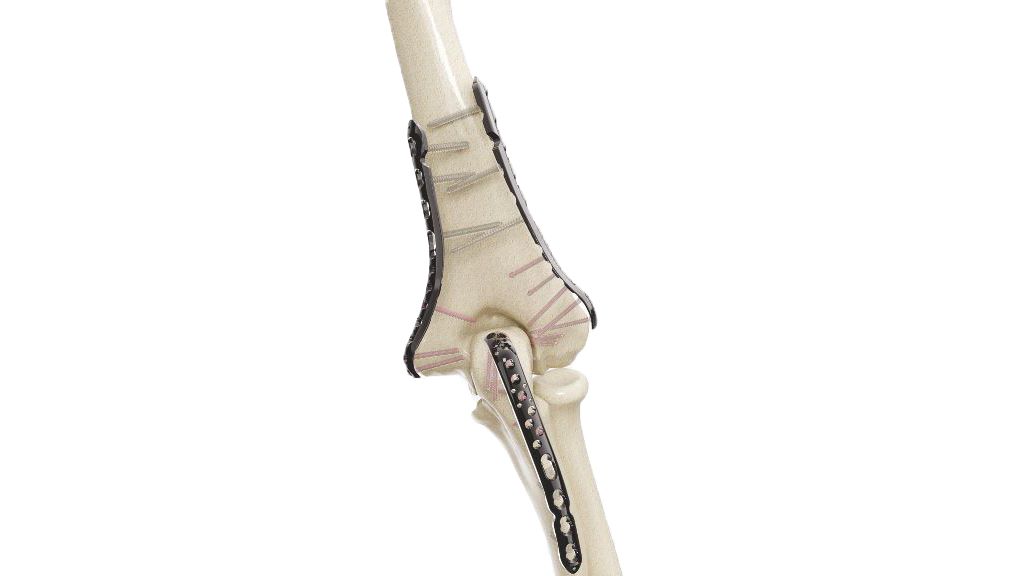
Distal Humerus Plate (ASLP) - Posterolateral Without Support
Product Overview
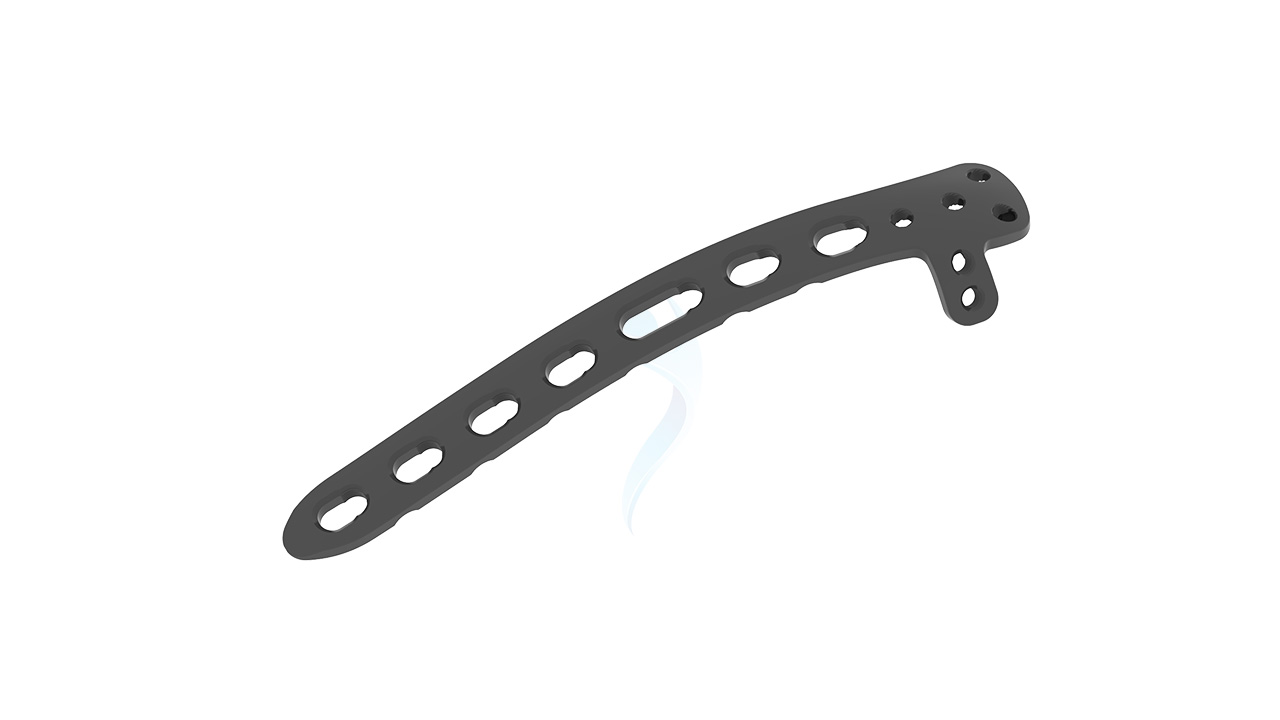
The 2.7/3.5 Distal Humerus Posterolateral ASLP implant is designed for effective fracture fixation of the distal humerus. This orthopedic implant provides exceptional stability and support without the need for additional plates, making it an optimal choice for surgical procedures. Crafted with precision, it ensures reliable performance and aids in the efficient recovery of patients. Ideal for addressing complex fractures, the ASLP implant is a trusted solution in orthopedic care.
