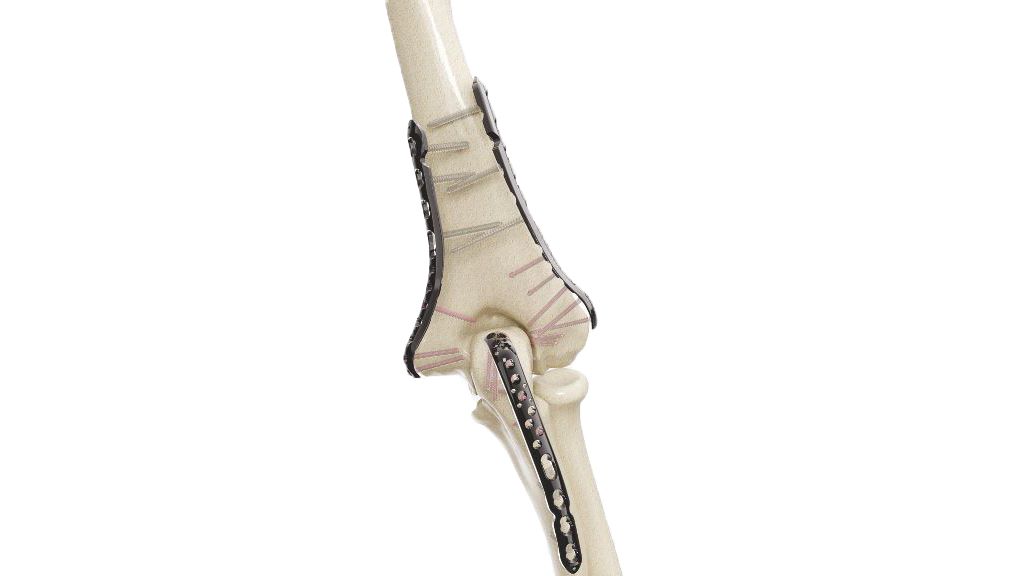
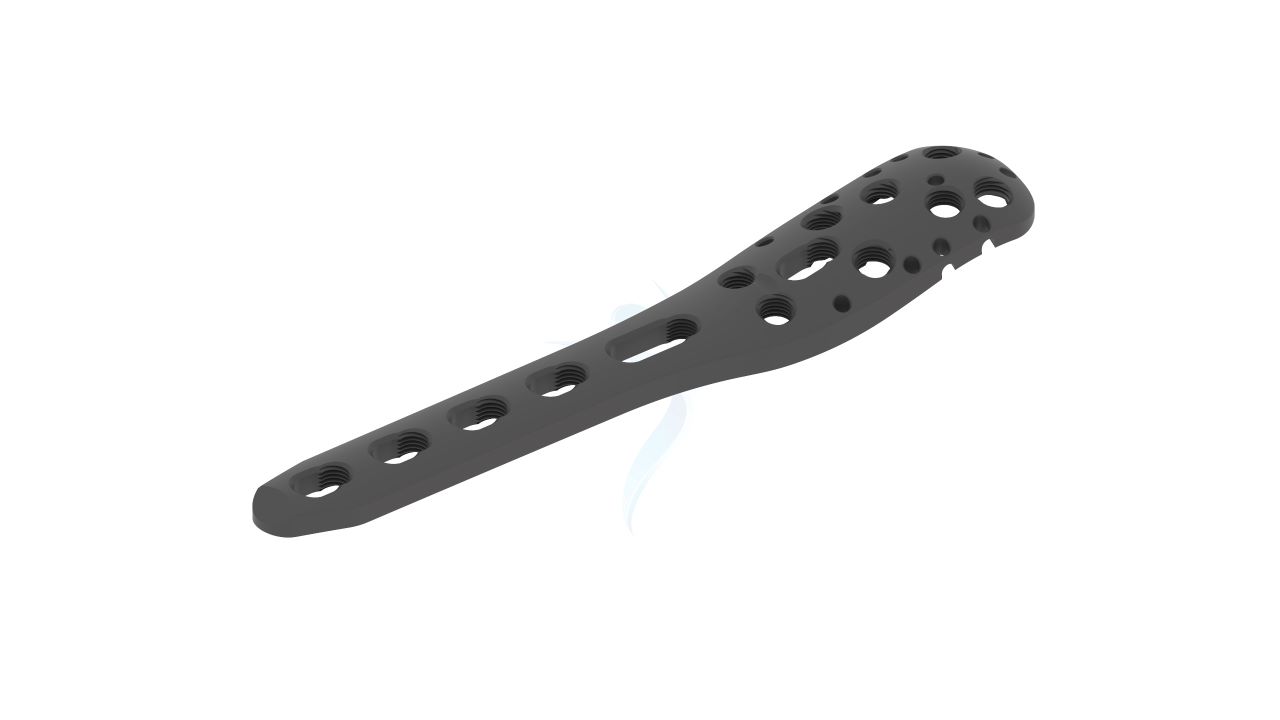
Proximal Humerus Plate (ASLP) - 3.5 mm Periarticular
Product Overview
The Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5 mm Periarticular is a specialized medical device designed for the treatment of fractures and orthopedic conditions involving the proximal humerus. It is anatomically contoured to fit the shape of the proximal humerus bone, providing stable fixation. The plate is made from durable materials such as stainless steel (LVM) or titanium alloy and is accompanied by a set of screws for comprehensive fixation. It is commonly used in proximal humerus fracture fixation, osteotomies, and cases of nonunion or malunion.
