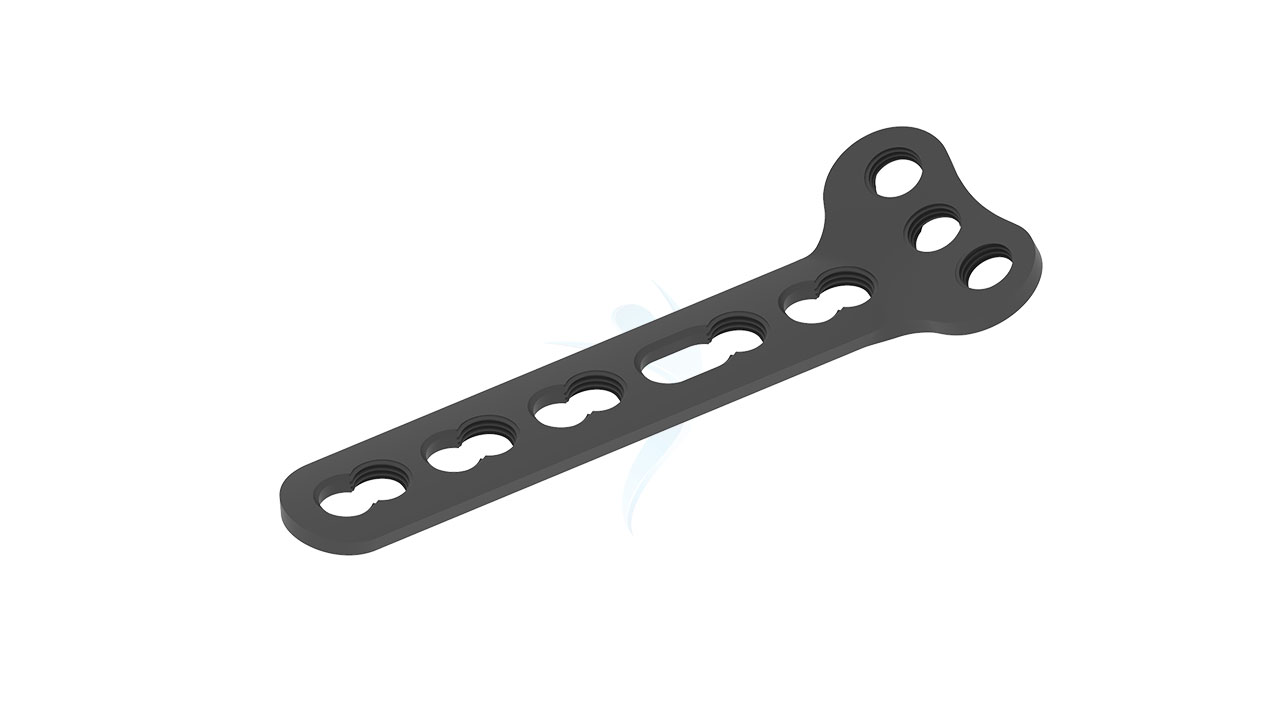
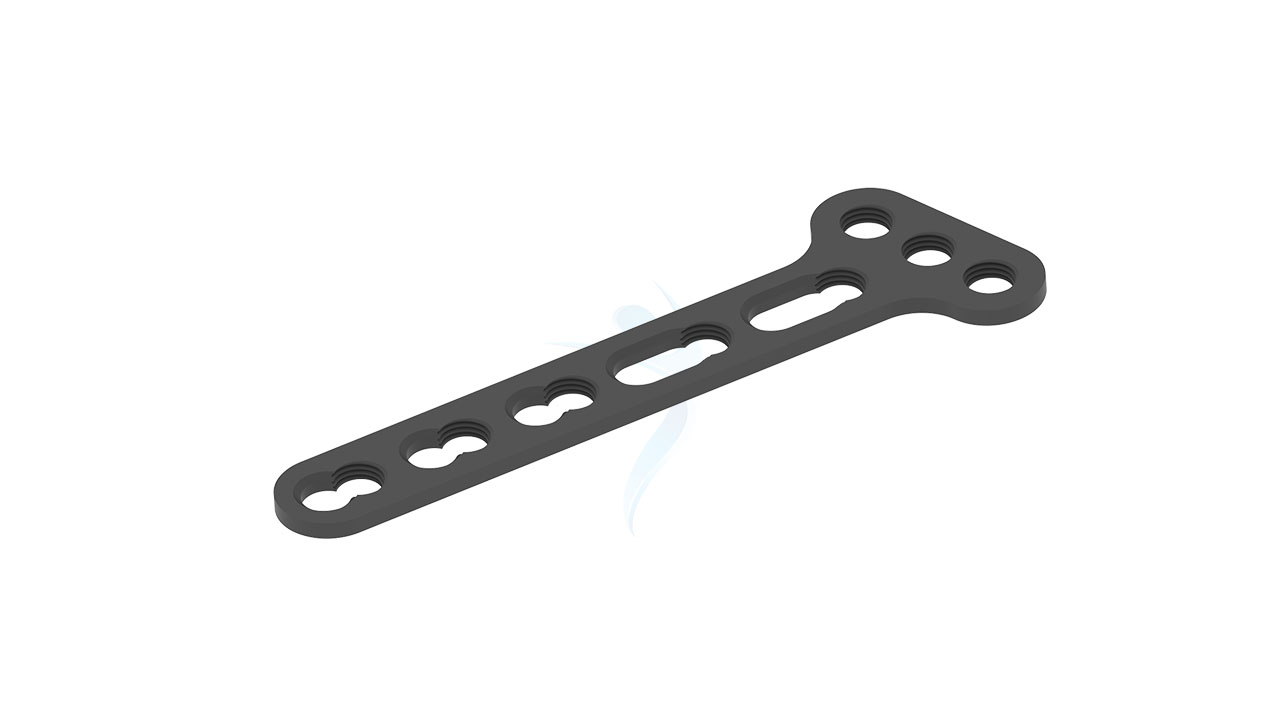
Radial Head Plates - Neck 2.4 mm
Product Overview
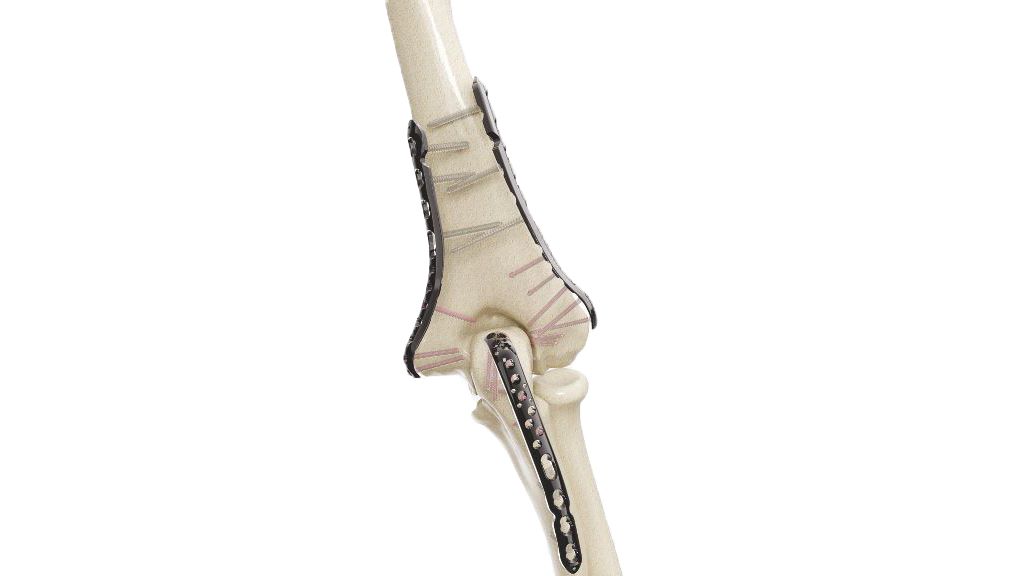
Introducing our cutting-edge solution, the Radial Head Plates (Neck) 2.4mm. These specialized orthopedic implants are meticulously crafted to address fractures in the proximal radius head and neck region. Engineered for reliable and stable fixation, these plates play a pivotal role in restoring bone integrity and promoting optimal healing. Our commitment to quality ensures that these plates are designed with precision, enabling orthopedic surgeons to deliver effective fracture management. Trust in our Proximal Radius Plates for superior solutions in orthopedic care.