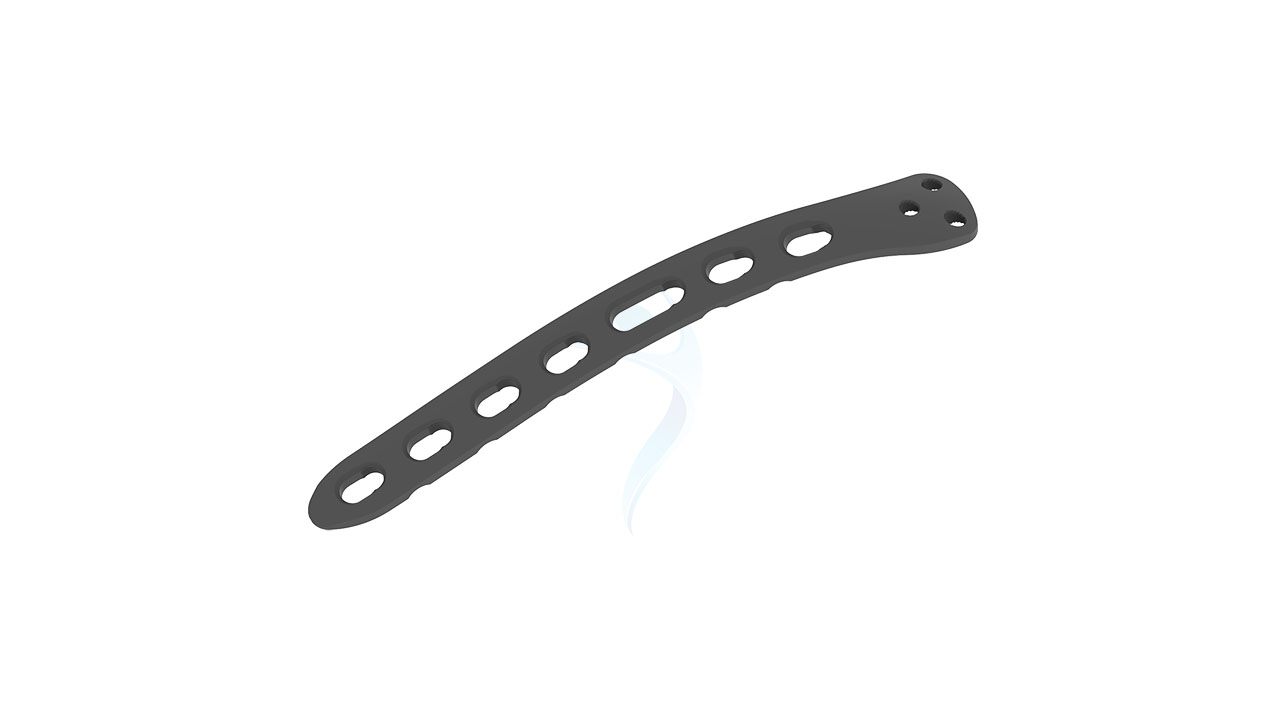
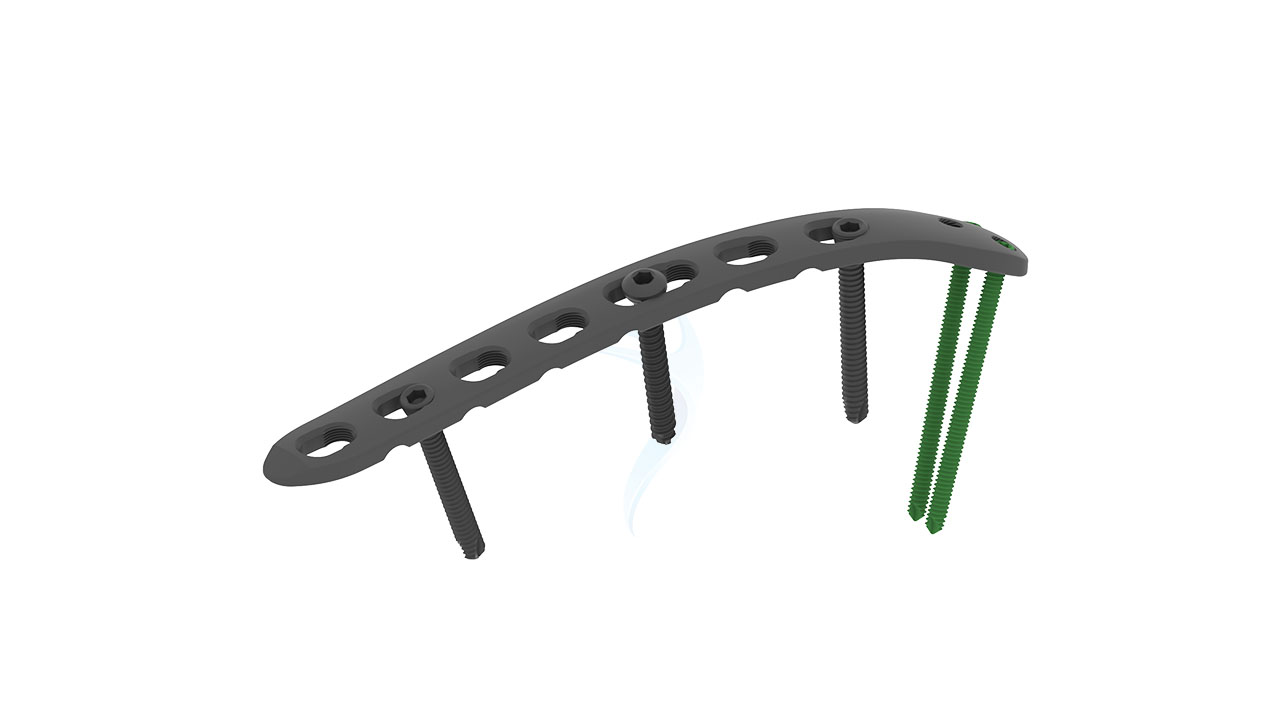