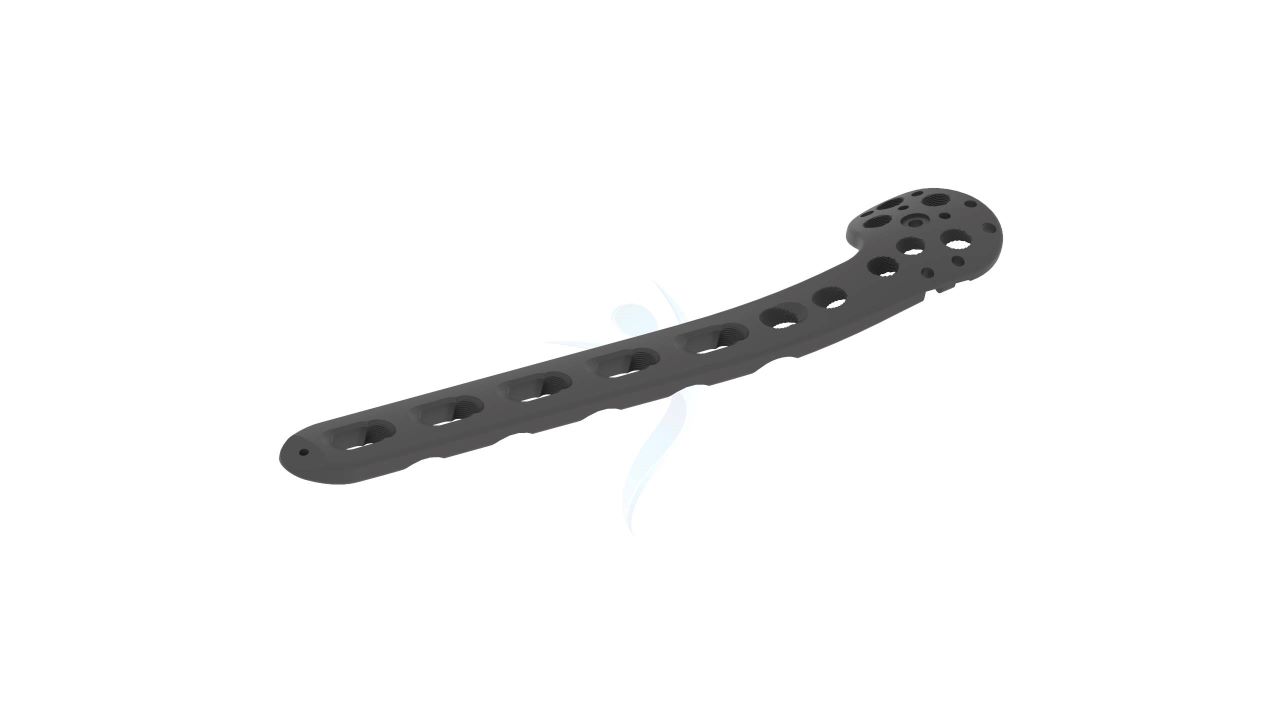
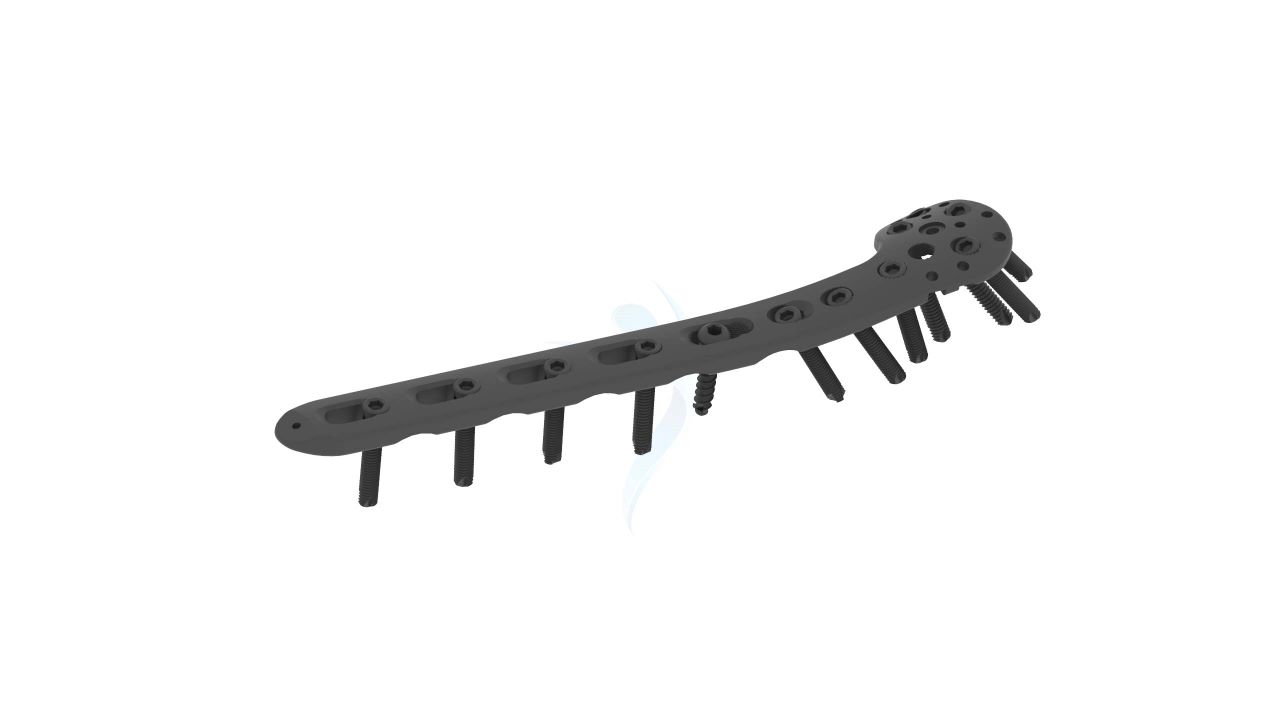
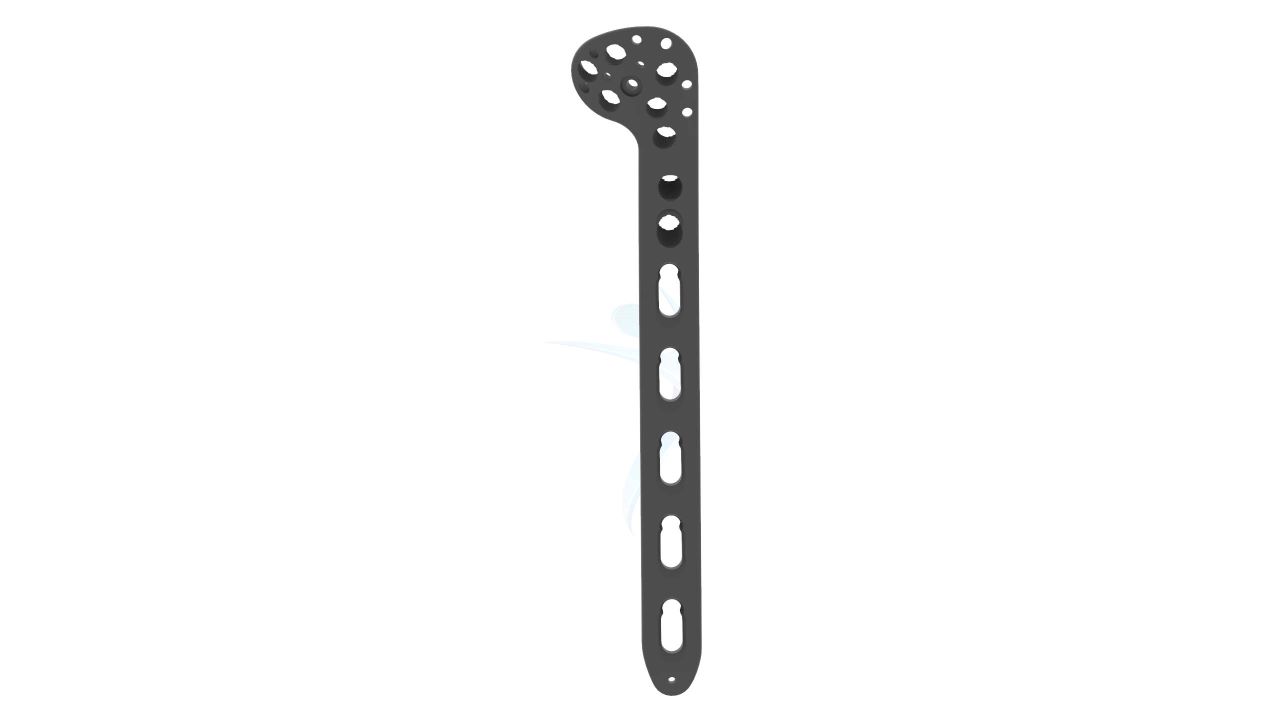
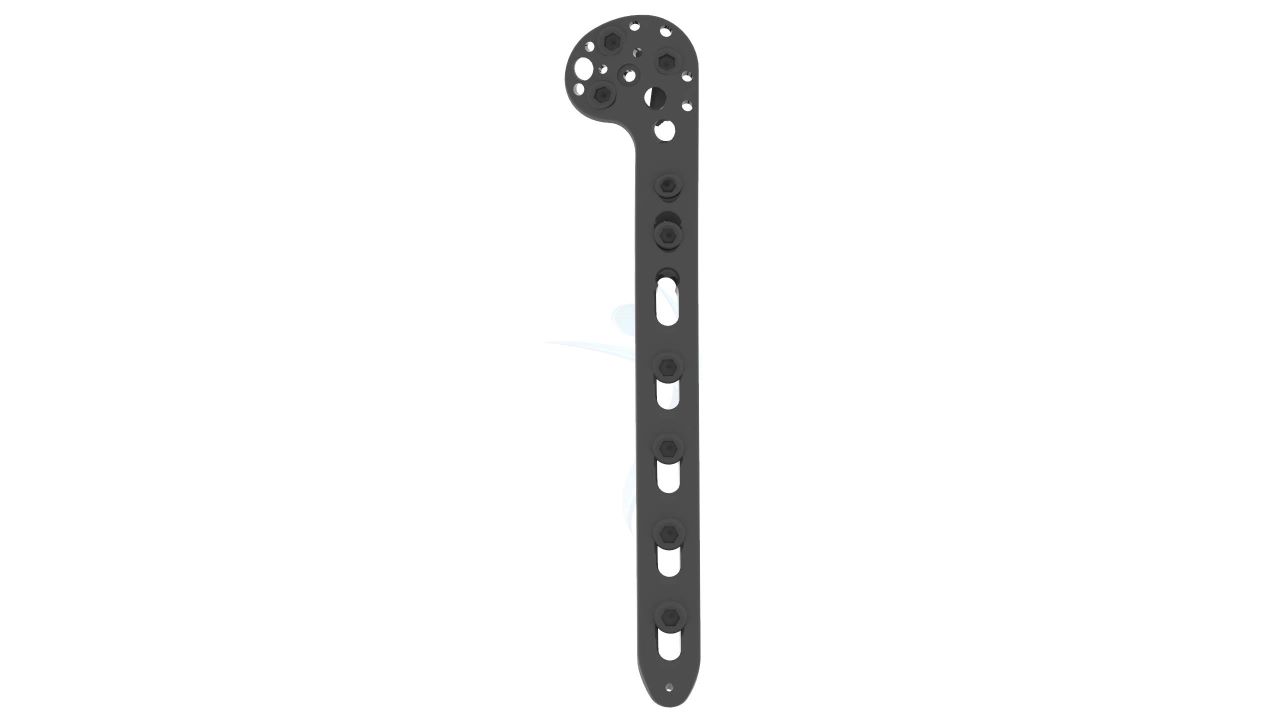
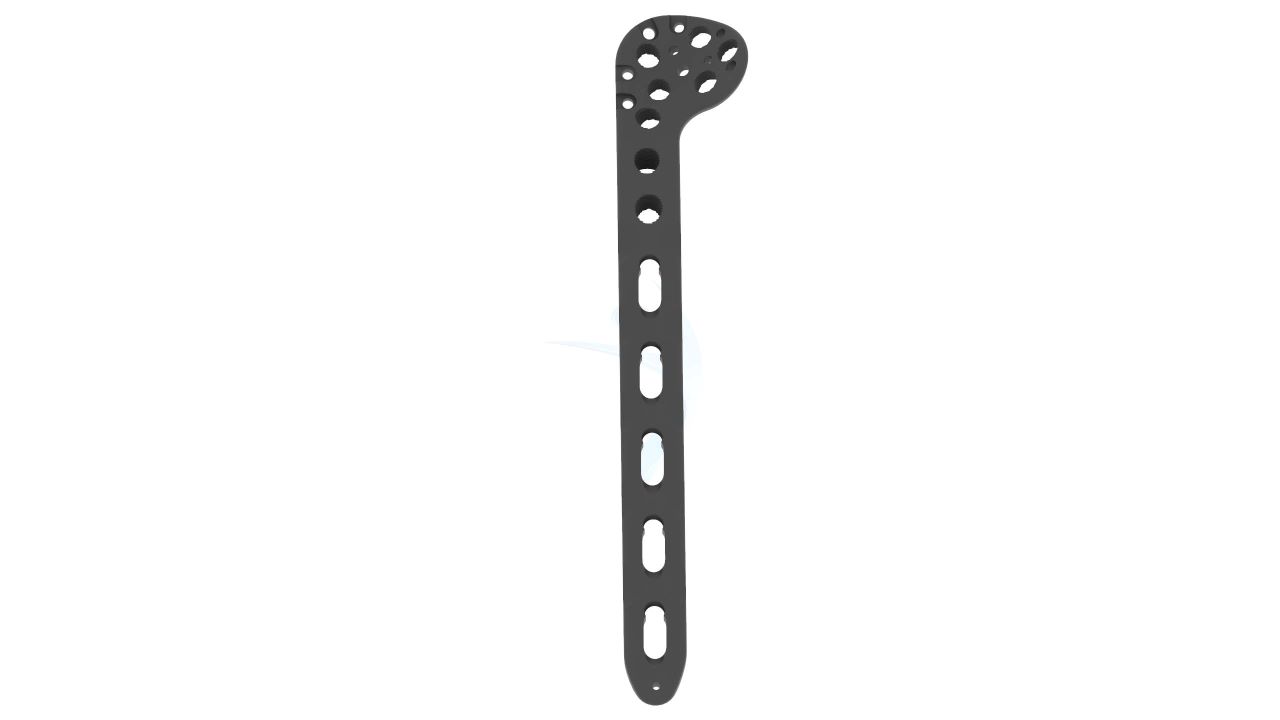
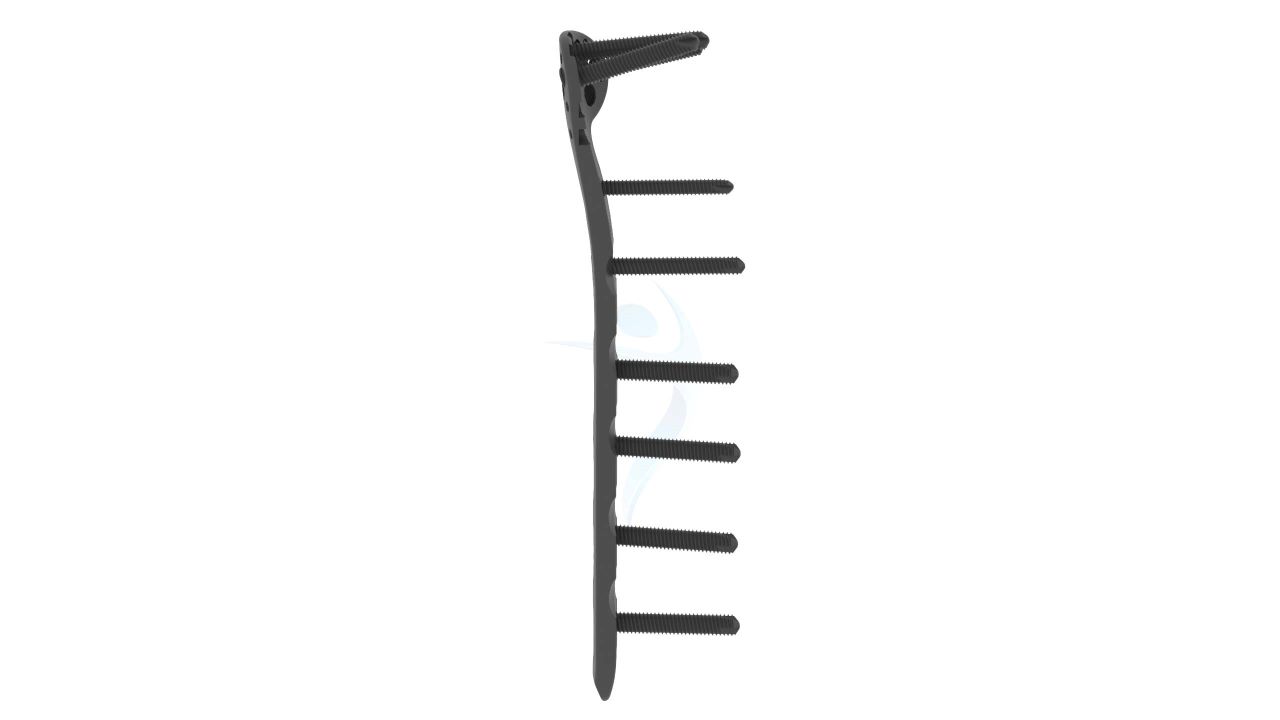






Product Uses
- Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation : The plate is utilized in the surgical treatment of fractures near the shoulder joint, including two-part, three-part, and four-part fractures. It provides stable fixation, allowing for proper alignment and healing of the fractured bone.
- Osteotomies : The plate can be used in corrective osteotomy procedures to realign and stabilize the proximal humerus. It helps restore the bone's anatomical position, promoting improved function and reducing pain.