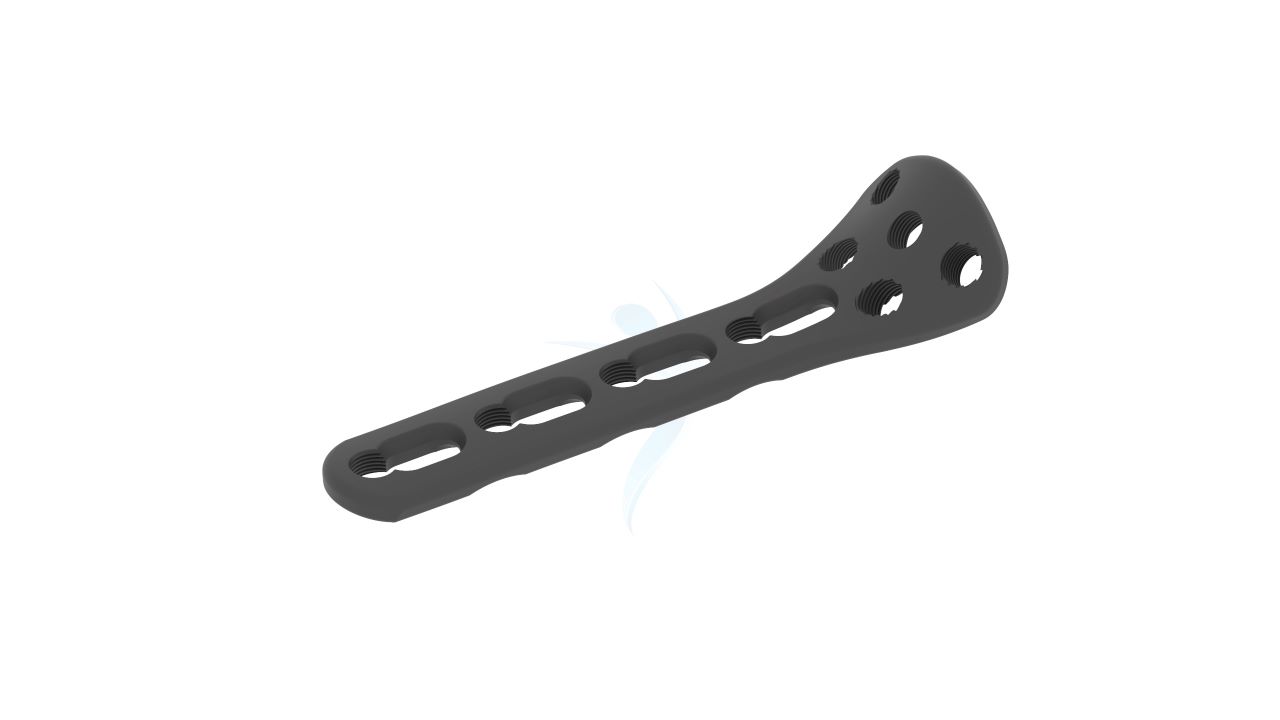
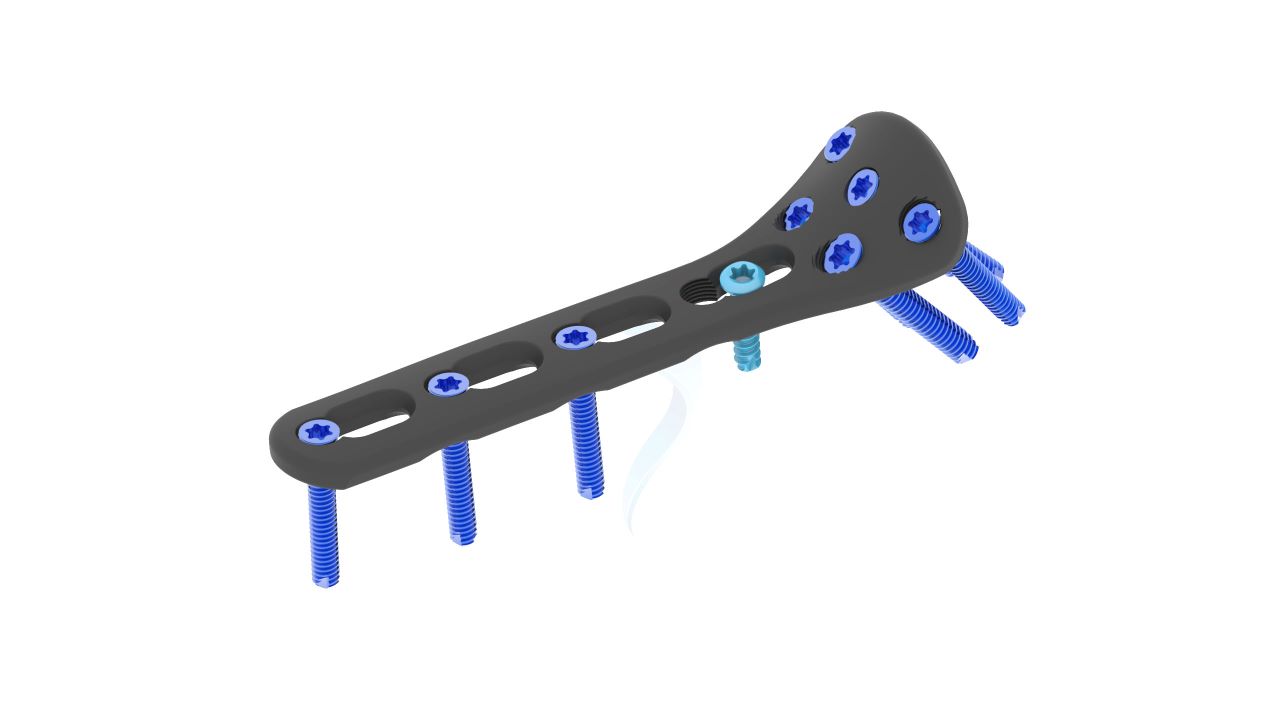
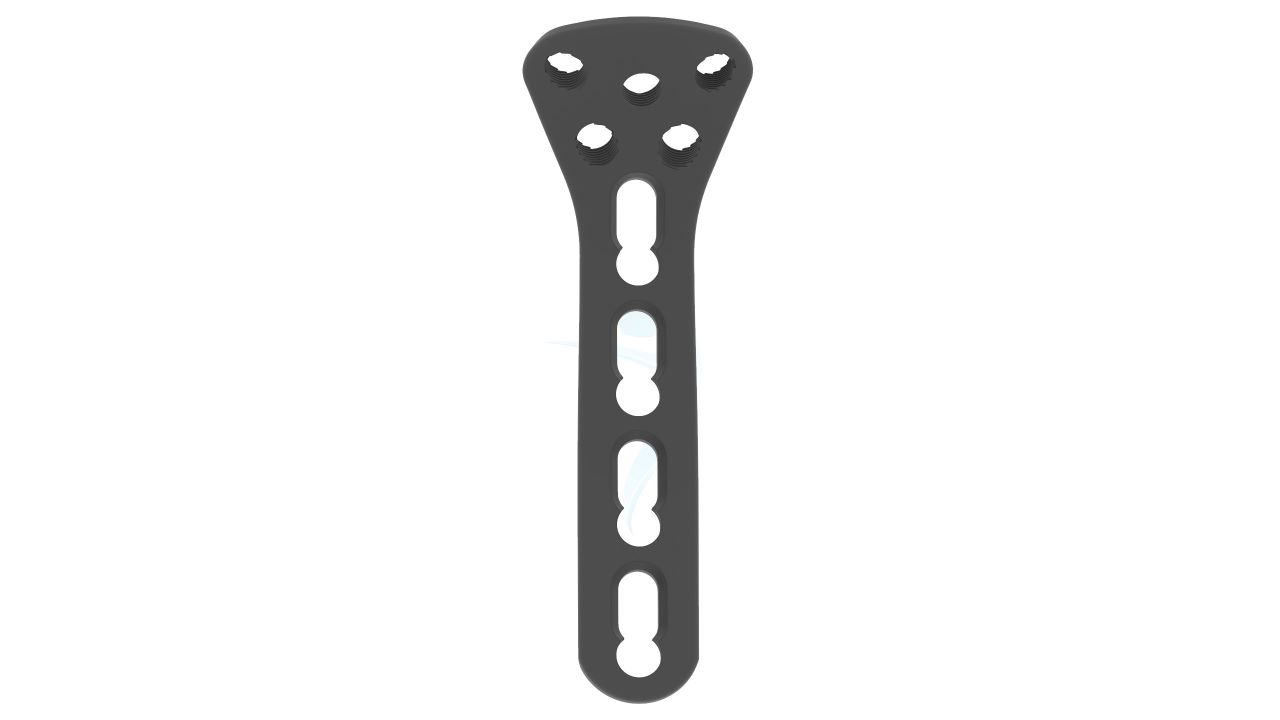
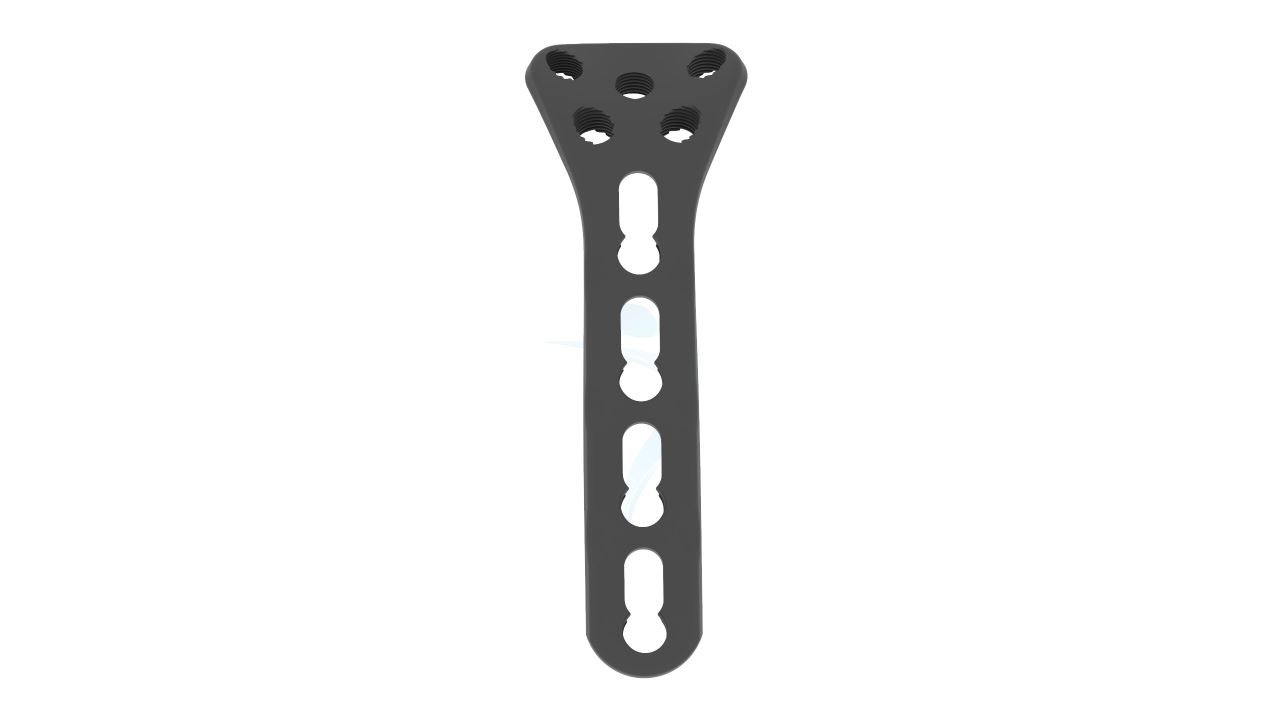
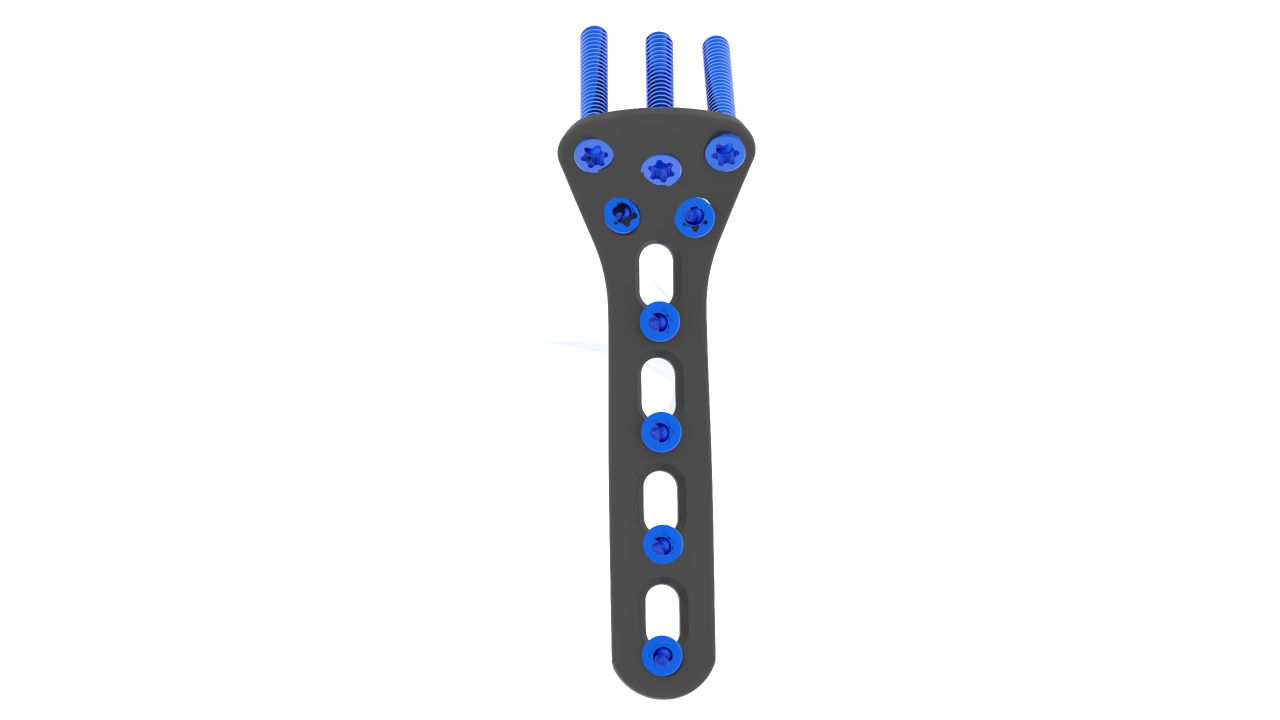
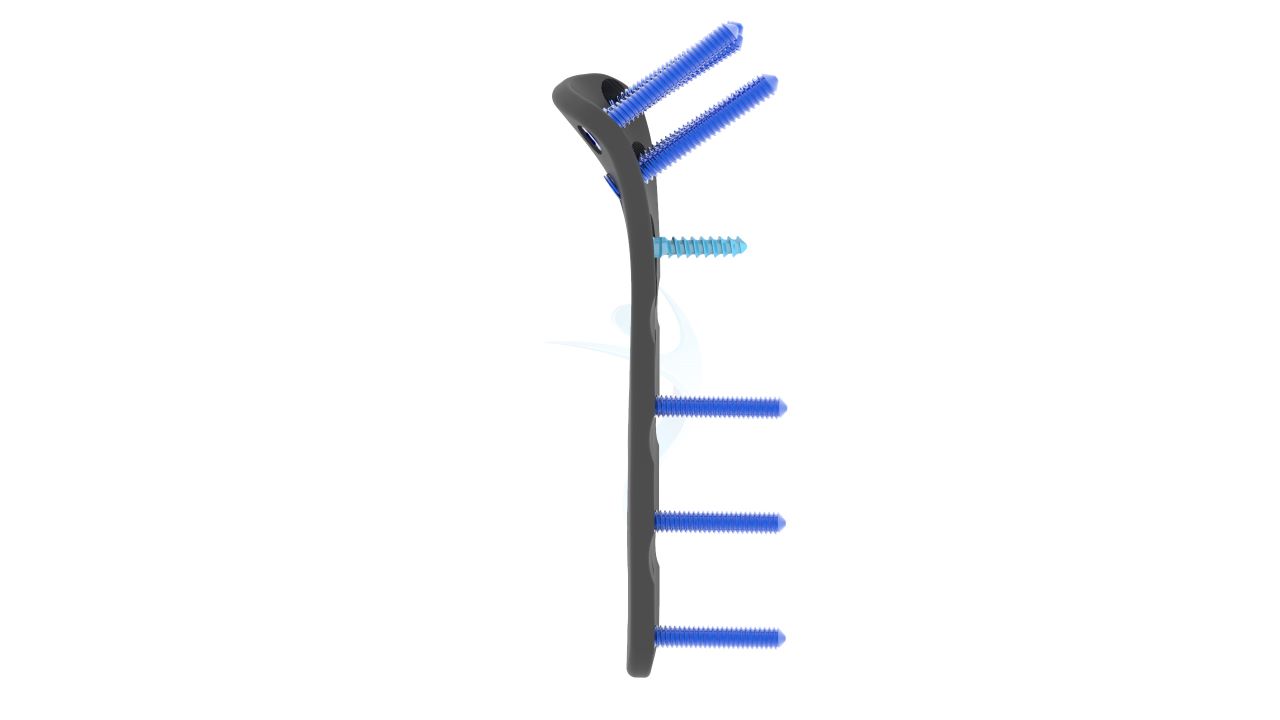









Product Uses
- Fracture Fixation : The 2.4mm Proximal Radius Head Plates provide essential support in stabilizing fractures within the head and neck region of the proximal radius bone.
- Osteotomy Procedures : These plates aid orthopedic surgeons in performing osteotomy procedures, ensuring accurate alignment and fixation during bone repositioning.