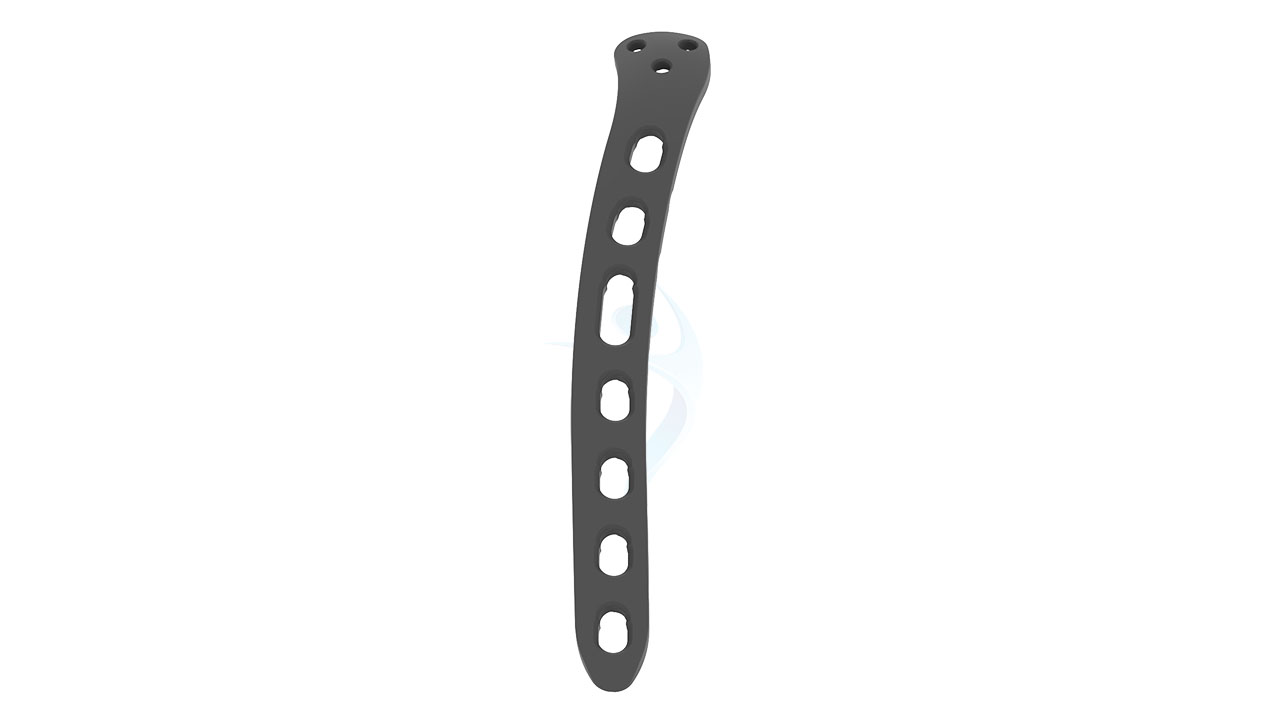
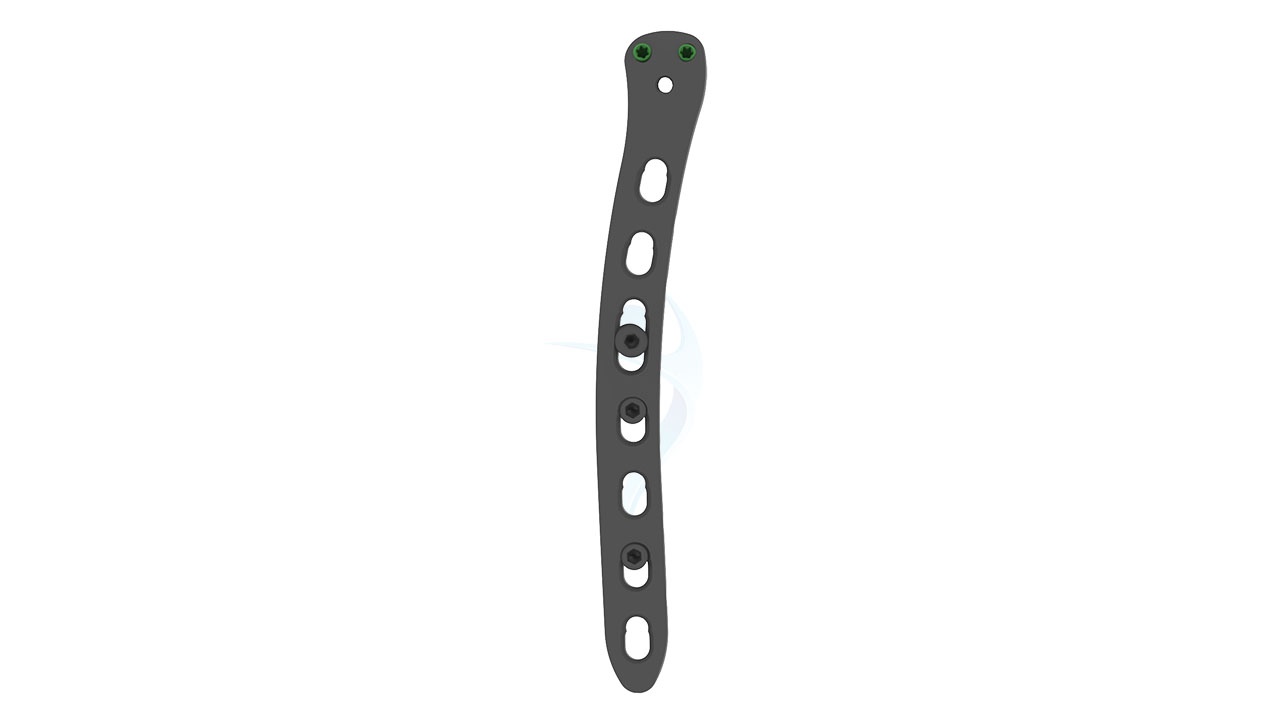