- Nonunion and Malunion Cases : In situations where the bone fails to heal properly (nonunion) or heals in an undesirable position (malunion), the plate can be employed to stabilize the bone and facilitate proper healing. It provides support and stability, allowing for successful bone union.
Product Specification
- Material : The plate is made from high-quality stainless steel or titanium alloy. These materials offer strength, durability, and biocompatibility.
- Design: The plate is anatomically contoured to match the shape of the proximal humerus, allowing for proper fit and alignment.
- Screw Holes : The plate features multiple screw holes of various sizes and configurations. This provides flexibility in screw placement to accommodate different fracture patterns and bone quality.
- Locking Mechanism : The plate may incorporate a locking screw mechanism. Locking screws provide additional stability by engaging the plate, minimizing screw backout, and reducing the risk of construct failure.
Proximal Humerus Plate (ASLP) - 3.5 mm Periarticular Sizes
Comprehensive Guide for Proximal Humerus Plate (ASLP) - 3.5 mm Periarticular
- Patient Evaluation : Imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans are performed to assess the condition of the proximal humerus and surrounding structures.
- Surgical Planning : The surgeon evaluates the extent of the injury or condition and determines the appropriate size and placement of the implant.
- Patient Preparation : The patient receives instructions on pre-operative preparations, which may include fasting prior to surgery and discontinuation of certain medications that could interfere with the procedure or recovery.
- Consent and Education : The surgeon discusses the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes with the patient, ensuring informed consent.
- Anesthesia : The patient is placed under general anesthesia to ensure comfort and immobility during the procedure.
- Incision : The surgeon makes an incision over the proximal humerus to access the fracture or area of concern.
- Reduction and Fixation :The fracture fragments are carefully aligned (reduced) to restore normal anatomy. The Proximal Humerus Plate (ASLP) - 3.5 mm Periarticular implant is then positioned over the fracture site.
- Closure : Once the implant is securely in place, the incision is closed with sutures or staples.
- Recovery Room : The patient is monitored closely in the recovery room as they wake up from anesthesia. Pain management medications are administered as needed to ensure comfort.
- Physical Therapy : Depending on the patient's condition and surgeon's recommendations, physical therapy may begin soon after surgery to promote mobility and strength in the shoulder joint.
- Follow-Up Care : The patient will have regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon to monitor healing progress and assess the function of the implant.
- Activity Restrictions : The patient will be instructed on activity restrictions and proper care of the surgical site to minimize the risk of complications and support optimal healing.
- Long-Term Management : Long-term management may involve ongoing physical therapy, periodic imaging studies, and monitoring for any signs of implant failure or complications.








.png)