- Trauma Cases : Ideal for managing traumatic injuries to the proximal radius head and neck, these plates facilitate proper bone healing and restoration.
- Non-Union Fractures : In cases of non-union fractures, the plates promote successful bone fusion by maintaining stability and alignment for optimal healing.
- Revision Surgeries :These plates can be utilized in revision surgeries to correct previous fixation failures or complications, ensuring improved outcomes.
Product Specification
- Plate Thickness : 2.4 mm
- Material : Medical-grade titanium alloy
- Plate Length : Range of sizes available (specify options).
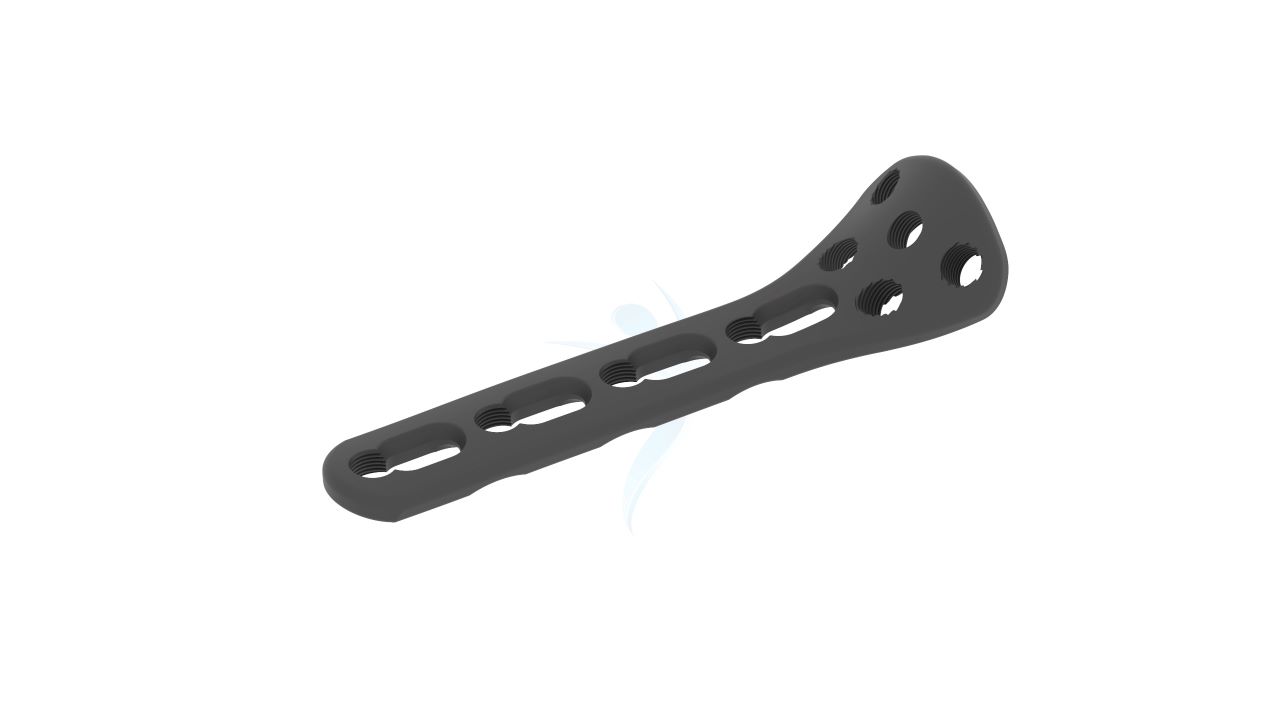
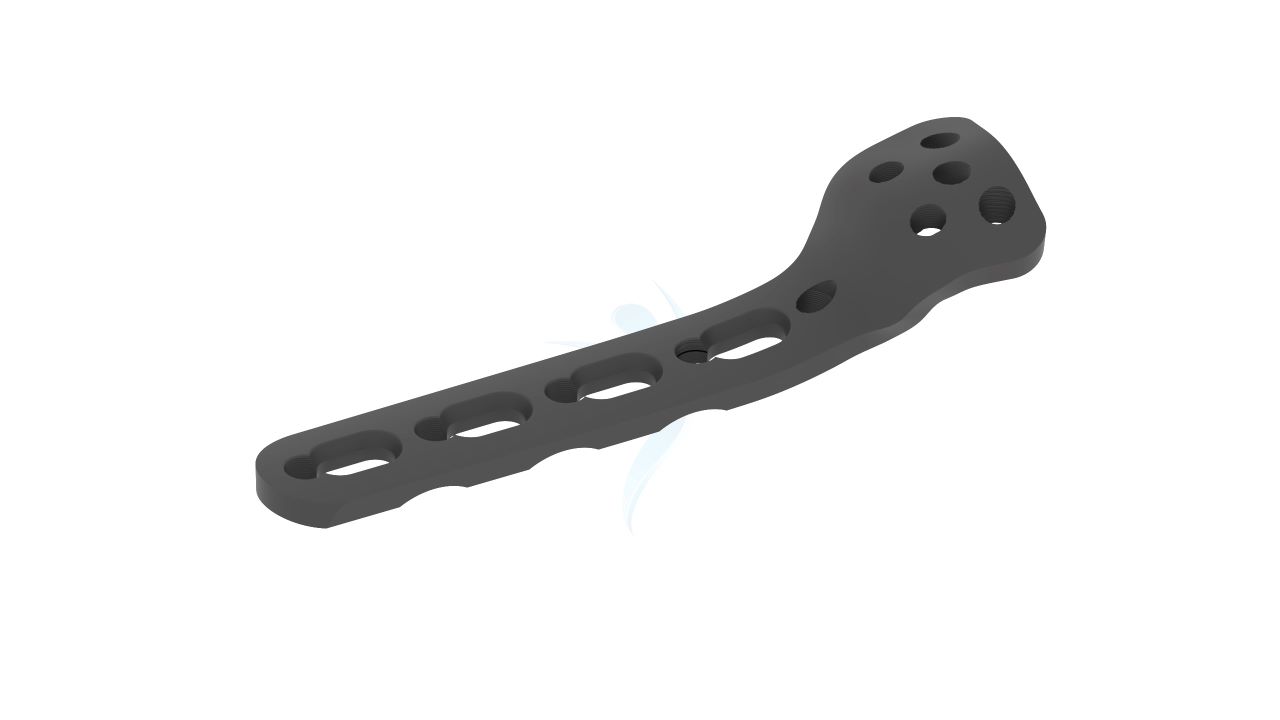
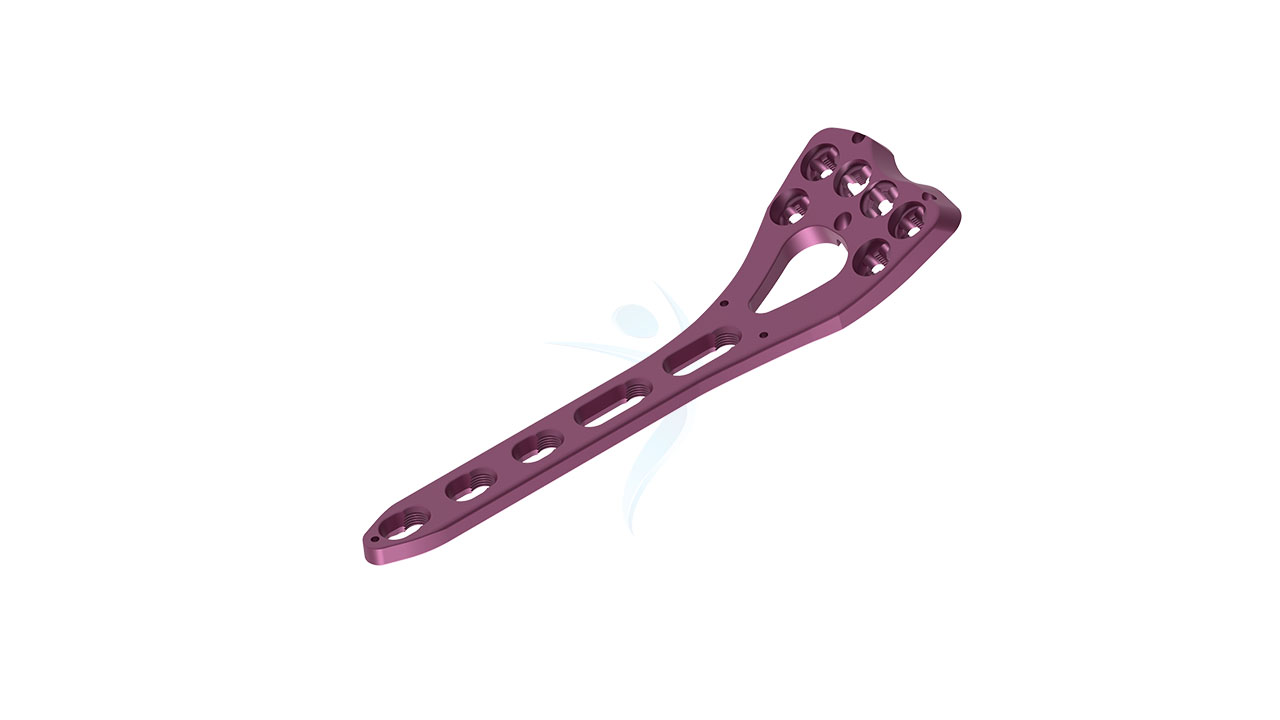
- Plate Design : Contoured and anatomically shaped for proximal radius head and neck.
- Screw Holes : Multiple screw holes for versatile fixation.
- Screw Compatibility : Designed for use with 2.4 mm locking and non-locking screws.
- Locking Mechanism : Locking screws for enhanced stability and angular stability.
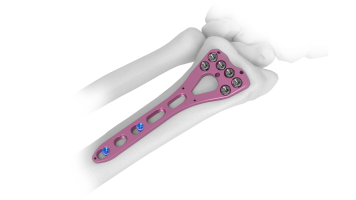
Radial Head Plates -(Neck) 2.4mm Sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Radial Head Plates - (Neck) 2.4mm