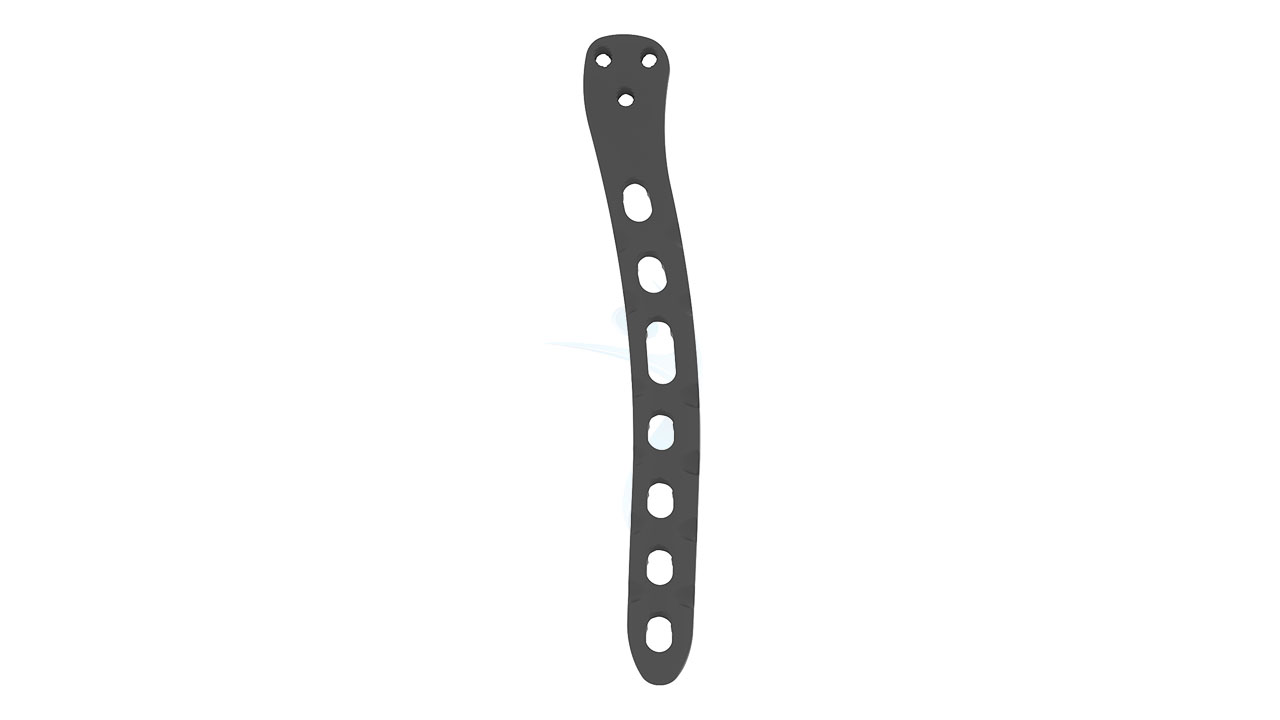
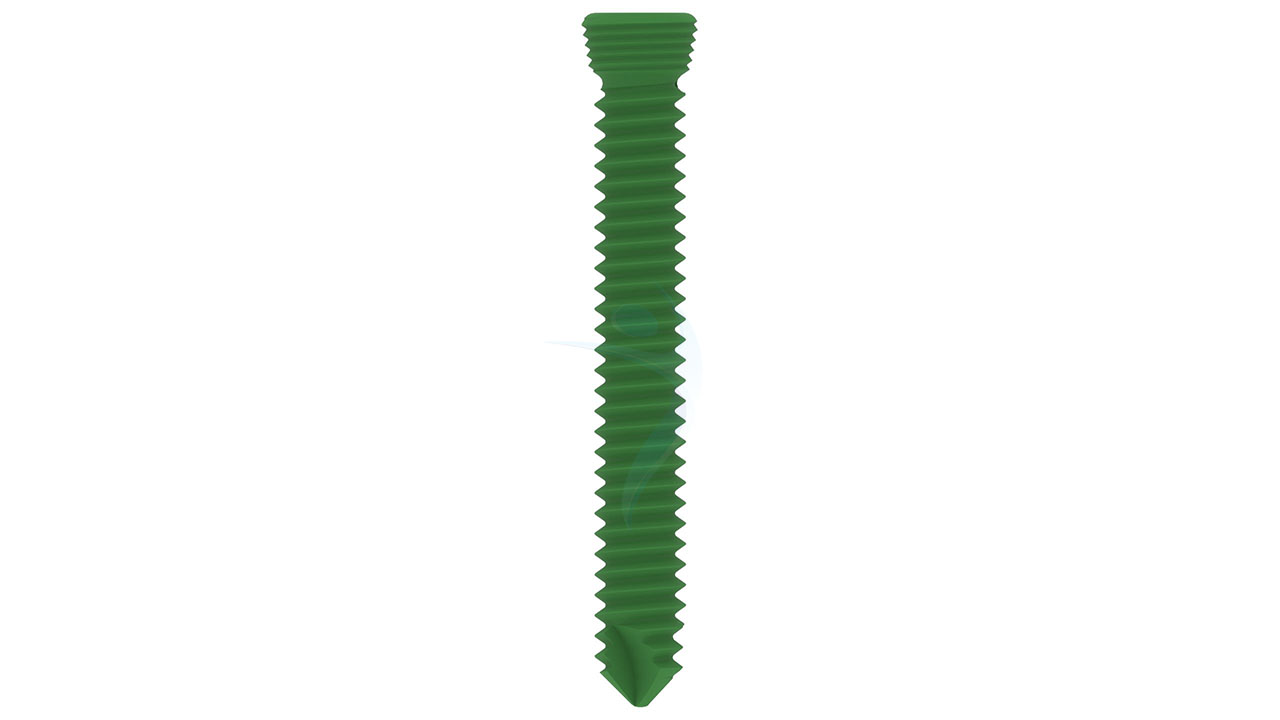
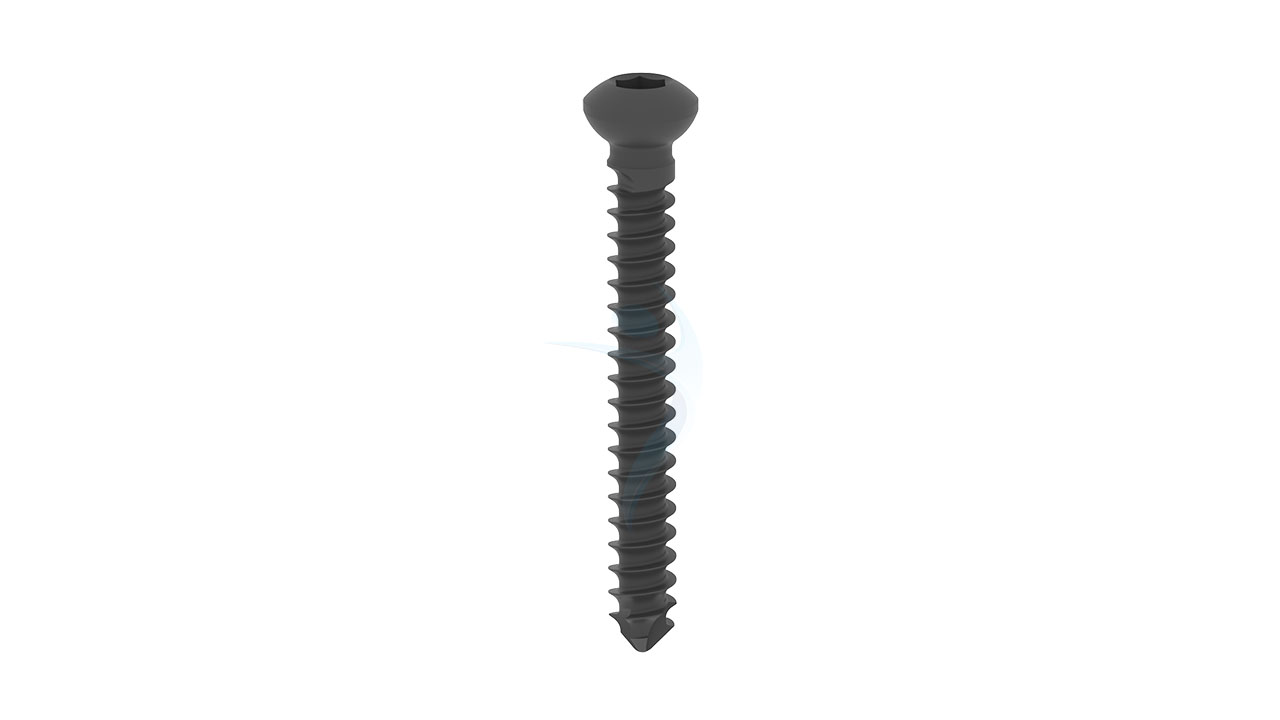





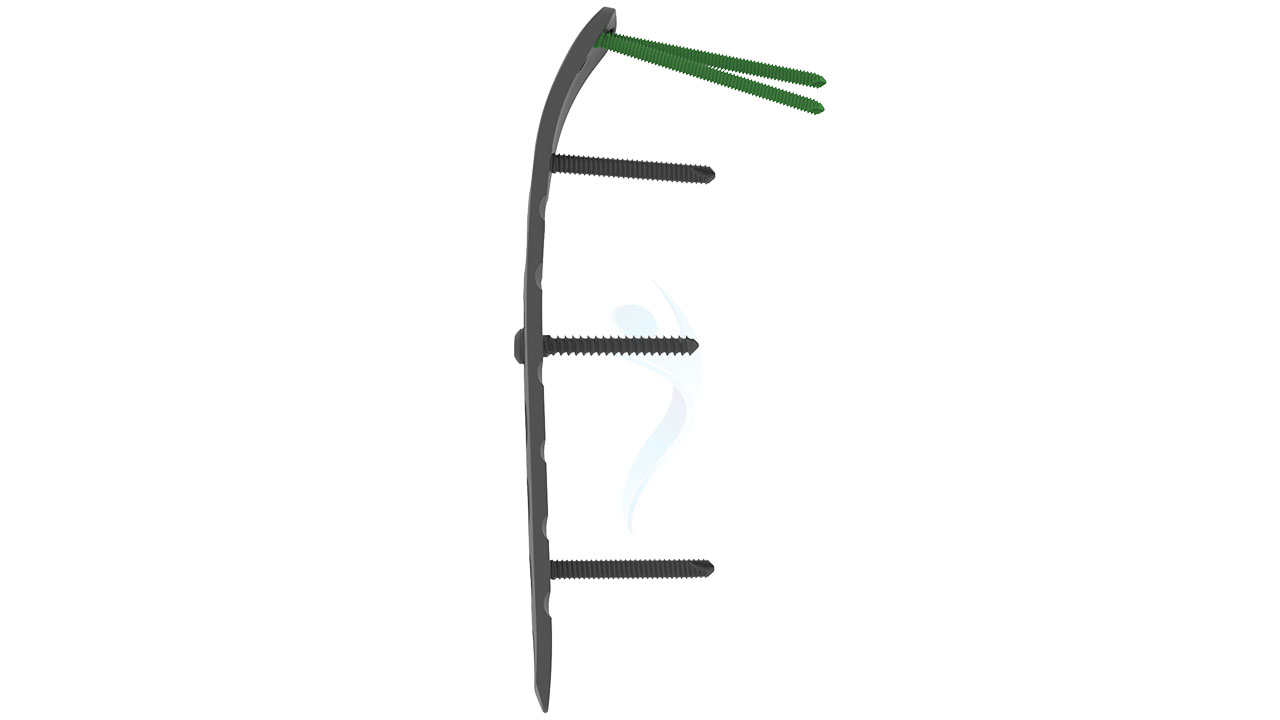



Product Uses
- Fractures : Effective management of distal humerus fractures, including intra-articular, comminuted fractures, and those with bone loss.