- Patient Assessment : Review medical history, allergies, medications, and overall health status.Perform imaging (X-rays, CT scans) to assess fracture pattern and severity.
- Surgical Planning : Consult with the orthopedic surgeon to determine surgical approach, plate size, and screw placement.
- Informed Consent : Explain the procedure, potential risks, benefits, and alternatives to the patient. Obtain signed consent.
- Preoperative Tests : Conduct necessary blood tests, ECG, and other relevant tests to ensure the patient's fitness for surgery.
- Skin Preparation : Instruct the patient to shower with an antibacterial soap the night before or the morning of surgery.
- Anesthesia : Administer anesthesia as discussed with the anesthesia team.
- Incision and Exposure : Make an incision to access the fractured proximal radius head and neck area.
- Fracture Reduction : Carefully align and reduce the fracture to restore proper bone alignment.
- Plate Placement : Select and position the appropriate Proximal Radius Plate. Secure it to the bone using screws.
- Screw Fixation : Insert locking and non-locking screws through the plate to stabilize the fracture.
- Closure : Close the incision using sutures or staples and apply sterile dressings.
- Recovery Room : Monitor the patient's vital signs and awakening from anesthesia.
- Pain Management : Administer pain relief medication as necessary and monitor pain levels.
- Immobilization : Apply a cast, splint, or sling, as prescribed by the surgeon, to protect the treated area.
- Follow-Up Care : Schedule follow-up appointments for wound checks and X-rays to monitor healing progress.
- Physical Therapy : Begin a customized rehabilitation program to regain strength, mobility, and function.
- Medication and Instructions : Prescribe antibiotics, pain medication, and provide detailed post-operative care instructions.












.png)