- Osteotomies : Correcting deformities or malunions through precise surgical bone cuts near the distal humerus.
- Non-unions : Treating non-healing fractures or failures from previous fixation attempts.
- Revision Surgeries : Revising failed or inadequate prior surgical procedures involving the distal humerus.
- Trauma : Addressing traumatic injuries to the distal humerus, such as fractures resulting from accidents or falls.
- Reconstruction : Restoring bone anatomy and alignment in cases of bone defects or deformities.
Product Specification
- Plate Thickness : 2.7 mm and 3.5 mm options available.
- Length Options : Multiple lengths to accommodate different fracture patterns and patient anatomies.
- Screw Compatibility : Accepts 2.7 mm and 3.5 mm cortical screws.
- Design : Anatomically contoured for the distal humerus with a posterolateral approach.
- Hole Configuration : Combination of locking and non-locking screw holes for versatile fixation.
- Surface Finish : Polished or anodized for reduced tissue irritation and enhanced biocompatibility.
- Sterilization : Provided sterile or non-sterile, suitable for autoclaving.
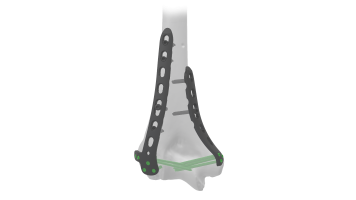
Distal Humerus Plate (ASLP) - Posterolateral Without Support Sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Distal Humerus Plate (ASLP) - Posterolateral Without Support
- Patient Assessment : Thoroughly evaluate the patient's medical history, including any prior surgeries, current medications, and underlying health conditions. Conduct a physical examination focusing on the affected arm and overall limb functionality.
- Imaging : Obtain high-quality radiographs of the distal humerus in multiple views (AP, lateral, and oblique) to accurately assess the fracture pattern. Consider advanced imaging techniques such as CT scans for complex or intra-articular fractures to gain a detailed understanding of the fracture geometry.
- Planning : Develop a detailed surgical plan, including the selection of implant size and configuration based on the patient’s anatomy and fracture type. Pre-select the appropriate 2.7 mm and 3.5 mm cortical screws and ensure availability of various lengths to accommodate intra-operative needs.
- Patient Preparation : Instruct the patient on pre-operative fasting and medication adjustments. Ensure the patient has a clear understanding of the surgical procedure, potential risks, benefits, and post-operative care.
- Patient Positioning and Anesthesia : Place the patient in a supine position on the operating table. Administer appropriate anesthesia, typically general anesthesia or regional block, based on patient and surgeon preference.
- Surgical Approach : Make a posterolateral incision over the distal humerus, following anatomical landmarks and surgical principles. Dissect through the soft tissues to expose the fracture site while protecting nerves, vessels, and surrounding structures.
- Fracture Reduction : Perform fracture reduction using appropriate reduction instruments to restore anatomical alignment. Ensure adequate visualization of the fracture ends and the articular surface for precise reduction.
- Implant Placement : Insert the ASLP implant into the prepared bone surfaces, ensuring proper seating and alignment with the fracture site. Secure the implant in place using the selected 2.7 mm and 3.5 mm cortical screws, following the designated hole configuration.
- Stability Assessment and Final Adjustments : Perform stability testing to ensure adequate fixation and alignment of the implant. Make any necessary adjustments to screw placement or implant positioning to optimize stability and fracture reduction.
- Monitoring : Transfer the patient to the recovery area and monitor vital signs, pain levels, and neurovascular status.
- Pain Management : Administer analgesics as prescribed to manage post-operative pain and discomfort.
- Wound Care : Inspect the surgical incision for signs of bleeding, infection, or wound dehiscence. Apply a sterile dressing as needed.
- Immobilization : Ensure proper limb immobilization using a splint or sling to protect the surgical site and promote healing.
- Rehabilitation : Coordinate ongoing physical therapy sessions to regain strength, range of motion, and functional abilities.
- Patient Education : Emphasize the importance of adherence to post-operative instructions, including activity modification and follow-up care.







.png)